Key Approaches to Preventing and Managing Deep Vein Thrombosis
Learn essential strategies for preventing and managing deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This guide covers risk factors, including genetic and lifestyle influences, and offers practical prevention tips like maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and thoughtful medication use. Understanding and addressing these elements can significantly reduce the risk of developing DVT and its serious complications, such as pulmonary embolism. Implementing these approaches promotes vascular health and ensures proactive management of this condition.

Proactive Strategies for Deep Vein Thrombosis Prevention and Care
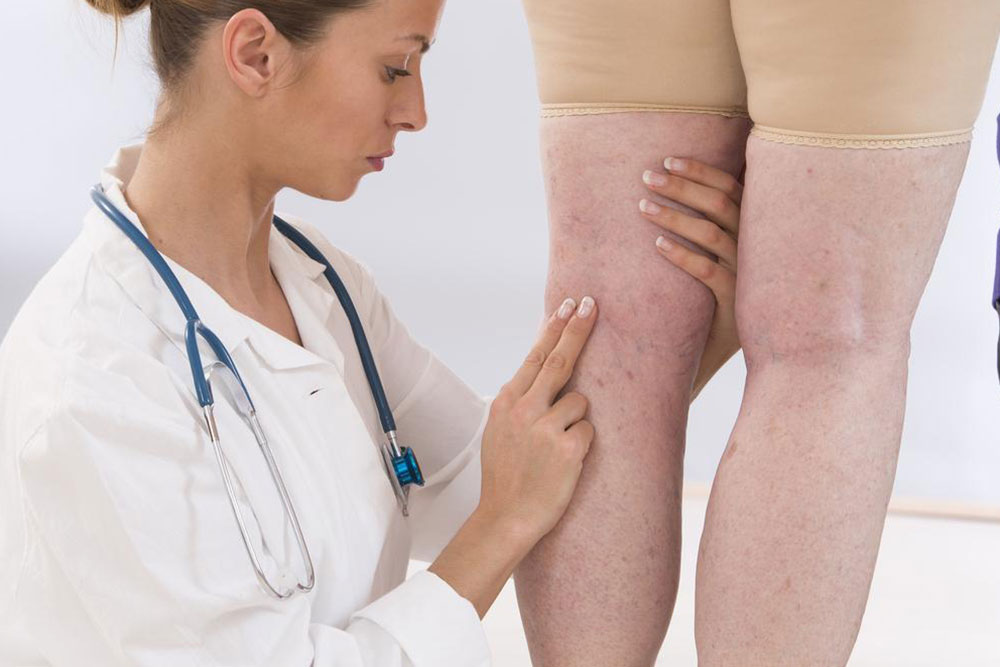
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) occurs when blood clots form in the deep veins of the legs. Common symptoms include swelling, pain, and redness. If not treated, DVT can cause a pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition resulting from a dislodged clot. Recognizing risk factors such as lifestyle habits and genetic tendencies is crucial for prevention. Addressing these factors reduces the chances of developing DVT significantly.
Risks can be acquired, genetic, or a combination of both. Taking preventive steps is vital for individuals at higher risk.
Adjustable Risk Factors
Factors like aging, post-surgical recovery, certain cancers, inactivity, pregnancy, injuries, oral contraceptive use, and inflammatory diseases can increase DVT risk. Keeping these under control helps prevent clot formation.
Inherited Factors
Deficiencies in proteins such as antithrombin, protein C, and protein S are inherited and can raise clotting risks. Genetic screening can help evaluate individual susceptibility.
Multiple Contributing Factors
Conditions like elevated homocysteine, high fibrinogen, and resistance to protein C can also contribute. Managing these underlying issues is key to prevention.
Preventive strategies include:
Medication Precautions
Limit the use of estrogen-containing drugs like some birth control pills and hormone therapies, as they increase clotting risk. Non-hormonal options can reduce this risk.
Family Health Insights
Knowing your family’s medical history can identify risks, allowing personalized preventive measures.
Healthy Weight Maintenance
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight eases pressure on veins and enhances blood circulation, reducing DVT danger.
Regular Movement
Engaging in routine physical activity and leg exercises helps promote blood flow. Avoiding long periods of immobility is crucial.
Diet and Nutrition
Consuming omega-3-rich foods like fish or supplements such as fish oil can nearly halve DVT risk, supporting vascular health.