Cutting-Edge Insulin Delivery Technologies for Type 1 Diabetes Control
Explore state-of-the-art insulin delivery systems for type 1 diabetes management, including insulin pumps and CGM technology. Learn how these devices improve blood sugar control, provide personalized treatment, and enhance quality of life for patients. Discover the differences between traditional tubed and modern tubeless patch pumps, and understand their benefits for active lifestyles and precise insulin management.
Advanced Devices for Managing Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, resulting in little or no insulin production. It often manifests in childhood or young adulthood but can develop at any age. Treatment mainly involves insulin therapy facilitated by innovative delivery methods like insulin pumps, combined with continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems for precise blood sugar tracking.
What is an insulin pump?
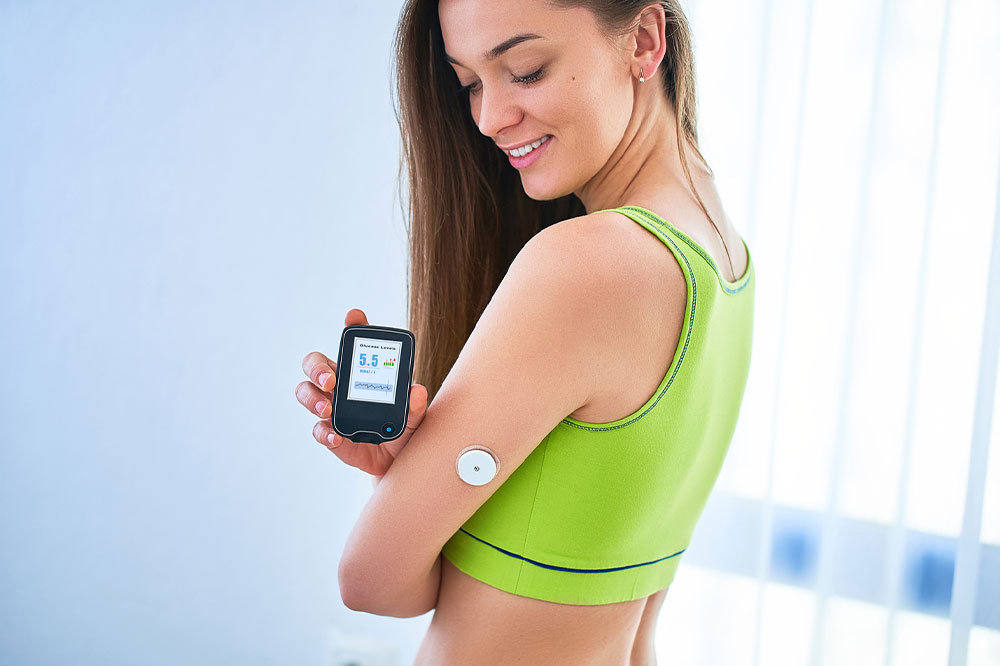
Insulin pumps are small, wearable devices that deliver consistent insulin doses. Similar in size to a small box, they provide rapid-acting insulin through a catheter under the skin, offering a modern alternative to traditional injections.
Many current pumps incorporate CGM technology, enabling real-time glucose monitoring and automated insulin adjustments. This seamless integration improves blood sugar control and reduces manual calculations for users.
How do insulin pumps function?
Insulin pumps aim to mimic the pancreas by delivering small, continuous insulin amounts called basal rates, which vary throughout the day based on activity, meals, and bodily needs. They can also provide bolus doses for meals or high blood sugar episodes, calculated according to carbohydrate intake and glucose readings.
These devices are programmable and customizable to suit individual lifestyles, often paired with CGM systems for dynamic insulin management. Users can set doses with healthcare guidance, ensuring personalized treatment plans.
Types of insulin pumps
Advances have led to two main types: traditional tubed pumps and tubeless patch pumps.
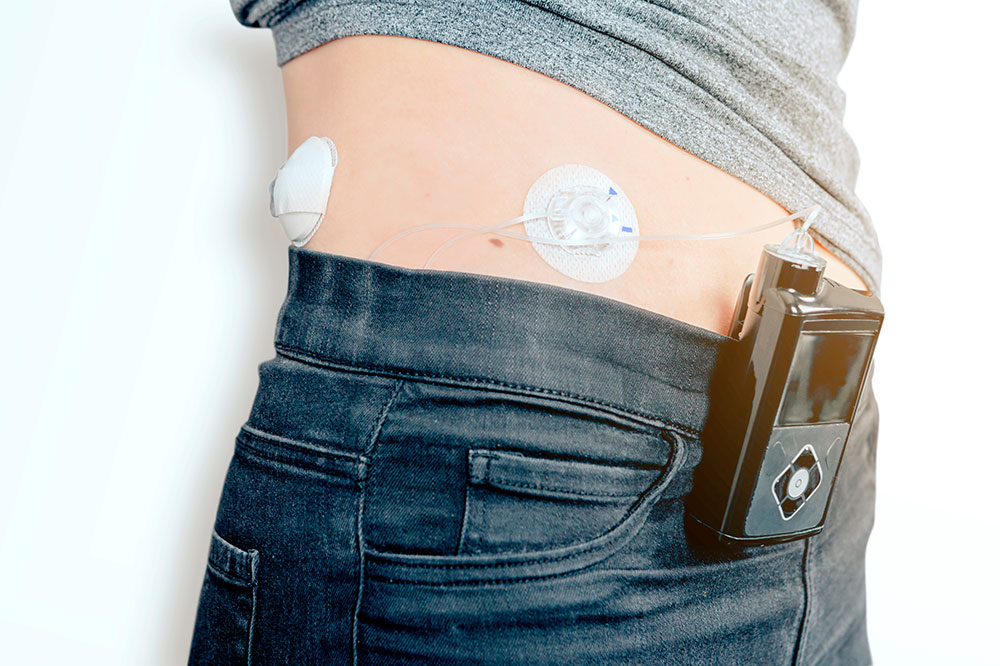
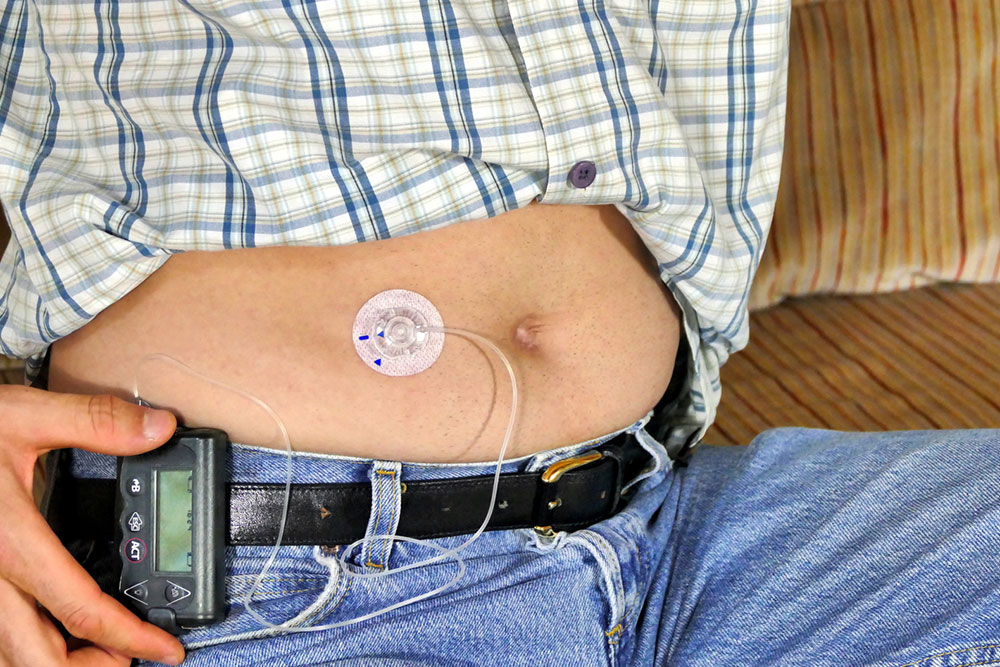
Tubed insulin pumps
These traditional models connect to an infusion set via a narrow tube, with a display for control. They hold insulin in a reservoir that needs refilling every few days. Their portable design allows attachment to clothing, with the flexibility to disconnect for activities like swimming or bathing.
Patch insulin pumps
Also known as patch pumps, these are self-adhesive devices worn directly on the skin. They combine the insulin reservoir and cannula into a small, waterproof pod that can be replaced every 2-3 days, offering greater mobility and ease of use for active individuals.
Benefits of using insulin pumps
For many with diabetes, especially type 1, insulin pumps provide precise dose management aligned with daily activities and meals. When paired with CGM, they enable proactive blood sugar control, data sharing, and better treatment adjustments. Pumps support flexible lifestyles and enhance overall quality of life.
Disclaimer: The health information provided is for general educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare professionals for diagnosis and personalized treatment options.