Smart Approaches to Stabilize Blood Glucose Levels
Discover effective strategies to manage blood sugar levels through balanced diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications. This comprehensive guide offers practical tips for maintaining glucose stability, essential for individuals with diabetes or those seeking better health. Learn about meal timing, healthy carbs, green tea, vinegar, sleep, and physical activity to optimize blood glucose control and overall well-being.
Smart Approaches to Stabilize Blood Glucose Levels
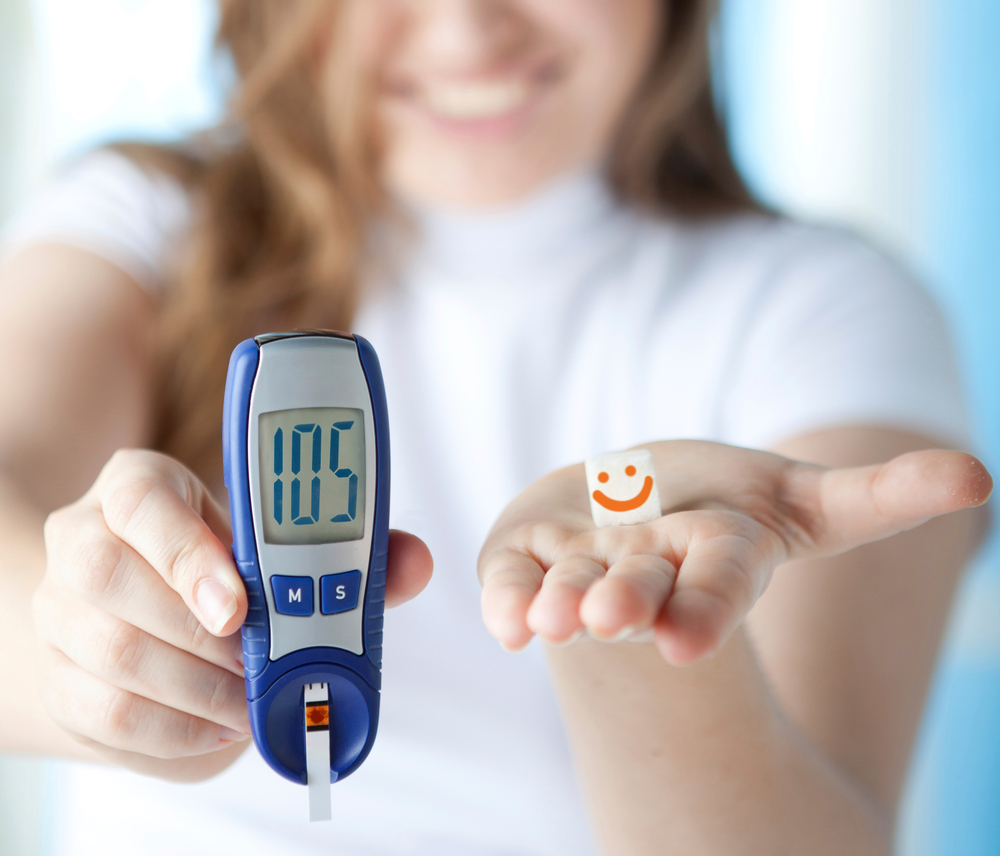
Keeping blood sugar levels balanced is crucial for your overall health, especially for those with diabetes. When the pancreas produces insufficient insulin or the body resists its effects, blood glucose levels can become erratic. Achieving stability requires a synergy of nutritious eating habits and consistent physical activity to maintain optimal levels.
Effective blood sugar control tips include:
Regular Meal Scheduling: Avoid skipping meals, especially breakfast, as it can cause glucose spikes due to liver glucose release. Eating balanced, timely meals helps sustain steady blood sugar.
Selecting Healthy Carbohydrates: Opt for complex carbs such as legumes, vegetables, and whole grains to prevent rapid glucose increases and to provide essential nutrients.
Smart Use of Meal Replacements: Diabetic-friendly shakes and snack bars are convenient for busy days—always review ingredients to ensure health benefits.
Incorporate Green Tea: Swapping sugary drinks for green tea can lower calorie intake, supply antioxidants, and improve insulin response.
Add Vinegar to Meals: Including vinegar in salads may slow digestion and help regulate blood sugar, but consult your healthcare provider first.
Get Adequate Sleep: Sufficient rest helps balance hormones linked to hunger and insulin, preventing fluctuations in blood sugar.
Stay Active Regularly: Engaging in activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can boost metabolism, enhance sleep quality, and stabilize blood glucose levels. Target at least 30 minutes daily.
Adopt a Low-Glycemic Diet: Foods like whole grains, non-starchy veggies, beans, and oats aid in maintaining consistent blood sugar. Watch portion sizes to avoid overeating.
If symptoms such as abnormal temperature or blood in urine occur, seek emergency medical help immediately. Consistent monitoring, dietary discipline, and exercise are key to effective glucose management. Always consult healthcare professionals for tailored advice and treatment options.
Note:
This guide emphasizes practical methods for maintaining healthy blood sugar through diet, activity, and lifestyle choices. It is informational and not intended to replace professional medical care. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized health strategies.