Effective Approaches to Controlling Elevated Blood Glucose Levels
This article provides effective strategies for managing high blood glucose levels, emphasizing medication adherence, diet, and physical activity. It highlights the importance of monitoring and personalized care to prevent complications associated with hyperglycemia, helping diabetics maintain optimal health and avoid organ damage.

Effective Approaches to Controlling Elevated Blood Glucose Levels
Managing elevated blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, is critical for individuals with diabetes. Sudden blood glucose spikes can lead to long-term health issues if not properly controlled. Persistent high glucose levels may cause damage to essential organs such as the kidneys and brain. The body produces glucose in the liver and muscles, utilizing dietary carbs for energy. Proper management strategies are vital to prevent complications and maintain overall health.
Glucose travels through the bloodstream to nourish cells, relying on insulin produced by the pancreas. In diabetic individuals, insulin deficiency or poor function results in excess glucose in the blood, elevating levels.
The circulating blood sugar fuels cellular activity, which depends on adequate insulin levels. When insulin production is compromised or ineffective, blood sugar rises.
Causes of High Blood Glucose
Factors that contribute to sustained hyperglycemia include overeating carbohydrates, stress, insufficient insulin secretion, sedentary lifestyles, illnesses, infections, and certain medications like steroids.
Blood Sugar Level Guidelines
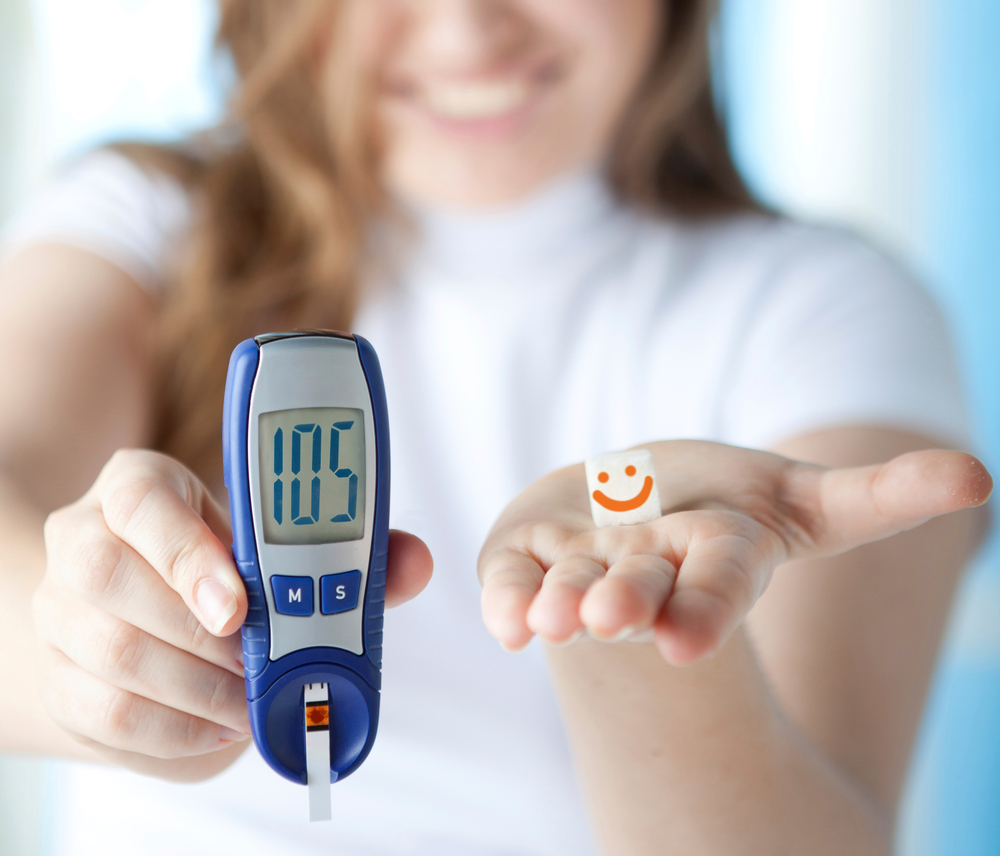
Reference charts help interpret fasting and post-meal glucose levels. Maintaining fasting levels below 130 mg/dl and post-meal readings under 180 mg/dl is recommended. Regular monitoring helps evaluate control strategies. Since target levels vary with age, health status, and lifestyle, personalized guidance from healthcare professionals is essential. Blood sugar management techniques include:
Medications — Adhere to prescribed treatments, adjusting doses or timing as recommended to keep blood glucose within the desired range.
Dietary Management — Embrace a nutritious diet emphasizing vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. Limit sugars and processed carbs. Avoid alcohol and tobacco, and opt for small, frequent meals to stabilize sugar levels.
Physical Activity — Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity and supports overall well-being. Follow medical advice, especially if certain health conditions restrict activity.