Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis: Symptoms, Risks, and Prevention
This article explores the causes, symptoms, and risks associated with Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and timely treatment to prevent serious complications like pulmonary embolism. Understanding risk factors such as inactivity, obesity, and genetic predisposition can help in preventive strategies and promote awareness among at-risk groups, particularly older adults.
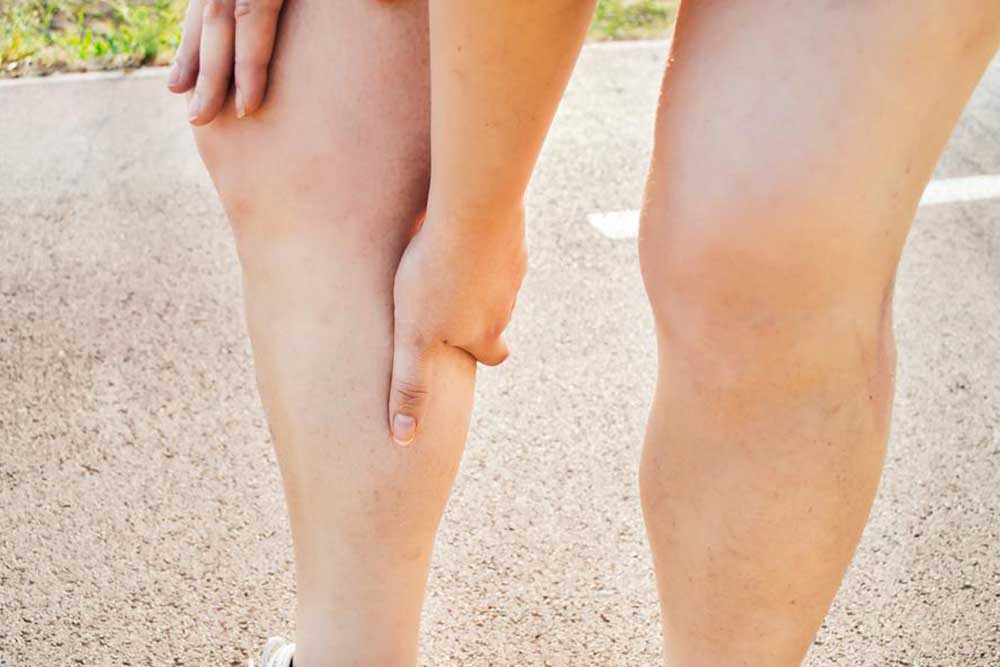
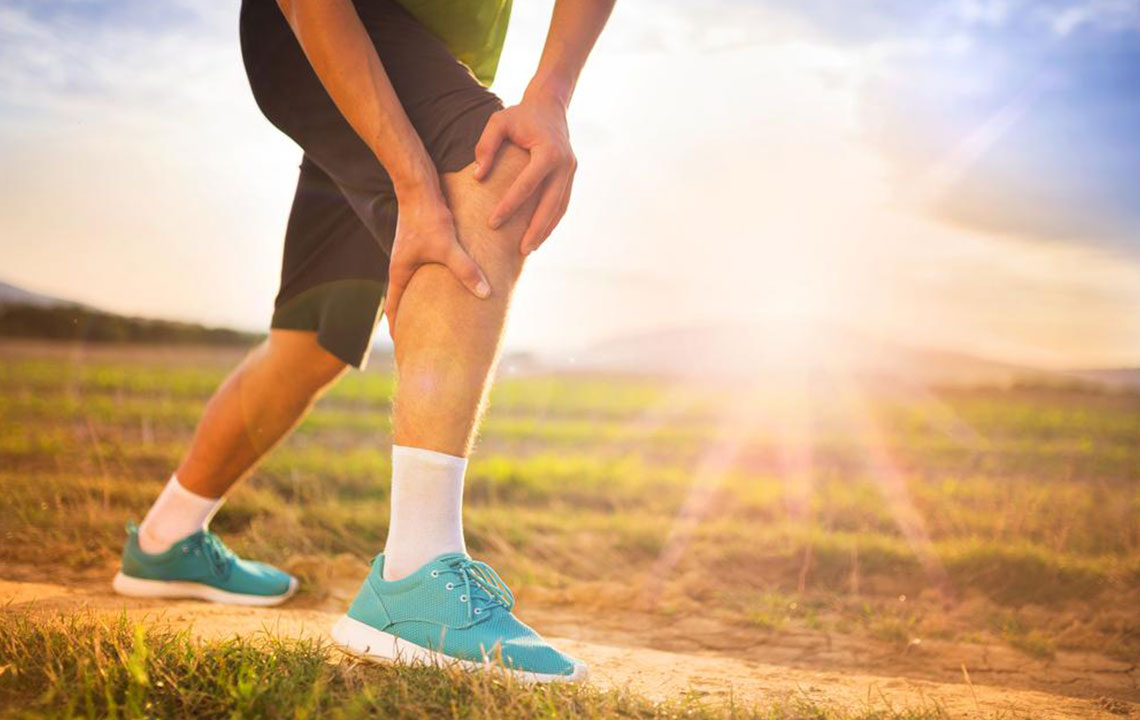
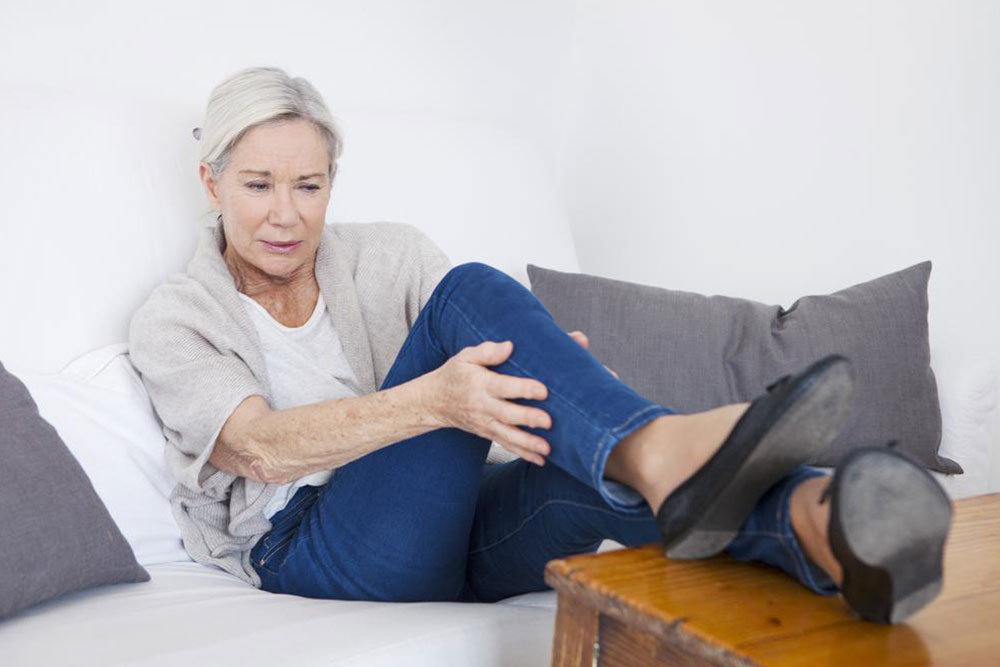
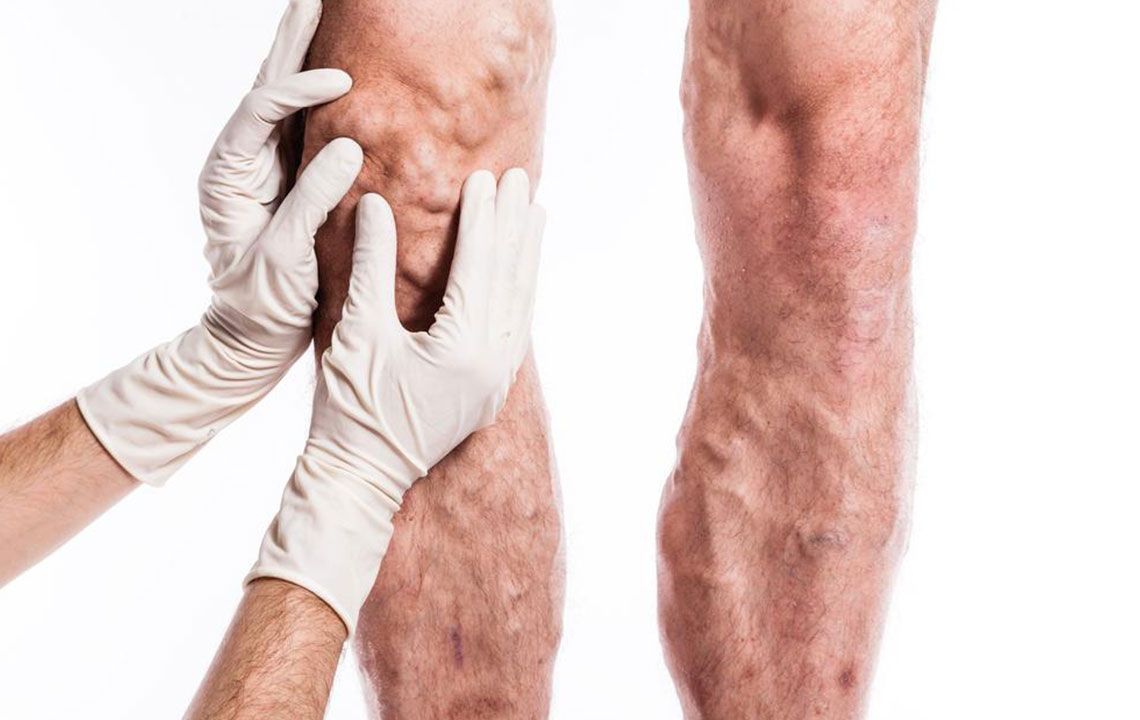
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) involves the formation of blood clots within deep veins, most often in the legs. These clots can block normal blood flow and pose serious health threats, such as pulmonary embolism. Factors increasing DVT risk include prolonged periods of inactivity, leg injuries, obesity, smoking habits, hormonal therapy, and hereditary conditions. Common signs are leg swelling, tenderness, warmth, and skin discoloration; however, some individuals may remain symptom-free. Immediate medical evaluation is essential if symptoms like chest discomfort, breathlessness, or hemoptysis occur. DVT predominantly impacts adults over 50, especially those with additional risk factors. Early detection and treatment are key to avoiding life-threatening complications.