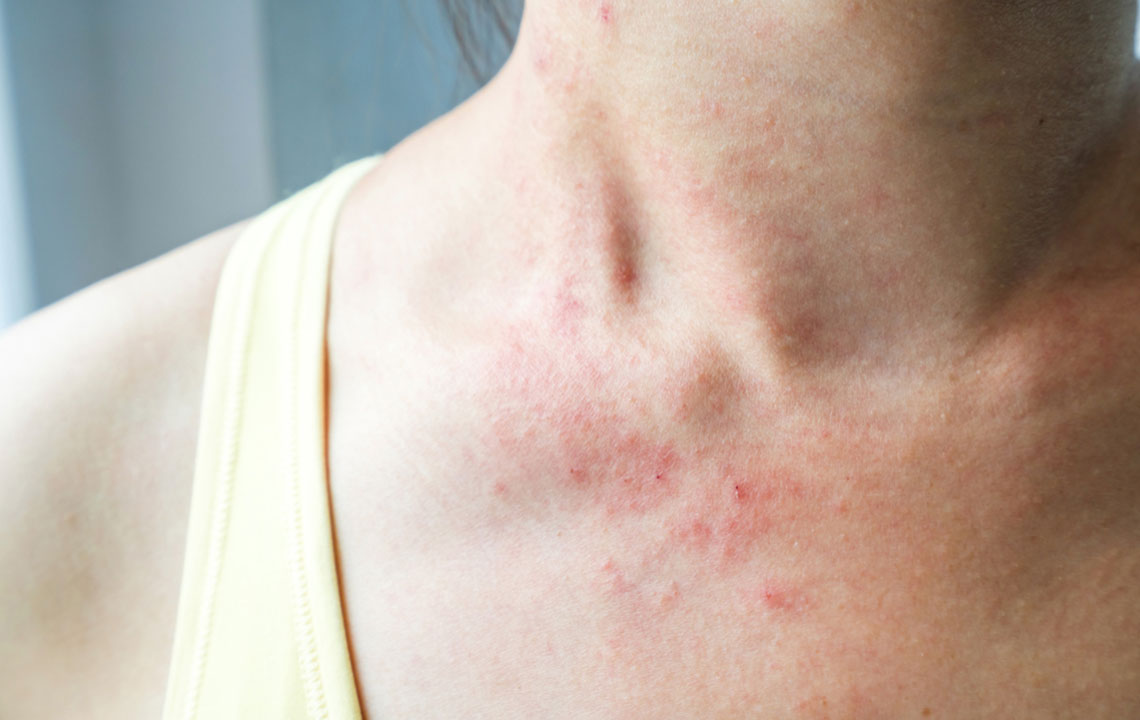
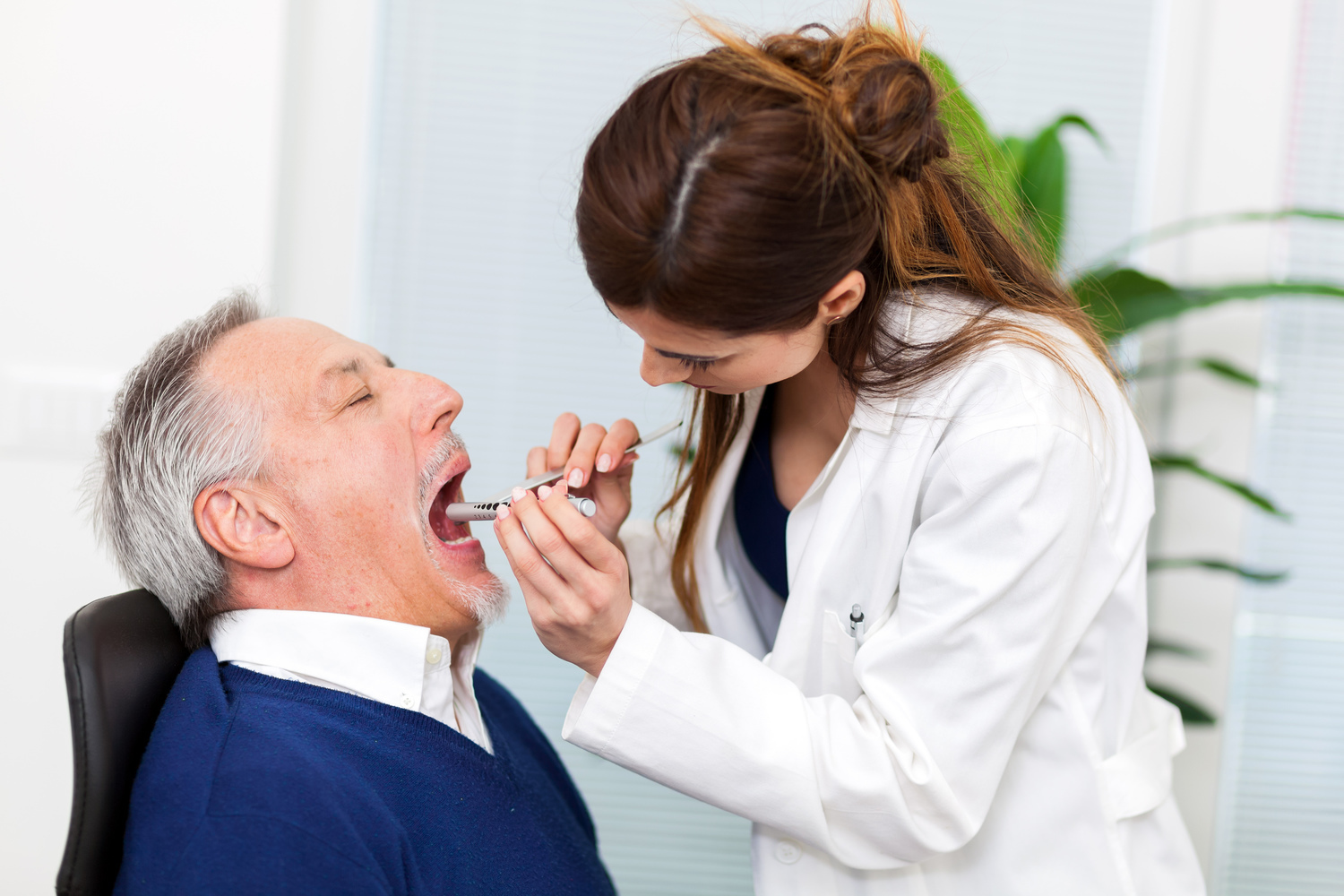
Understanding Impetigo: Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Strategies
Impetigo is a contagious skin infection caused by bacteria, affecting children and adults. This article covers causes, risk factors, and preventive measures. Prompt medical consultation is essential for effective treatment, especially in severe cases. Maintaining good hygiene and avoiding sharing personal items can reduce the risk. Seek professional medical advice for diagnosis and proper care. Early treatment prevents complications and helps manage outbreaks effectively.
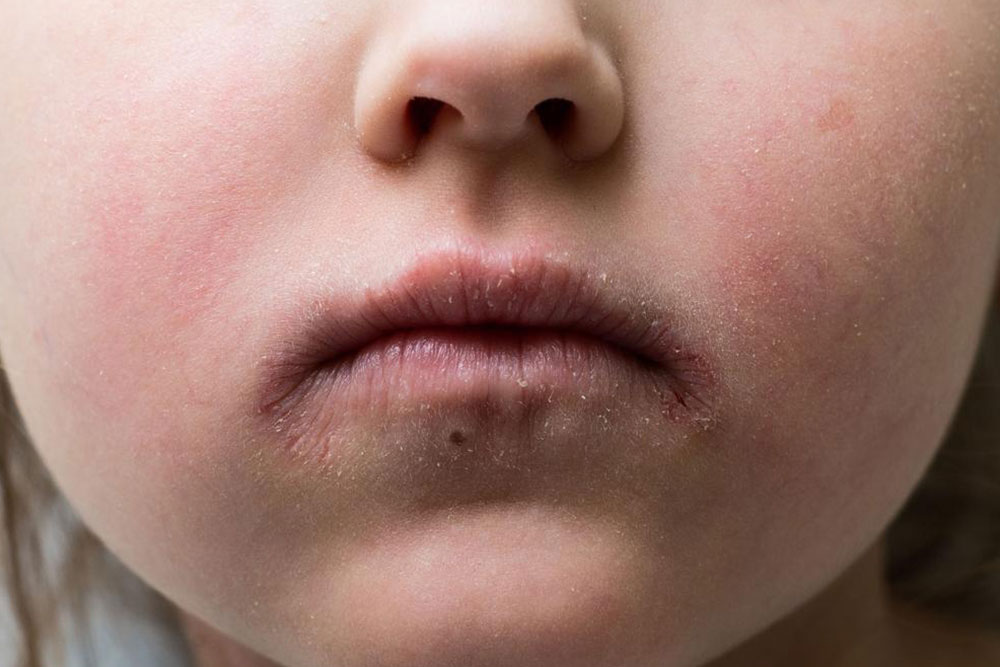
Know the Causes, Risks, and Prevention Tips for Impetigo in All Ages
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection predominantly caused by Staphylococcus and Streptococcus bacteria. It primarily affects children aged 2 to 5 but can appear in adults. Symptoms include red blisters with yellowish fluid that may crust over, mainly on the face, hands, neck, or diaper area.
How children acquire impetigo
Direct contact with infected individuals
Sharing personal items like towels or toys
Skin injuries such as cuts or abrasions
Bites from insects or animals
Risk factors for adults
Poor hygiene habits
Conditions like diabetes or weakened immunity
Exposure in crowded places such as public transportation or schools
High humidity increases susceptibility
Prevention and treatment advice
If you notice signs of impetigo, seek consultation from a healthcare professional promptly. During travel or remote areas, online images can help with initial assessment. Do not attempt self-treatment without medical guidance. Treatments typically include topical antibiotics or oral medications, especially in severe or persistent cases. Deep infections like ecthyma, often affecting the legs, are more common among the elderly and those with compromised immune systems and require medical intervention.
Disclaimer:
Our content provides general information but should not replace professional medical advice. Always see a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The website is not liable for inaccuracies or decisions based solely on this information.