Comprehensive Guide to Insulin Types and Delivery Devices for Diabetes Care
This article provides an in-depth overview of various insulin types and delivery devices essential for effective diabetes management. It discusses the differences between rapid, short, intermediate, and long-acting insulins, along with inhaled options. The piece also highlights the importance of proper insulin administration, regular blood sugar monitoring, and the use of insulin pens and injection methods to maintain optimal health in diabetes patients.
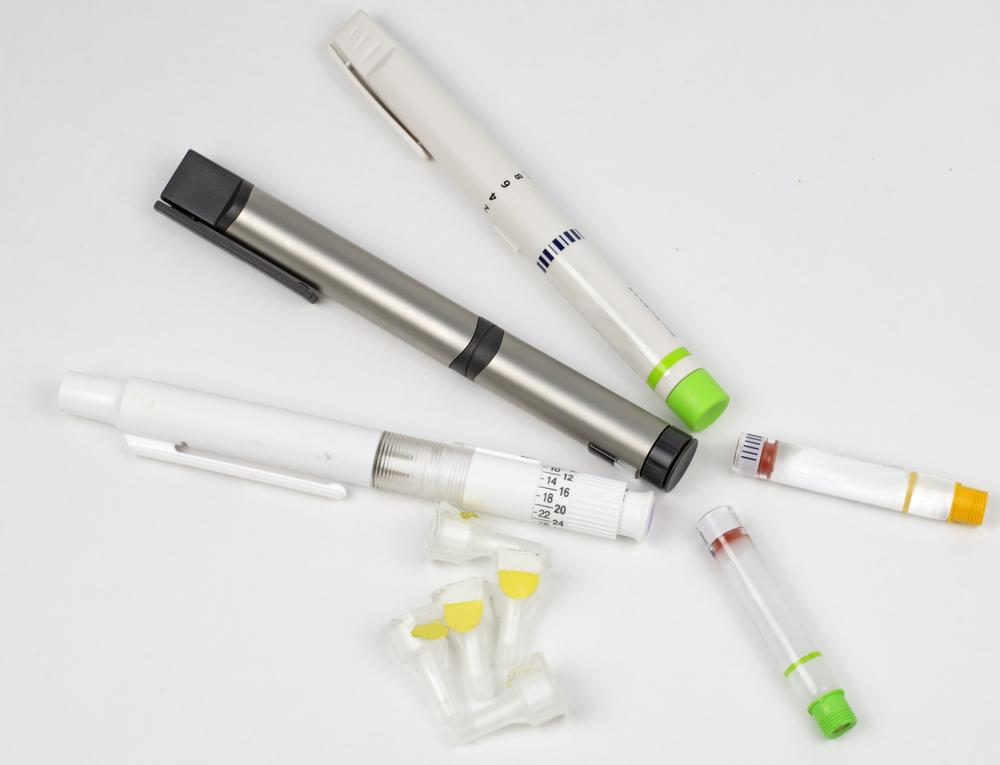
Different Insulin Forms and Administration Devices for Effective Diabetes Management
According to the American Diabetes Association, diabetes is a condition marked by high blood sugar levels resulting from the body's inability to produce enough insulin or use it efficiently. Insulin, a vital hormone, facilitates the transport of glucose from food into body cells for energy. Lack of sufficient insulin causes glucose to build up in the bloodstream, leading to damage to organs such as the kidneys, eyes, nerves, and heart.
Diabetes Types
Type 1
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the immune system destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with this form require multiple daily insulin injections. It accounts for approximately 5-10% of all diabetes cases.
Type 2
This most common type represents 90-95% of cases. It develops when the body doesn't produce enough insulin or cannot use it effectively. Often symptomless initially, it is influenced by age and lifestyle factors. Management may include lifestyle changes, medications, and insulin therapy such as injections and pens to regulate blood sugar levels.
Effective glucose management is supported by test strips, which allow daily blood sugar monitoring. These disposable strips are crucial tools in diabetes control.
Types of Insulin
Rapid-acting insulin: Examples include Insulin Glulisine (Apidra), Insulin Lispro (Humalog), and Insulin Aspart (NovoLog). They begin working within 15 minutes, peak around 1 hour, and last 2-4 hours.
Short-acting insulin: Such as Humulin R and Novolin R, start acting in about 30 minutes, peak at 2-3 hours, and last approximately 3-4 hours.
Intermediate-acting insulin: NPH insulin (Humulin N, Novolin N) takes 2-4 hours to work, peaks at 4-12 hours, and provides coverage for 12-18 hours.
Long-acting insulin: Detemir (Levemir) and Glargine (Lantus) release steadily to maintain consistent glucose levels over 24 hours.
Inhaled insulin: Afrezza, using the Technosphere inhalation system, acts rapidly within 12-15 minutes, peaks at 30 minutes, and clears in about 3 hours.
Insulin is administered through injections or via insulin pens, which contain pre-filled or replaceable cartridges. Dose control is managed with the dial, making consistent insulin delivery vital for optimal health and precise management.