Comprehensive Guide to Eczema: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Care Methods
This comprehensive guide on eczema covers symptoms, causes, and management strategies. It highlights key signs, triggers, potential complications, and effective care techniques. Aimed at raising awareness, it encourages readers to consult healthcare providers for personalized treatment. Understanding eczema helps in better control, reducing discomfort, and improving overall skin health.
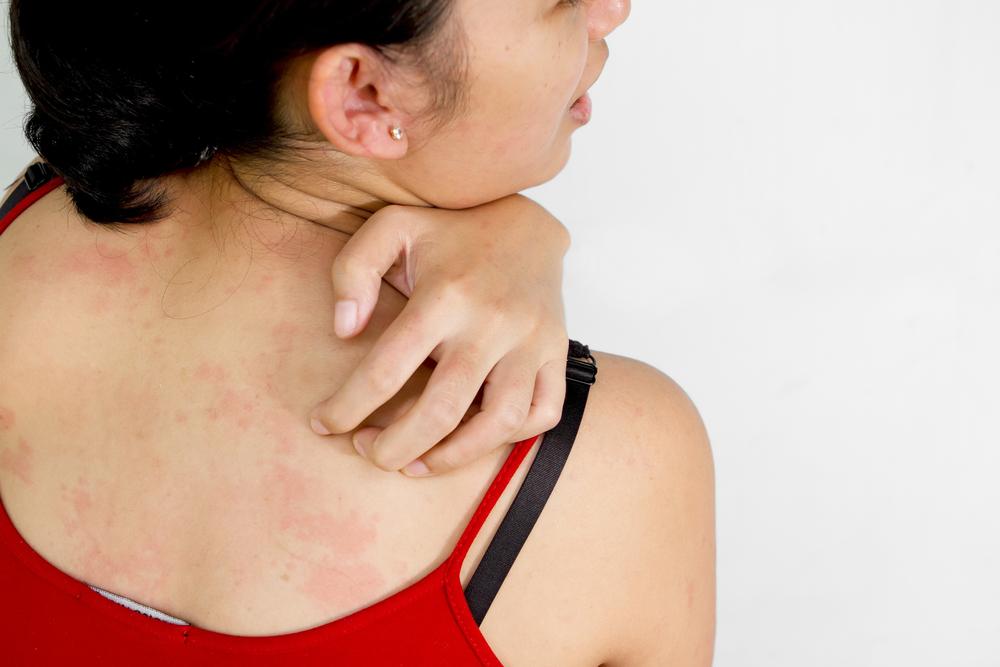
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a prevalent skin condition marked by dryness, itchiness, and irritation. It can affect people of all ages, from infants to adults, and may last for months depending on severity. Commonly, rashes appear on the face, behind the knees, hands, feet, or wrists, causing discomfort and skin discoloration.
The skin often becomes thickened and dry, with infants experiencing oozing and crusting on the face and scalp. Though the precise cause is unknown, an overactive immune response plays a role. Irritants like harsh soaps, chemicals, and pet dander can worsen symptoms.
Triggers include rough fabrics, certain detergents, and specific allergens. Key signs are:
Red, itchy patches on various body parts
Intense nocturnal itching
Swollen bumps that may leak fluid when scratched
Fragile, irritated skin prone to further issues
Potential complications include:
Sleep problems: Nighttime itching interrupts sleep
Secondary infections: Cracked skin can become infected
Chronic skin changes: Scratching leads to thickened skin
Respiratory allergies: Conditions like asthma often coexist with eczema
Management strategies involve:
Use of topical treatments such as hydrocortisone and antihistamines
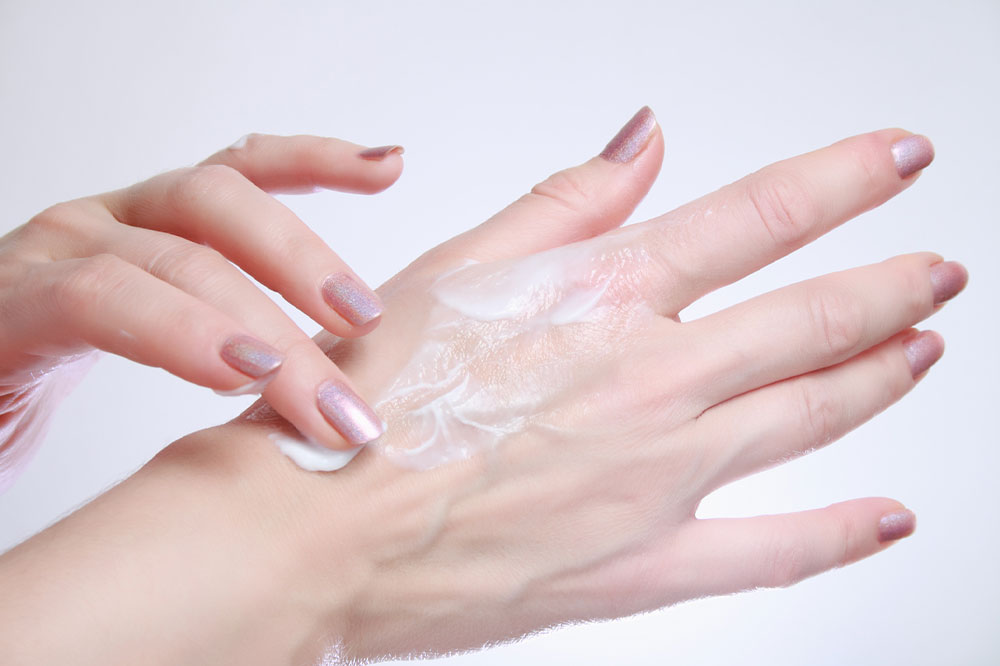
Gentle cleansing with mild products and regular moisturizing
Humidifiers to keep skin hydrated
Phototherapy in severe situations
Stress reduction and dietary modifications to prevent flare-ups
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding triggers, and practicing good skincare can greatly reduce flare-ups. Educating oneself about eczema is essential for better control and improved quality of life.
Note:
This article offers general information based on current research. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized diagnosis and treatment. The content should not replace professional advice or treatment plans.