Comprehensive Guide to Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
Learn about deep vein thrombosis (DVT), including its causes, symptoms, and effective prevention strategies. Recognizing risk factors like prolonged immobility, pregnancy, obesity, and injuries can help you reduce the likelihood of clot formation. Incorporate simple lifestyle changes such as regular movement, hydration, and early post-surgical mobilization to protect your health. Seek medical attention if experiencing symptoms to prevent severe complications. This comprehensive guide aims to raise awareness and promote proactive health measures against DVT.

Comprehensive Guide to Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
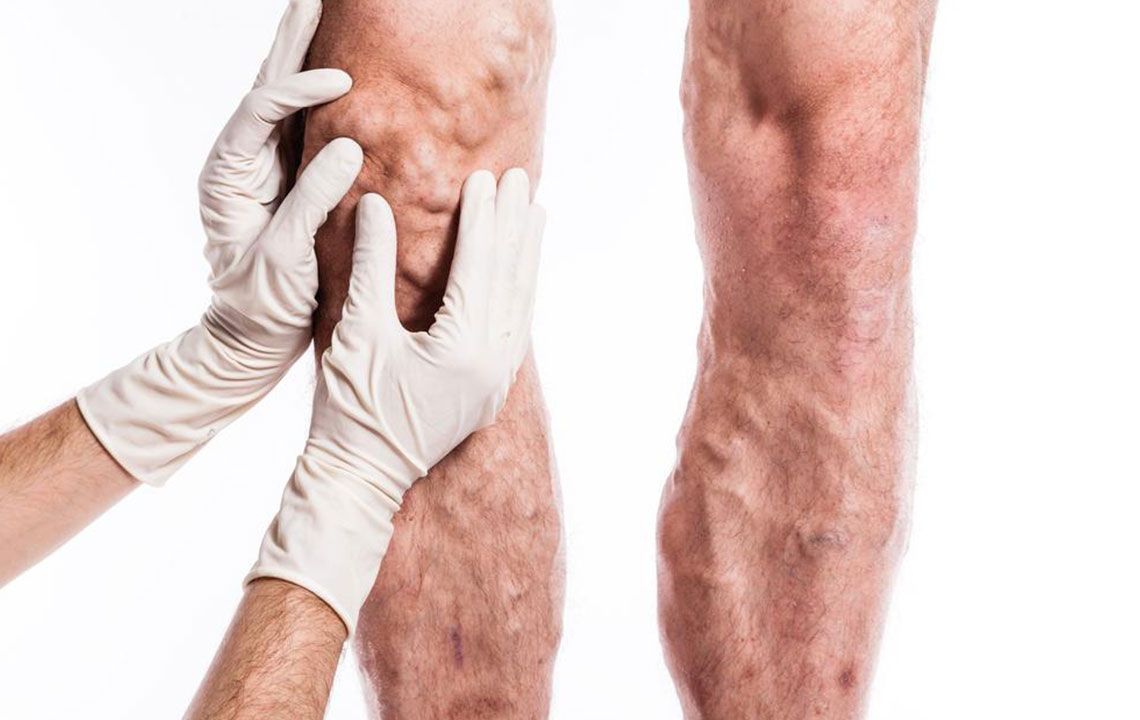
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins, most commonly in the legs. It may cause swelling or develop silently, making awareness vital. Identifying risk factors and implementing preventive steps can help avert serious health issues.
Major causes of DVT
Prolonged immobilization or bed rest hampers blood circulation in leg veins, increasing clot risk. Normal blood flow is essential for preventing clot formation.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy elevate estrogen levels, which can promote clotting. Hormone-based contraceptives and therapies also contribute to DVT risk.
Being overweight or obese strains the venous system, reducing circulation and increasing susceptibility to clots.
Injuries damaging the vein’s lining can initiate clot development, especially following trauma.
Preventive measures against DVT
Change positions frequently during long periods of sitting. Incorporate standing, stretching, and walking into your routine to encourage healthy blood flow.
Start moving promptly after surgeries or when immobilized to prevent clots. Early mobilization is crucial.
Maintain an active lifestyle, avoid tight clothing, stay well-hydrated, and limit alcohol intake to support circulation.
If you experience symptoms such as dizziness, sweating, or rapid heartbeat, consult a healthcare professional immediately, as DVT can lead to dangerous complications like pulmonary embolism.
Disclaimer: This article offers general health insights and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Seek personalized diagnosis and treatment from healthcare providers.