Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Preventive Measures
This comprehensive overview explains psoriasis, highlighting its symptoms, risk factors, and management tips. While no cure exists, lifestyle changes can improve quality of life. The article emphasizes the importance of medical consultation for proper diagnosis and treatment.
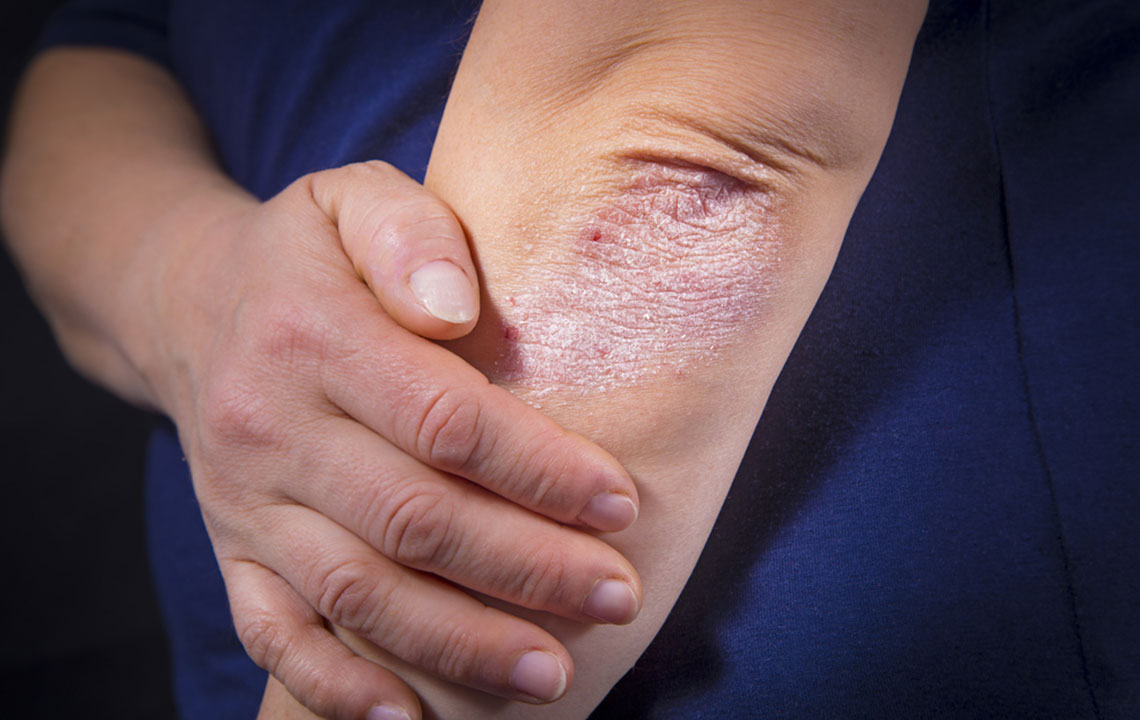
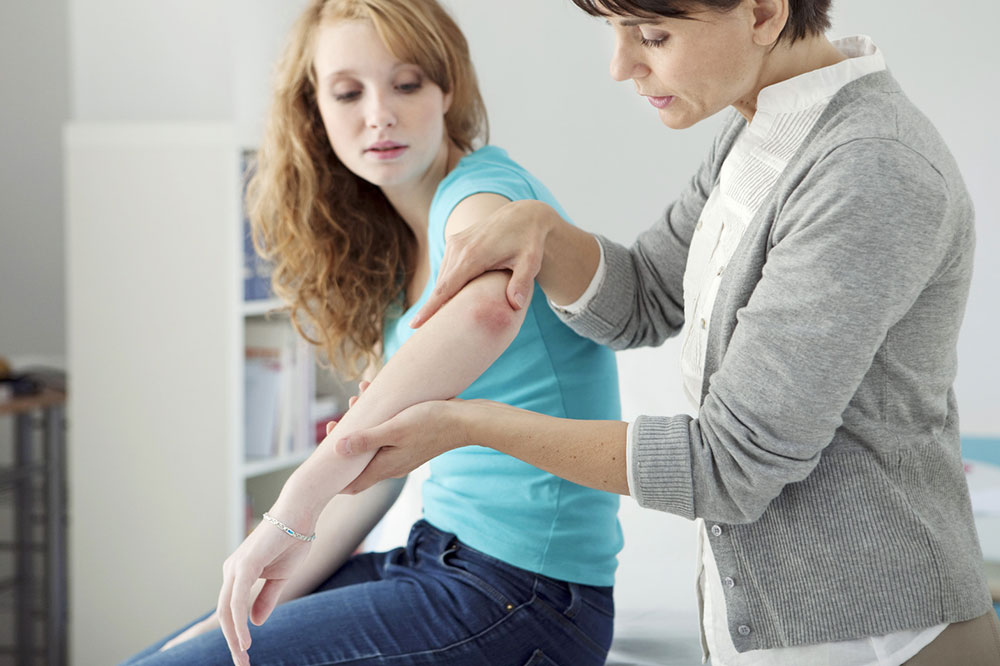
Psoriasis is a common chronic skin condition marked by rapid skin cell turnover, leading to the development of thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. These patches often cause discomfort, including itching and soreness. The disease features periodic flare-ups lasting from weeks to months, followed by remission phases. While a definitive cure remains unavailable, symptom control through lifestyle adjustments—such as quitting smoking, managing stress, and moisturizing—can enhance daily comfort.
Learn more about the indicators and risk factors associated with psoriasis below.
Red, inflamed patches with silvery-white scales
Scaly lesions, notably in children
Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
Itching, burning sensations, or pain
Pitted or thickened nails
Joint stiffness and swelling
Symptoms vary from small patches to extensive skin coverage. Psoriasis tends to follow a cyclical pattern, with periods of exacerbation and remission.
Key risk factors include:
Genetic factors: Family history greatly increases susceptibility, especially if relatives are affected.
Infections: Immune system impairments or recurrent infections such as HIV boost the risk.
Stress: High stress levels can weaken immunity and trigger outbreaks.
Obesity: Excess weight predisposes individuals, especially in skin folds.
Smoking: Tobacco use not only raises the risk but can also intensify severity.
Note: This information provides general insights into psoriasis symptoms and factors. Always consult licensed healthcare providers for diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. This article is not a substitute for professional medical advice.