Innovative Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring Solutions: Benefits and Limitations
Explore how non-invasive glucose monitoring devices are revolutionizing diabetes management by offering painless, continuous, and real-time blood sugar tracking solutions. This article discusses various technological approaches, their benefits, and current challenges, highlighting future prospects for safer and more accessible diabetes care.
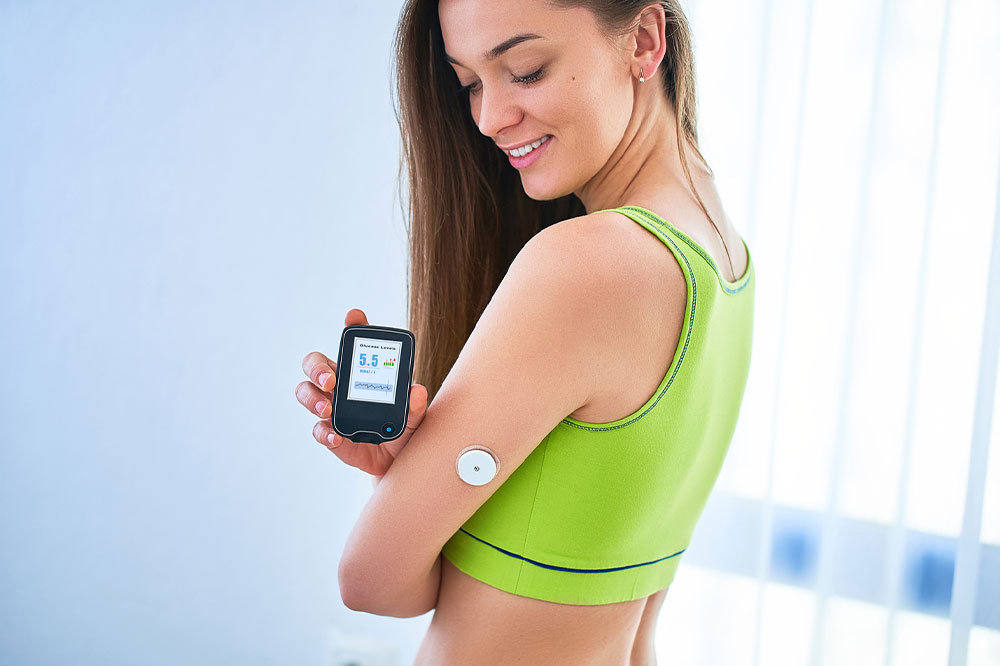

Revolutionizing Diabetes Care with Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring Devices
Non-invasive glucose monitoring tools are changing how people with diabetes track their blood sugar levels. These easy-to-use devices eliminate the need for finger pricks, reducing discomfort and making daily testing simpler. By employing advances in optical detection, electrical sensing, and breath analysis, these gadgets deliver continuous, real-time glucose insights. Understanding the different technological approaches, along with their benefits and potential drawbacks, is key to improving diabetes management and enhancing quality of life.
What Are Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring Devices?
Unlike traditional blood tests that require finger pricks, non-invasive meters analyze biological signals or use optical techniques to estimate glucose levels painlessly.
Technological progress has led to various non-invasive glucose measurement methods, including:
Electrical sensing: Utilizing electrical signals and impedance variations to approximate blood sugar, through techniques such as microwave sensing, impedance plethysmography, and bioimpedance spectroscopy.
Optical sensors: Using light-based measurements, these devices can be integrated into wearable gadgets like wristbands or smartwatches for continuous tracking by analyzing light reflection from skin.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs): Small sensors placed under the skin monitor interstitial fluid, providing ongoing data, trend insights, and alerts via connected devices or apps.
Sweat and breath analysis: Non-invasive methods that analyze sweat composition or exhaled air to estimate glucose levels, offering pain-free testing options.
Cutting-edge innovations: Research focuses on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, nanomaterials, plasmonic sensors, optical fiber technology, artificial intelligence, and wearable optical devices to improve precision and ease of use.
Benefits of Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
Pain-free testing: Avoids the discomfort of finger pricks.
Ease of use: Designed for daily, effortless monitoring, encouraging regular tracking.
Immediate data: Some devices provide continuous updates, aiding proactive blood sugar management.
Reduced infection risk: No need for blood samples minimizes infection chances.
Improved lifestyle: Less pain and increased flexibility enhance overall wellbeing for diabetics.
Limitations and Challenges
Accuracy concerns: Performance can vary among devices and may be affected by external factors or calibration errors.
Cost implications: State-of-the-art non-invasive systems tend to be more expensive upfront and for ongoing supplies.
Calibration needs: Some devices require precise initial setup and maintenance.
Environmental factors: Conditions like sweat, skin issues, or ambient circumstances can interfere with sensor effectiveness.
In summary, non-invasive blood sugar monitors are transforming diabetes care by providing safer, more comfortable options for glucose tracking. Technological advancements continue to improve their accuracy and accessibility, promising better management and quality of life for users.