Key Insights into Managing Psoriasis Effectively
Discover essential facts about psoriasis, including its causes, triggers, and treatment approaches. Learn how to manage flare-ups effectively through medications, lifestyle adjustments, and professional guidance to maintain healthier skin and improve quality of life.
Key Insights into Managing Psoriasis Effectively
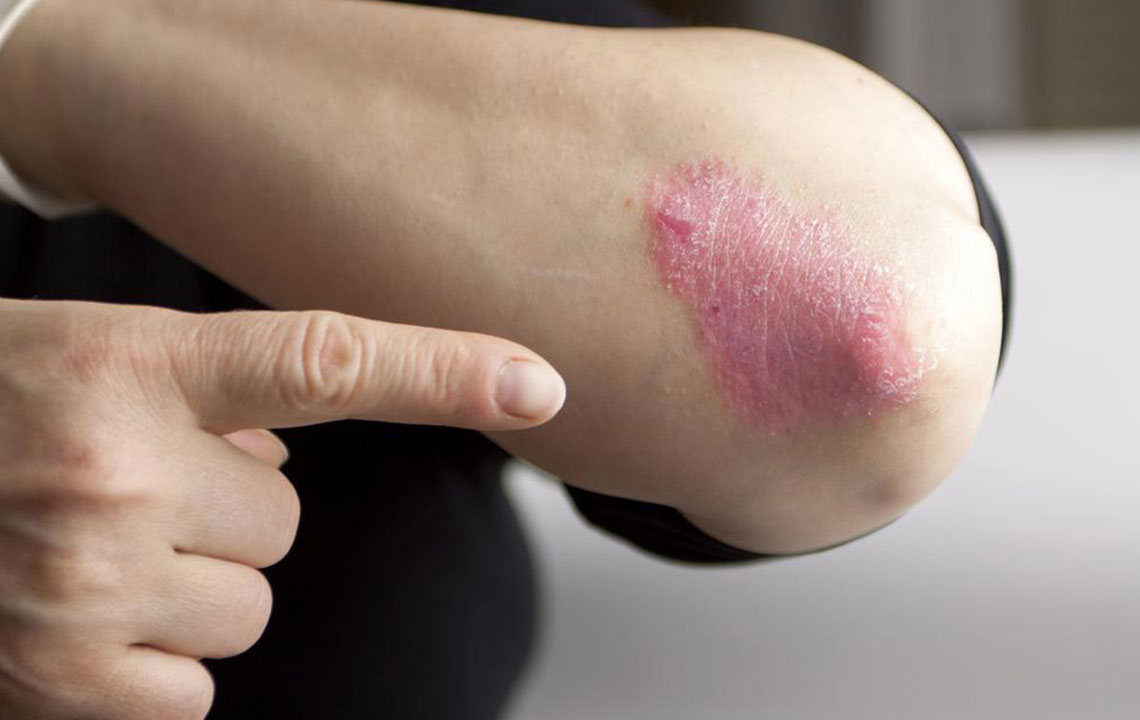
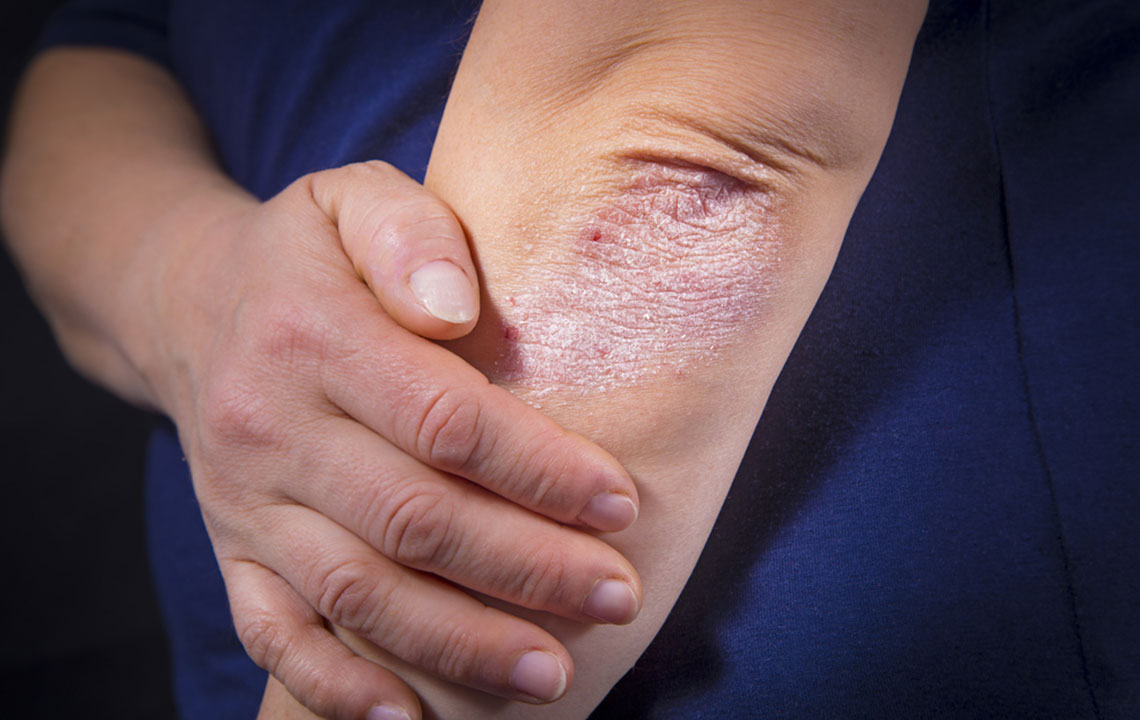
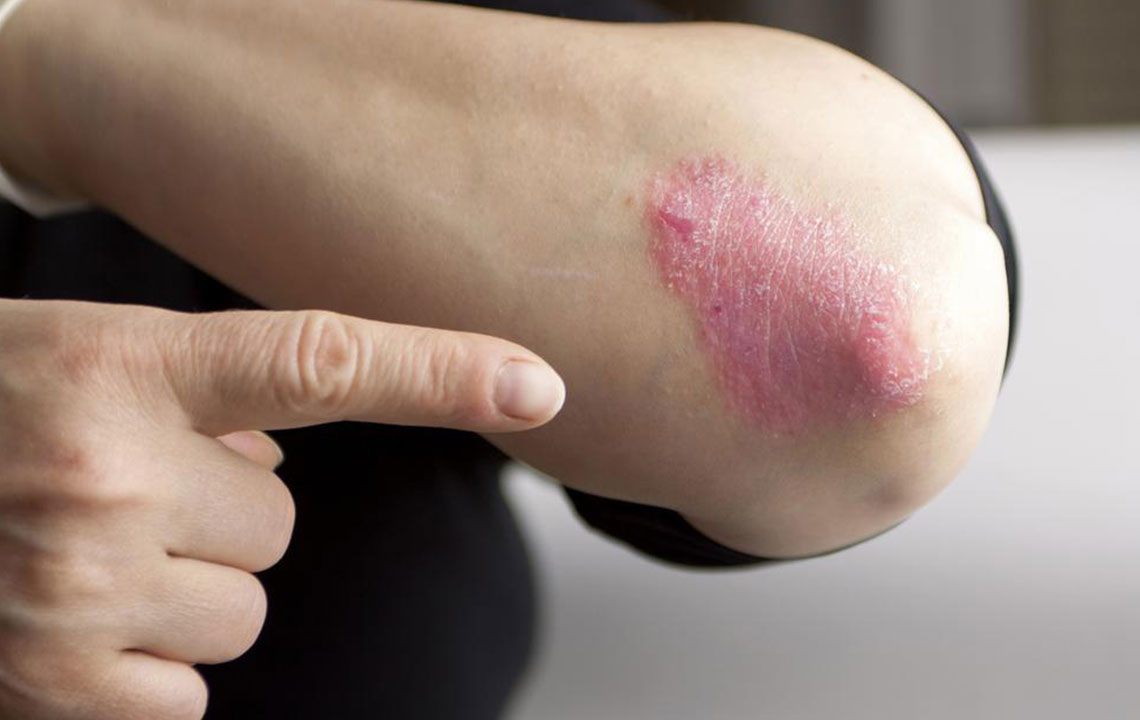
Psoriasis is a persistent autoimmune skin disorder marked by abnormal immune activity. It causes rapid skin cell buildup, resulting in flaky, scaly patches on the skin. While there's no cure, symptoms can be controlled through various treatments. Usually developing in adults, psoriasis often affects regions like the knees, scalp, and elbows. The severity ranges from minor patches to widespread skin lesions. Recognizing triggers and treatment options allows patients to manage flare-ups and maintain healthier skin.
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact origins are unclear, but genetic and environmental factors are key. A family history increases the likelihood, and immune system irregularities are central to its development.
Genetic predisposition accounts for about one-third of cases, especially with affected relatives. Nevertheless, only a small percentage of genetically predisposed individuals develop symptoms. Environmental factors such as climate, stress, infections, medications, skin injuries, smoking, and alcohol consumption can trigger or worsen the condition. Cold, dry weather often exacerbates symptoms by drying the skin. Stress and infections like strep throat frequently lead to flare-ups. Certain medications and skin trauma can also provoke outbreaks, intensifying symptoms.
In psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly targets healthy skin cells, leading to their rapid proliferation. This results in thickened, flaky patches often accompanied by inflammation and redness. The immune response causes discomfort and the characteristic rash.
Although no definitive cure exists, treatment aims to reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Options include topical creams, light therapy, and systemic drugs. Mild cases benefit from vitamin D analogs, retinoids, or salicylic acid. Phototherapy with natural sunlight or UVB light can alleviate symptoms. For more severe cases, healthcare providers may recommend oral or injectable immunosuppressants. Moisturizing regularly and avoiding known triggers are essential lifestyle strategies. Consult a dermatologist for personalized care plans and explore complementary therapies like natural oils for additional relief. Ongoing research continually enhances treatment options for psoriasis.
Note: The information provided is general guidance. Always seek professional medical advice for tailored treatment. Natural remedies may help, but professional consultation ensures safe and effective management. Advances in research are improving understanding and treatment of psoriasis.