Smart Approaches to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis and Gout Symptoms
This article explores effective strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis and gout, emphasizing early diagnosis, medication options, and lifestyle modifications. It highlights treatment approaches like NSAIDs, DMARDs, physiotherapy, and diet to improve joint health and reduce symptoms. Combining medical and supportive therapies provides a holistic approach to managing these inflammatory joint conditions and maintaining mobility and comfort.
Smart Approaches to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis and Gout Symptoms
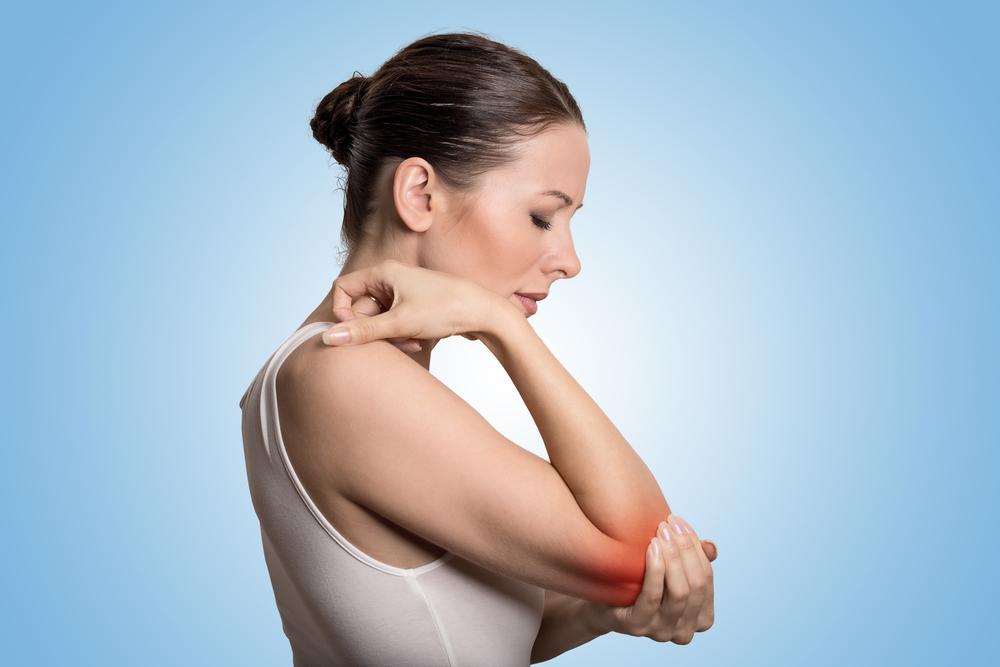
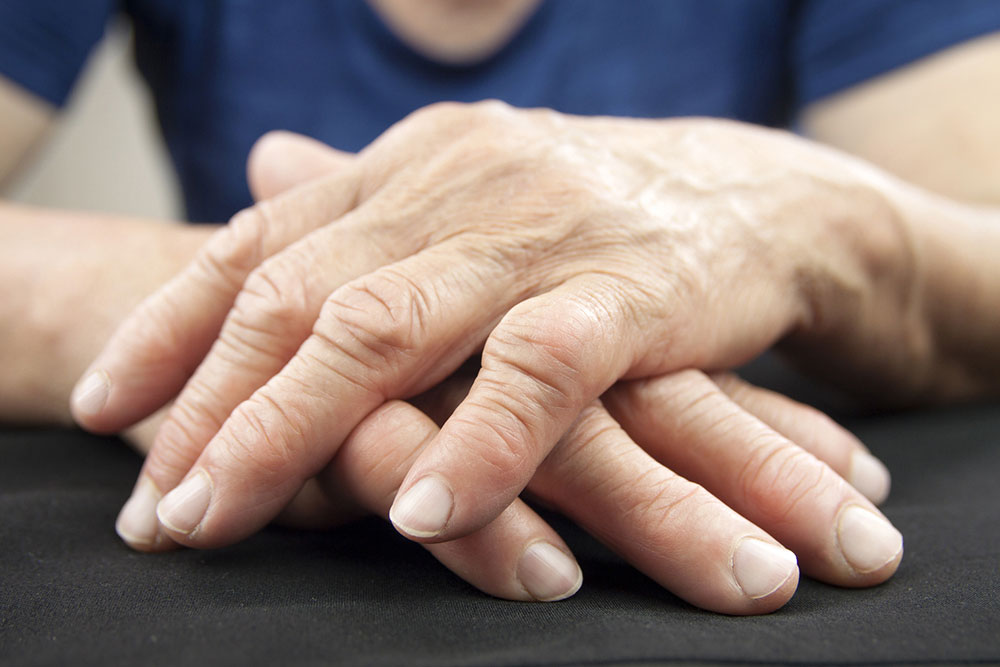
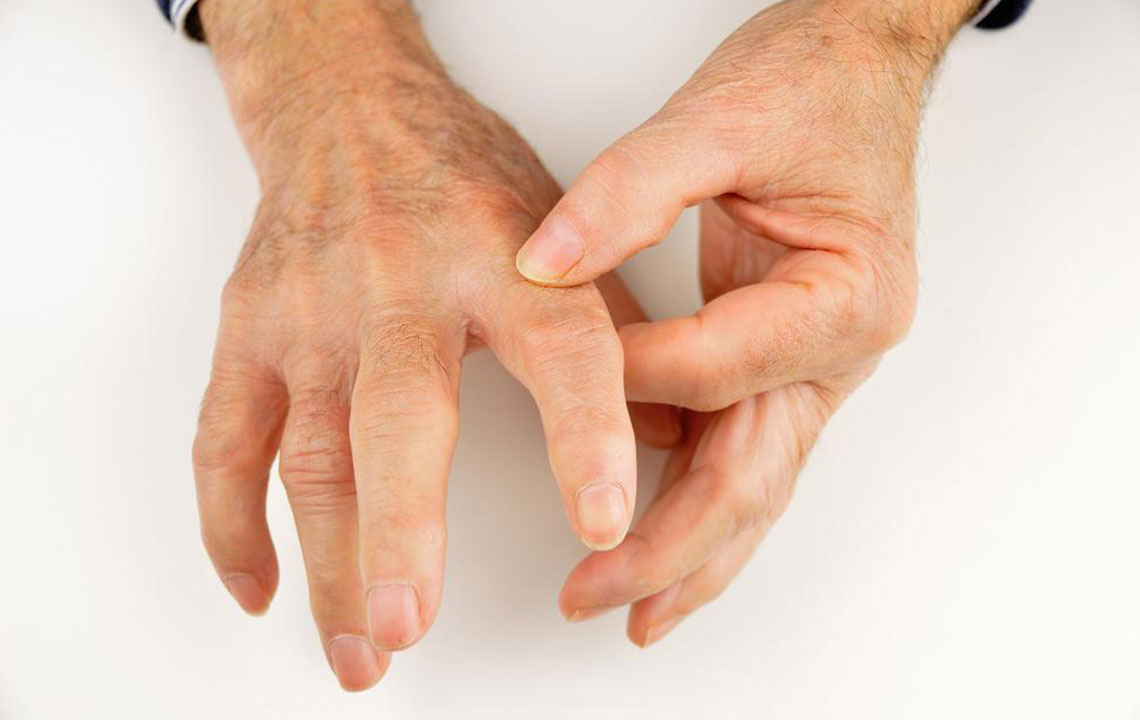
Recent research indicates that developing both rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and gout may be more common than previously thought, especially in men. RA is an autoimmune disease causing joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, while gout results from uric acid buildup forming painful crystals in joints. Although these conditions share inflammation features, their diagnosis involves specific signs: gout often affects the big toe, shows redness and swelling, whereas RA targets wrist and finger joints with sometimes less visible signs.
Early detection is vital for effective management. Treatment options focus on reducing pain, controlling inflammation, and preventing joint damage. Gout treatments include NSAIDs like ibuprofen for quick relief, corticosteroids, and colchicine for flare-ups and ongoing management. RA management involves DMARDs such as methotrexate, NSAIDs, corticosteroids, or biologic drugs to slow disease progression. Combining lifestyle changes with medication enhances overall well-being.
Supportive therapies like physiotherapy, relaxation practices, low-impact exercise, heat and cold therapy, and a nutrient-rich diet can significantly improve joint function and reduce discomfort. These strategies, alongside medical treatment, offer a comprehensive approach to managing both conditions effectively and enhancing quality of life.