Essential Insights into Tongue Cancer Prevention and Treatment
This comprehensive guide covers the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tongue cancer. It discusses early detection methods, surgical options, radiation and chemotherapy treatments, and lifestyle changes to reduce risk. Emphasizing prompt intervention, the article aims to improve patient outcomes and awareness of tongue cancer management.
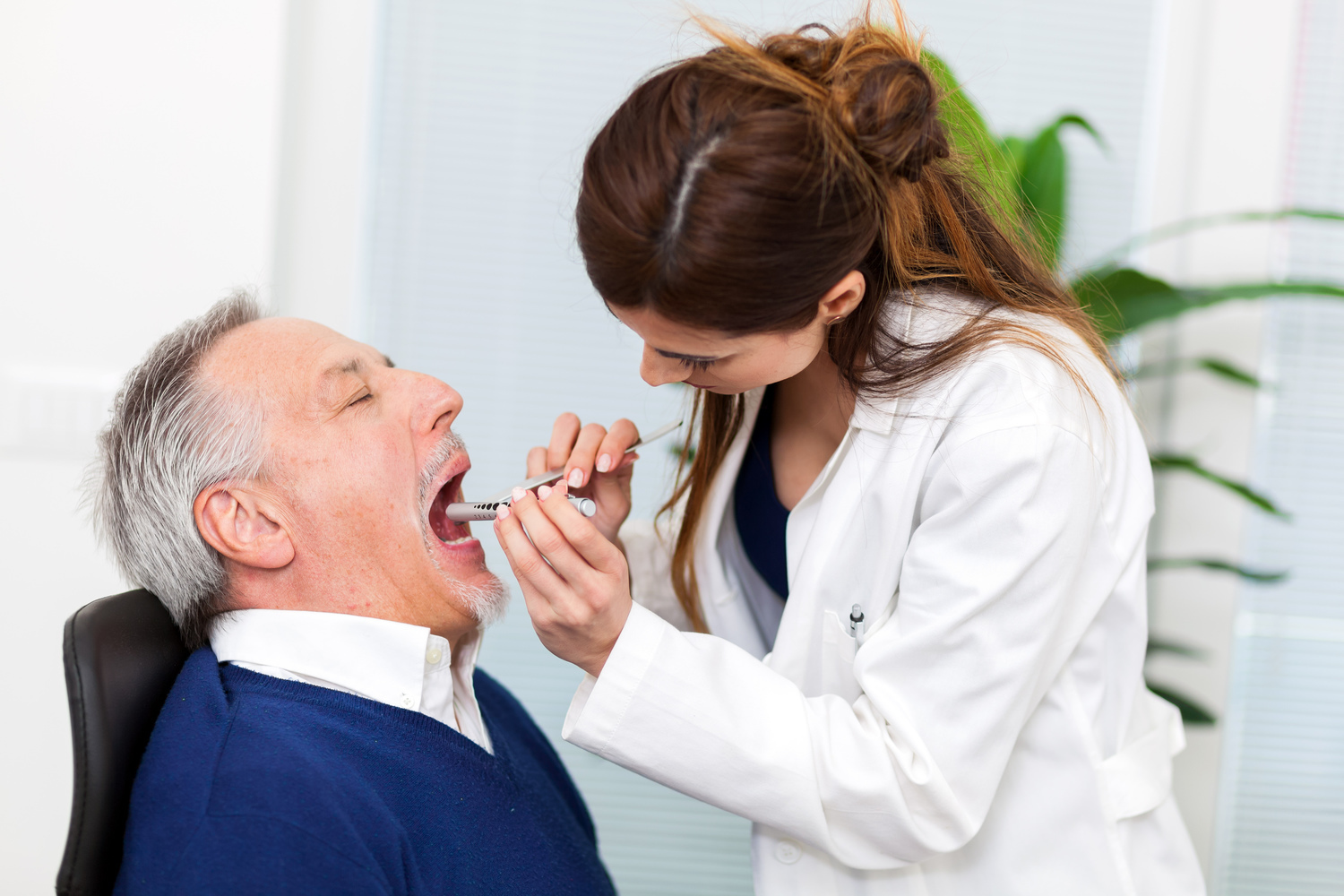
Effective Approaches for Managing Tongue Cancer
Tongue cancer is a malignancy originating from the front part of the tongue, primarily affecting adults. It develops from the squamous cells lining the tongue surface and differs from cancers in the rear section of the tongue, which are categorized separately in head and neck cancers. Recognizing early symptoms and signs is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Similar to other cancers, abnormal cell growth causes tumor formation. Though less prevalent overall, tongue cancer remains significant due to its impact on health and quality of life. Reviewing clinical indicators aids in early detection.
Below are the main treatment options available for tongue cancer patients.
How is tongue cancer diagnosed?
Medical history review by a specialist, including family cancer history, lifestyle habits like smoking and alcohol use, and HPV status.
Physical examination of the mouth to detect ulcers, lumps, or persistent sores.
Assessment of nearby lymph nodes for swelling or abnormalities.
Biopsies are performed if suspicious lesions are found to confirm the diagnosis.
Biopsy techniques include incisional biopsy, removing a small tissue sample under local anesthesia, or brush biopsy, which collects cells using a tiny brush.
Samples undergo lab analysis to identify malignant cells.
Imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs help determine the tumor's extent and spread.
Surgical options for tongue cancer
Early-stage tumors often respond well to surgical removal.
If lymph nodes are affected, their removal may be necessary.
Post-surgery outcomes vary—smaller tumors may leave minimal scarring, while larger ones can affect speech and swallowing.
Radiation therapy for treatment
High-energy radiation targets cancer cells to inhibit tumor growth.
Modern techniques allow precise delivery, minimizing side effects, typically administered over several weeks.
Chemotherapy strategies
Often combined with radiation, chemotherapy helps eliminate remaining cancer cells, especially in advanced cases.
Different drugs are used together to target various cancer stages, reducing resistance.
Post-surgical chemotherapy can lower recurrence risks or help manage inoperable tumors.
Preventive measures for tongue cancer
Avoid smoking and smokeless tobacco products.
Limit alcohol intake or abstain altogether.
Maintain good oral hygiene and visit the dentist regularly.
Eat a diet rich in fruits and leafy greens.
Get vaccinated against HPV as recommended.