Cellulitis Overview: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that can affect anyone. Recognizing symptoms early, including redness, swelling, and pain, is crucial for effective treatment. This article covers causes, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options, emphasizing the importance of prompt medical attention to prevent serious complications. With timely care, cellulitis is manageable and preventable. Always consult healthcare professionals for diagnosis and personalized treatment plans to ensure a full recovery.
Cellulitis Overview: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection affecting millions each year. Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent serious health issues. Recognizing symptoms promptly ensures effective care.
What is cellulitis?
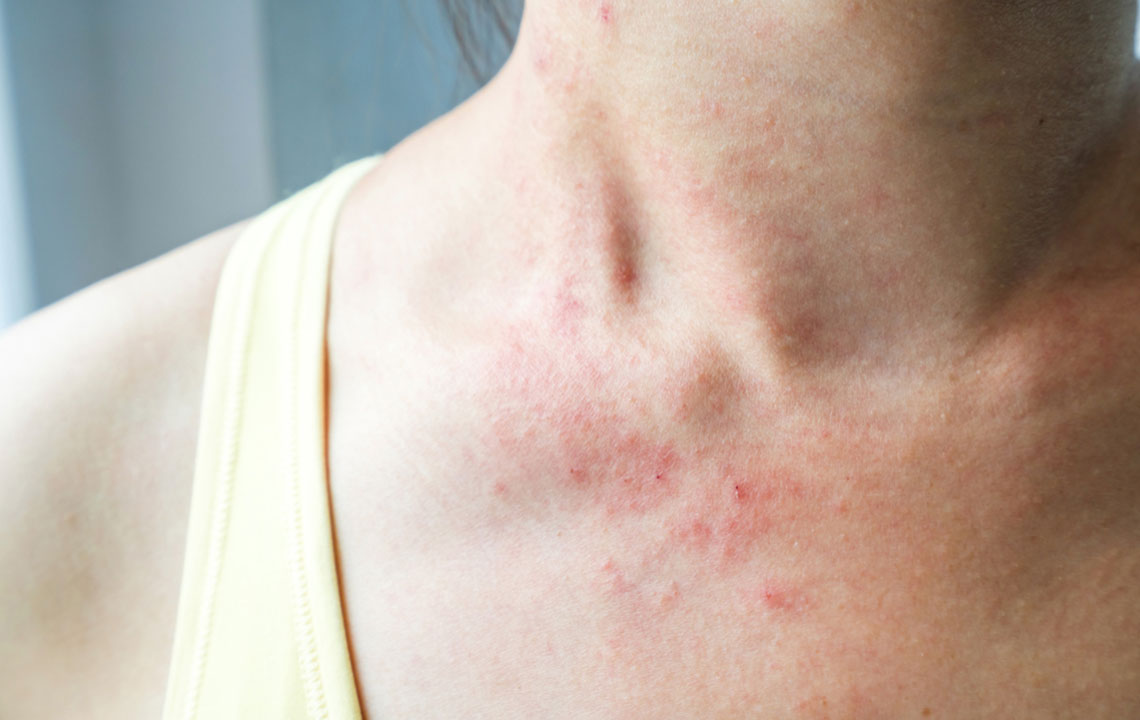
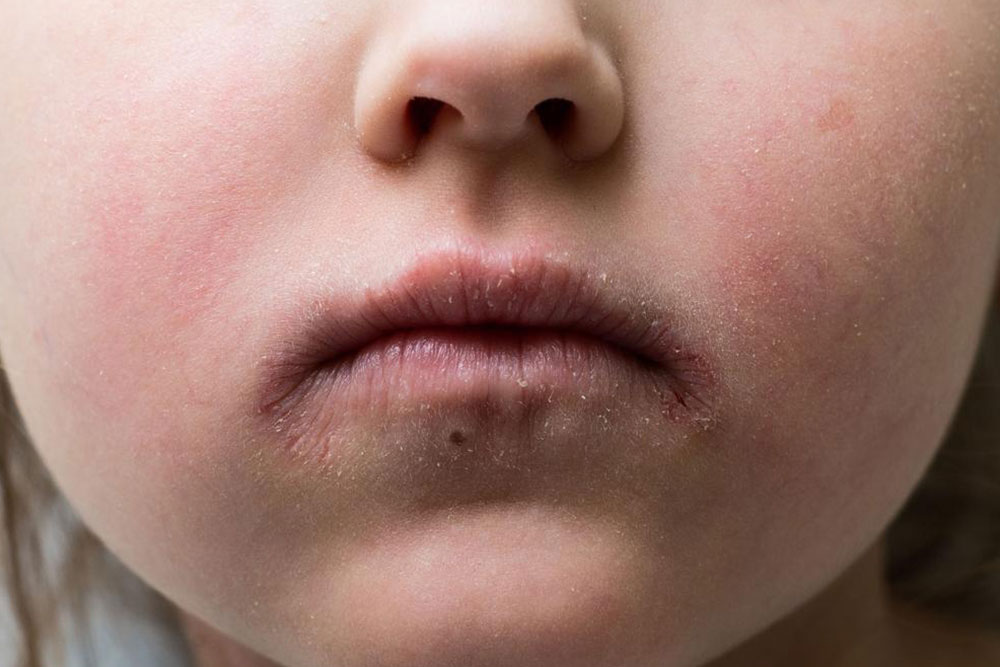
Cellulitis is an infection characterized by redness, swelling, and discomfort in affected skin areas, impacting individuals of all ages.

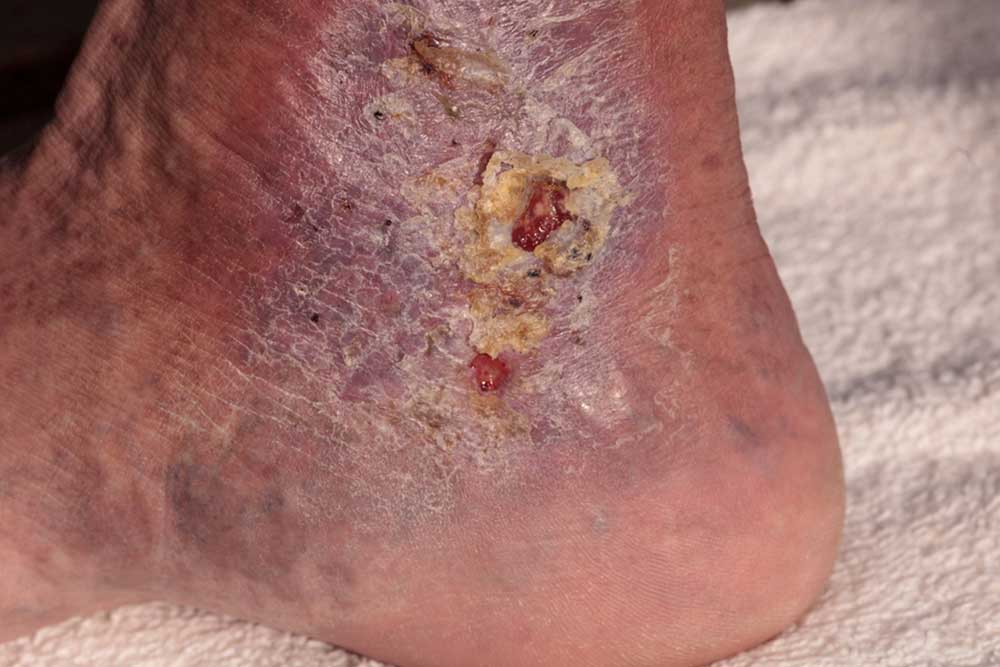
Those with previous cellulitis episodes are at increased risk. The condition commonly involves the limbs but can spread to areas like the eyes, mouth, or abdomen. On lighter skin, it appears as pink or red patches; darker skin may show purple, brown, or gray discoloration. The infection can progress from superficial skin tissues to lymphatic and bloodstream involvement, posing serious health threats.
What causes cellulitis?
Bacterial agents such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus are primary causes. These bacteria normally reside in the mouth and nose but can cause infection when they invade through cuts, animal bites, or water exposure. Certain groups are more susceptible, including:
Children
People with cuts, ulcers, surgeries, tattoos, or piercings
Individuals with chronic skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis
Those with chickenpox or shingles
Immunocompromised persons
Key symptoms to identify
Common signs include:
Redness: Skin turns pink or red, potentially spreading.
Swelling: Inflammation causing tenderness and enlargement.
Pain: Discomfort correlating with infection severity.
Blisters: Rapidly forming painful pustules.
Systemic signs: Fever, headaches, nausea, especially in severe cases. Immunocompromised individuals are more prone to these symptoms.
Additional indicators include warmth, bruising, chills, and fatigue. Seek urgent medical help if symptoms worsen, such as expanding skin patches or high fever, which could be life-threatening.
How is cellulitis treated?
Timely treatment is critical. Therapy usually involves antibiotics given orally or via injections. Pain management with analgesics may be advised for severe pain. Additional care tips include:
Using moist dressings on affected areas
Maintaining cleanliness and hygiene
Keeping the infected limb elevated
Getting plenty of rest
When treated promptly, cellulitis is often curable. Delayed or ignored treatment can lead to complications. Always consult a healthcare provider at the first signs of infection for best results.Disclaimer:
This article provides health-related information based on research but does not substitute professional medical advice. Always seek medical attention for diagnosis and treatment. The publisher is not responsible for inaccuracies.