Key Insights on Deep Vein Thrombosis and Prevention Strategies
This article highlights key facts about deep vein thrombosis (DVT), emphasizing risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures. Awareness of these aspects is crucial for early detection and management. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, knowing warning signs, and consulting healthcare providers can significantly reduce the risk of serious complications like pulmonary embolism. Regular health check-ups and prompt treatment are essential for staying safe. Protect yourself by understanding DVT risks and taking proactive steps to promote vascular health and overall well-being.
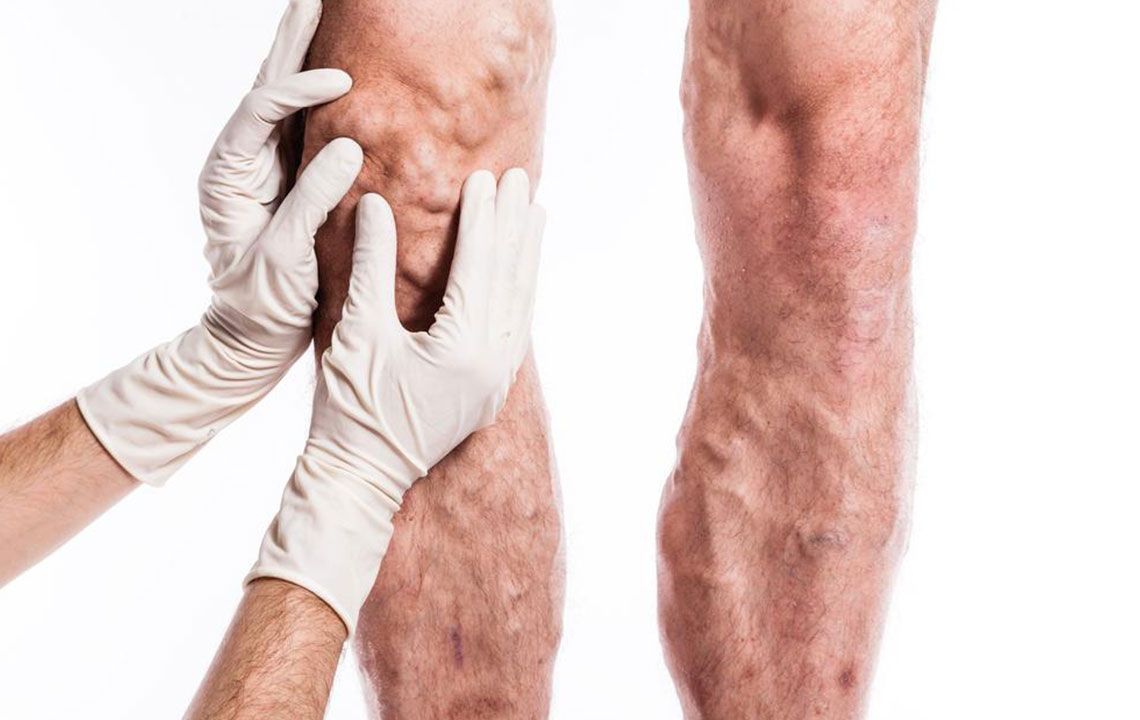
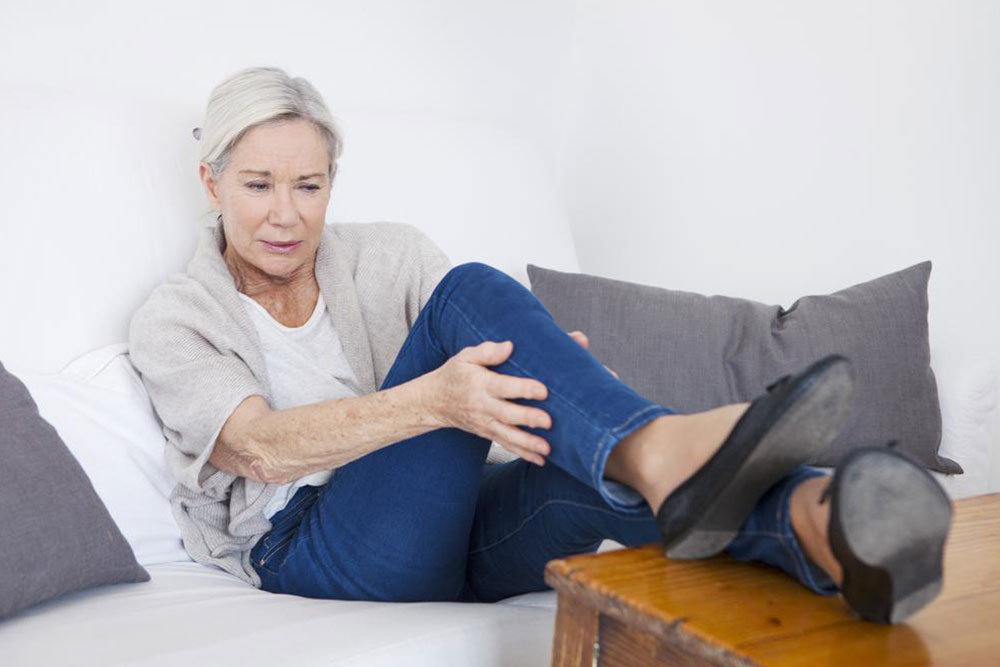
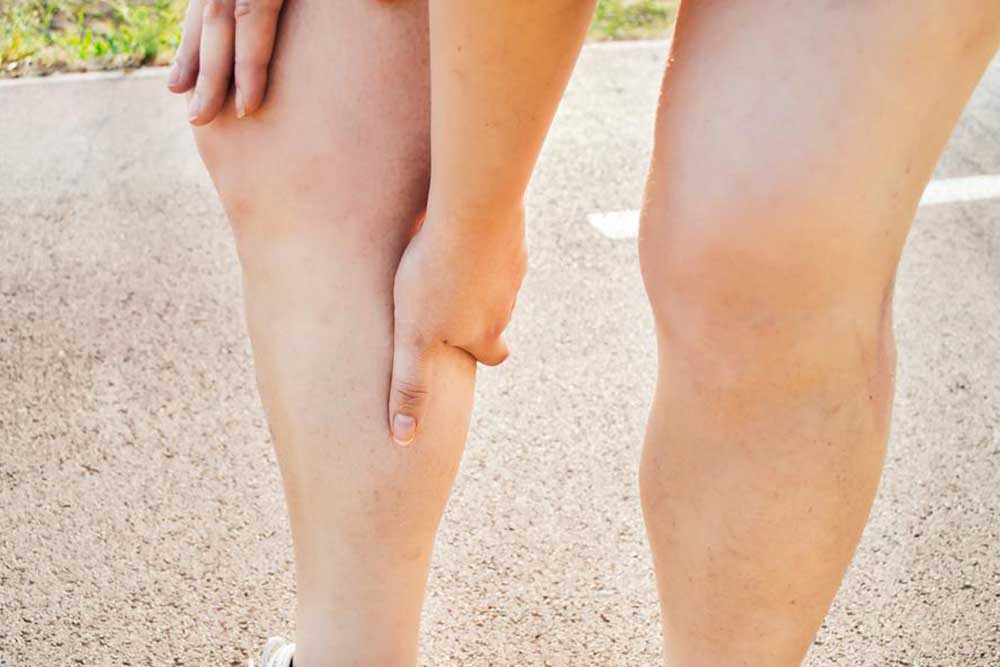
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) involves blood clots forming within deep veins, most often in the legs. These clots can thicken the blood and pose serious health dangers, potentially leading to life-threatening pulmonary embolisms. While DVT commonly occurs in the thighs and lower legs, it can develop elsewhere. Early recognition of symptoms, such as swelling, pain, and skin discoloration, along with understanding risk factors, is vital for successful prevention and treatment.
Who is at Greater Risk?
Individuals over 50 years old are more vulnerable to DVT. Several factors can heighten the likelihood, highlighting the importance of awareness and proactive health measures.
Contributing elements include vein damage, excess weight putting pressure on leg and pelvic veins, genetic predisposition, and hormonal therapies like birth control pills. Risk factors are also increased by smoking, sedentary living, and overall lack of activity.
Protect Yourself and Act Early
Older adults, especially those over 50, should be vigilant for symptoms such as swelling, warmth, pain, and color changes in the legs. Prompt diagnosis is essential to prevent complications like pulmonary embolisms. Symptoms can include unilateral leg swelling, cramps, sudden pain, and redness. Many cases show no symptoms, which underscores the importance of regular health screenings. If left untreated, DVT can be fatal if the clot migrates to the lungs.
Treatment options involve blood-thinning medications, compression stockings, and in severe cases, clot removal surgery. Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and quitting smoking can greatly reduce risk. Leading a healthy lifestyle is a key step toward preventing DVT. Prioritize your well-being for a safer, more active life.
Disclaimer:
Our platform offers comprehensive health information but does not substitute professional medical advice. For diagnosis and treatment, consult qualified healthcare providers. We disclaim responsibility for the accuracy of information and recommend verifying details with medical professionals for personalized care.