Comprehensive Overview of Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
This article provides a detailed overview of psoriasis, covering its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and modern treatment options. It also highlights the impact of stress and emotional health on disease management. Understanding these factors helps sufferers control flare-ups and improve quality of life through medication, dietary choices, and relaxation techniques.
Comprehensive Overview of Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
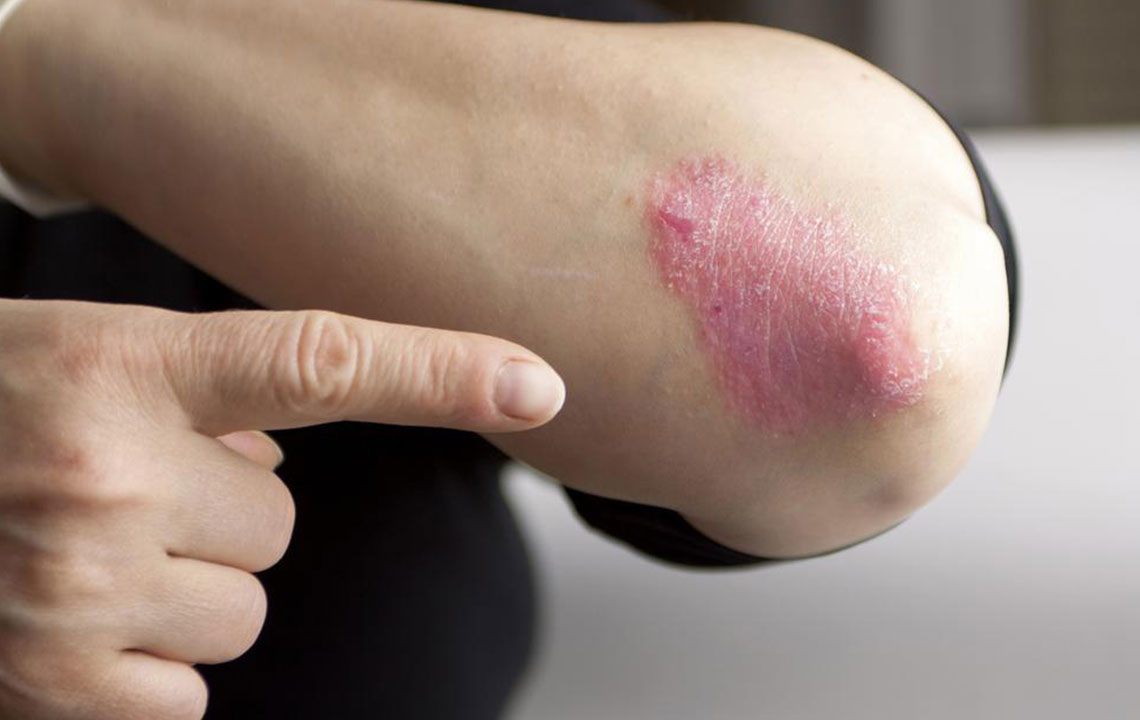
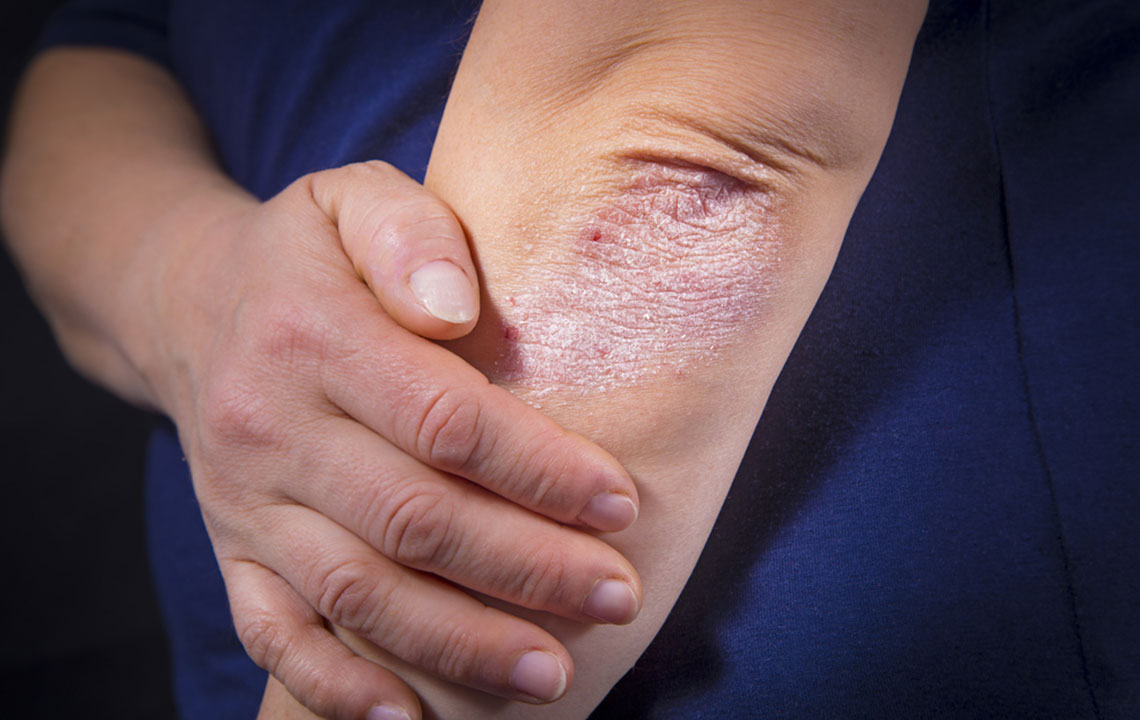
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition affecting approximately 7.5 million people across the country. Normally, skin cells renew monthly, but in psoriasis, this process accelerates to daily, resulting in thick patches and silver scales. Effective management combines medication and lifestyle changes. Recognizing symptoms, understanding causes, and adopting appropriate treatments can help minimize flare-ups and enhance quality of life.
What are the common signs of psoriasis?
Symptoms vary by type but generally include red, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales. These patches can be itchy, sore, and may crack or bleed. Severe cases may cause patches to merge or spread. Nail involvement can lead to discoloration, pitting, or detachment. Psoriatic arthritis might cause joint swelling and discomfort.

Factors Contributing to Psoriasis
While the exact cause is not fully understood, genetics combined with environmental factors play a significant role. Triggers such as injuries, emotional stress, infections, or medical procedures may worsen symptoms. Importantly, psoriasis is not contagious, so transmission is not a concern. It can also run in families, sometimes skipping generations due to genetic factors.
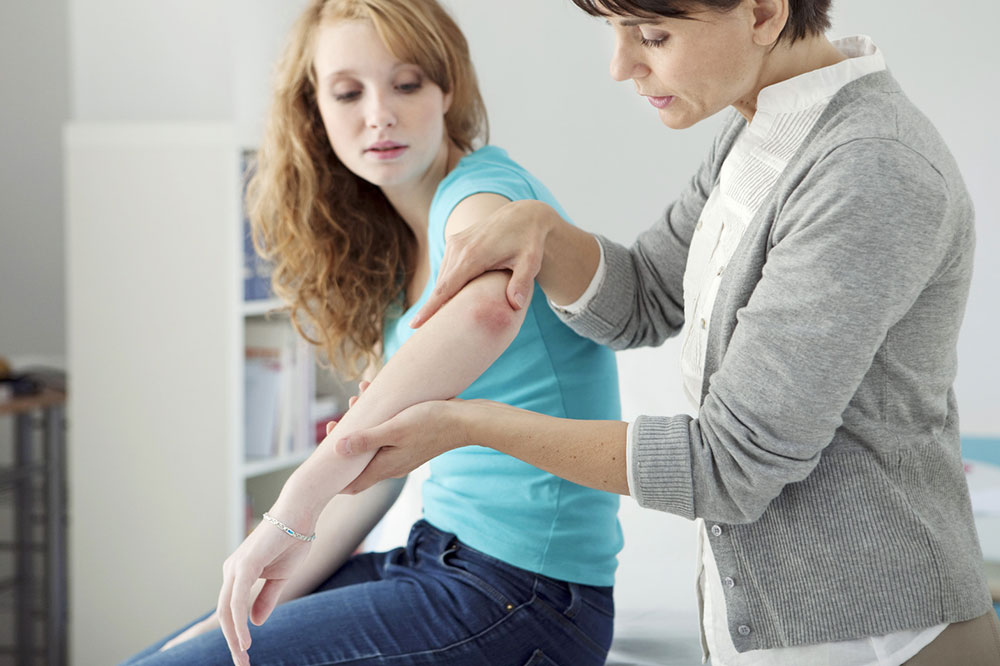
Diagnosis Procedures for Psoriasis
Most people identify psoriasis through symptoms like itching, redness, and scaling. Nonetheless, a professional diagnosis is vital. Dermatologists evaluate affected areas—scalp, ears, nails, elbows, knees, and abdomen—and review medical history. When needed, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Nutritional Approaches for Managing Psoriasis
Although diet doesn’t cure psoriasis, certain nutritional habits can help manage flare-ups. Maintaining a healthy weight, reducing processed foods, red meats, dairy, and sugar can decrease inflammation. Including lean proteins, vitamins, and anti-inflammatory foods supports skin health and reduces severity of symptoms.
The Role of Stress in Psoriasis
Stress is a known factor that can trigger flare-ups. Incorporating relaxation techniques like meditation, breathing exercises, yoga, and Tai Chi can significantly alleviate symptoms. Professional mental health support or therapy may also be beneficial in managing emotional stress associated with the condition.
Psychological Aspects of Psoriasis
Emotional health greatly influences disease progression. Psoriasis can impact self-esteem, cause depression, and lead to social withdrawal, creating a negative cycle. Support groups provide emotional comfort and coping strategies. Promoting a positive body image and social engagement are essential in handling the psychological toll of psoriasis.
Available Treatment Options for Psoriasis
While a cure remains elusive, treatments aim to control symptoms by reducing inflammation, scaling, and abnormal cell growth. Recent studies suggest that controlling inflammation may also lower risks of cardiovascular and metabolic issues. Treatment methods include topical therapies, phototherapy, and systemic medications. UV light-based phototherapy is effective in targeting overactive immune responses responsible for skin inflammation.