Proven Methods to Keep Blood Sugar in Check
Learn effective techniques to stabilize blood sugar levels, crucial for diabetes management. The article covers normal ranges, targets for diabetics, and practical strategies like monitoring, stress management, and lifestyle adjustments. Implementing these methods can help prevent complications and improve health outcomes.

Proven Methods to Keep Blood Sugar in Check
Managing blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes, a condition marked by high glucose due to inadequate insulin or the body's ineffective use of insulin. Insulin regulation is critical for controlling blood sugar. When insulin function is compromised, blood glucose levels can become unstable. Worldwide, approximately 8.5% of adults are diagnosed with diabetes each year.
Understanding Blood Sugar Norms
Maintaining blood sugar within healthy limits is vital for effective diabetes management.
What constitutes normal blood sugar? How are blood sugar charts interpreted?
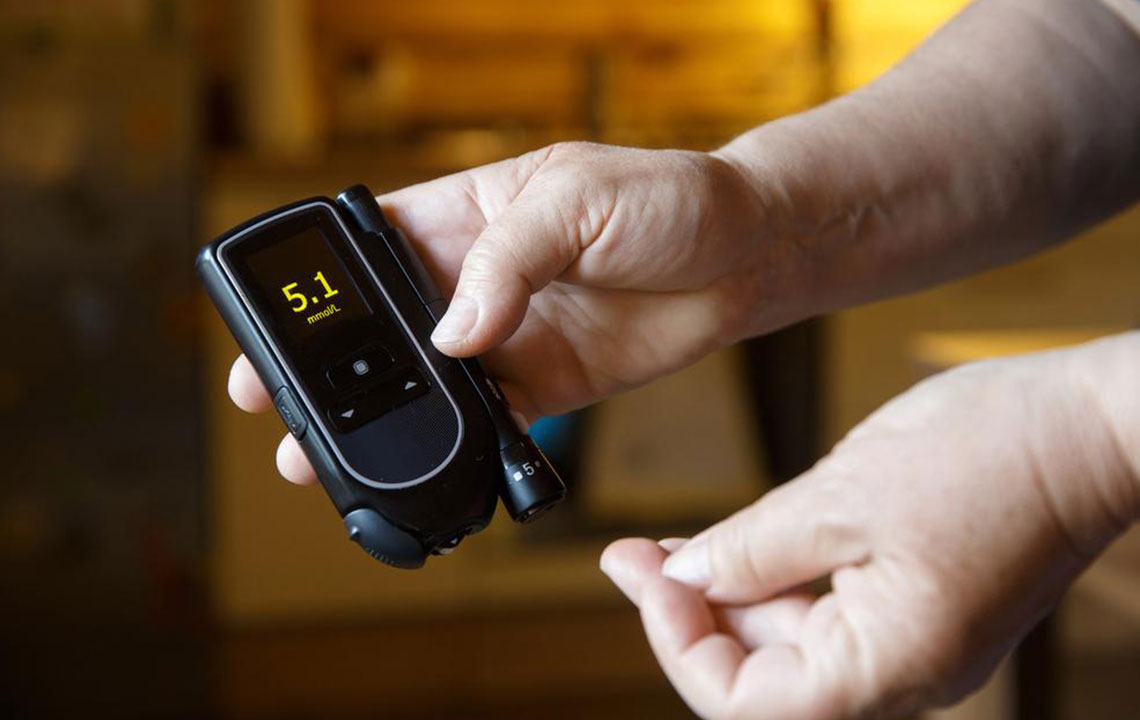
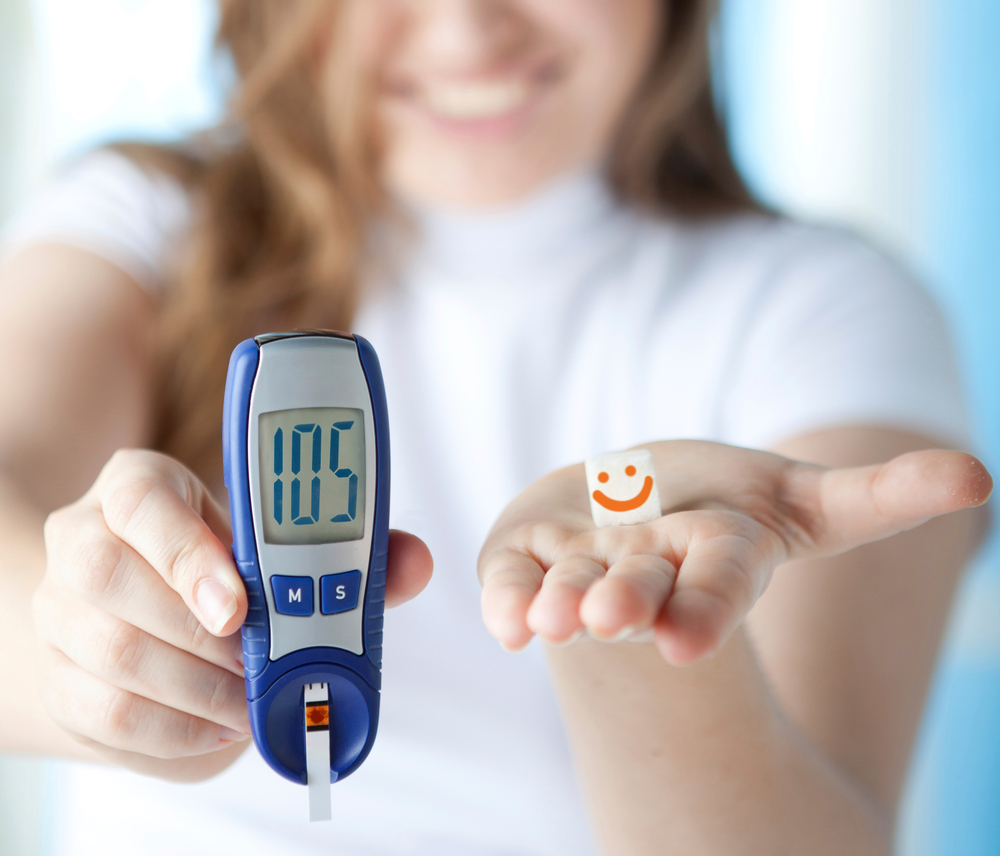
Blood glucose tests reference “normal” and “healthy” ranges. Since the body converts all forms of sugar into glucose, these terms overlap. Blood sugar levels are expressed in mg/dL. Throughout the day, levels naturally fluctuate. Key measurements include fasting glucose, post-meal glucose, and HbA1c.
Fasting Glucose: Reads glucose after overnight fasting, usually before breakfast. Normal is 70-100 mg/dL.
Postprandial Glucose: Measured two hours after eating. Healthy levels stay below 140 mg/dL.
HbA1c: Shows average blood sugar over 2-3 months by analyzing hemoglobin A1c bound with glucose. Normal range is 4-5.6%.
Blood Sugar Targets for Diabetics
Fasting: 80-130 mg/dL.
Post-meal: Below 180 mg/dL.
HbA1c: Less than 7% indicates good control.
Keeping blood sugar levels close to normal reduces the risk of nerve, eye, and kidney complications. Key strategies include regular testing, managing stress, and maintaining healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
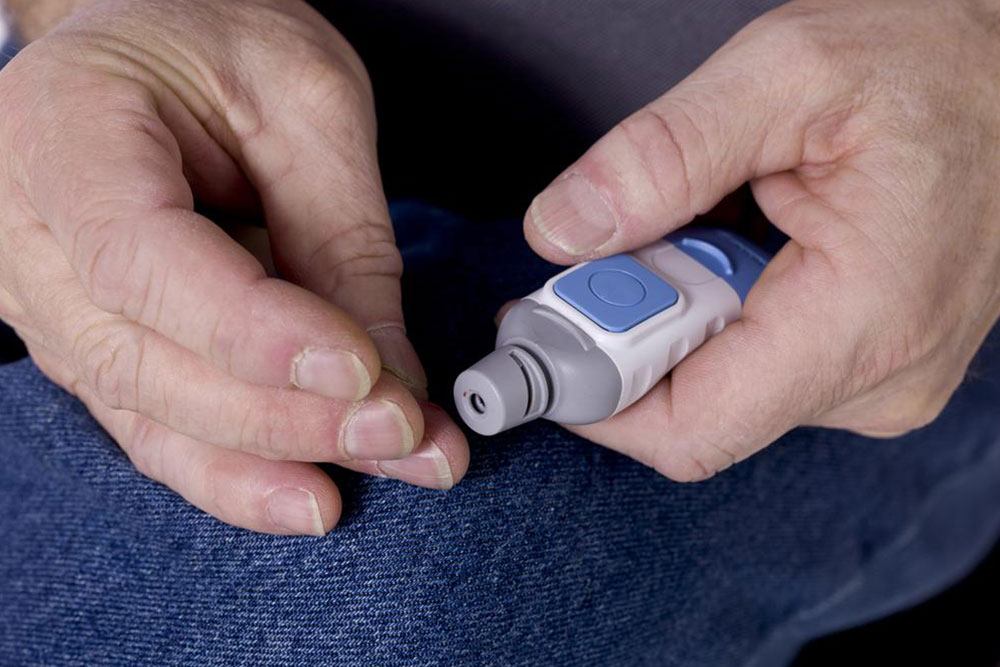
Regular Testing: Conduct routine blood sugar checks weekly, monthly, or quarterly to identify patterns and adapt habits. Quick checks are useful for immediate adjustments.
Diabetes Management: Recognize diabetes as a lifelong condition. Stress reduction through activities, exercise, and social interaction can positively influence blood sugar control.
Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Control: Aim for blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg and maintain low LDL cholesterol to lower cardiovascular risk associated with high blood sugar.
This holistic approach assists individuals in maintaining healthy glucose levels, reducing complications, and boosting overall well-being.