Eczema Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Strategies
Discover essential insights into eczema, including its causes, signs, and effective management strategies. This overview helps individuals understand triggers, symptoms, and preventive measures to better handle the condition and improve skin health.
Eczema Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Strategies
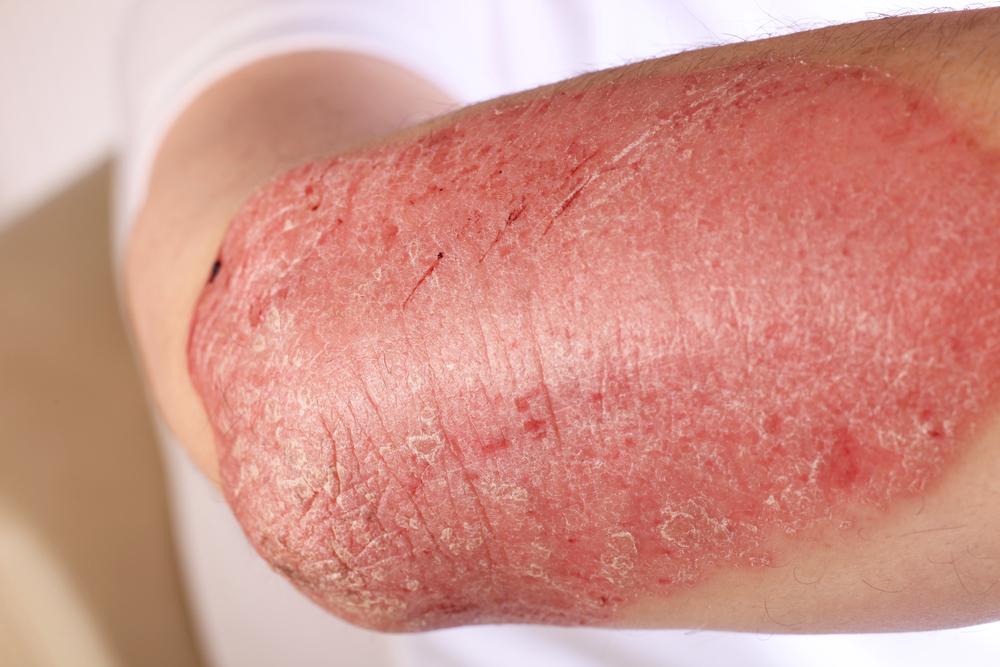
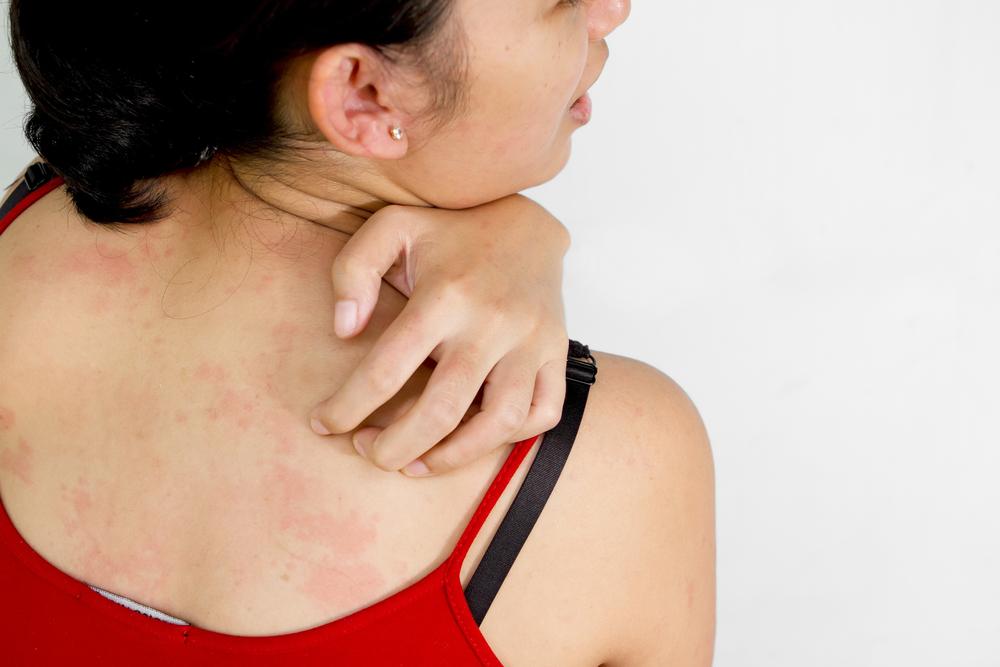
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common inflammatory skin disorder affecting millions worldwide. It is often linked with allergies such as hay fever and asthma. Nearly 17.8 million Americans experience this condition, which typically results in red, itchy patches on areas like the face, arms, and legs. Though more common in children, eczema can occur at any age and is not contagious.
What Causes Eczema?
Healthy skin normally creates a barrier that protects against irritants, allergens, and bacteria while retaining moisture. In eczema, genetic factors weaken this barrier, making skin more susceptible. Triggers include food sensitivities, environmental factors, genetic predispositions, immune system issues, and dry weather. Excessive hand washing and harsh environments may also exacerbate the condition.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms often appear before age five but can persist or flare at any time. Common signs include:
Small, fluid-filled bumps that may ooze when scratched
Intense itching, worse at night
Dry, rough skin
Discolored patches on the face, scalp, hands, elbows, knees, or neck
Thickened, flaky, or cracked skin
Heightened skin sensitivity due to scratching
Visual aids online can help identify eczema's typical appearance.
Complications and Risks
Repeated scratching can damage the skin, increasing infection risk from bacteria, viruses, or herpes simplex. People working with chemicals may experience irritant contact dermatitis. Many children with eczema develop asthma or hay fever later. Chronic itching can disturb sleep and cause skin thickening. Allergic contact dermatitis often accompanies eczema, adding to the complexity.
Preventive Tips
Moisturize skin regularly with suitable creams or ointments twice daily.
Reduce exposure to triggers like stress, harsh soaps, dust, pollen, and sweat.
Review diet; foods like milk, eggs, wheat, and soy may worsen symptoms. Consult your doctor for allergy testing.
Limit hot showers; choose warm water and keep baths brief.
Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers to avoid irritation.
Pat skin dry gently and apply moisturizer while skin is damp.
Try diluted bleach baths to decrease bacteria and prevent flare-ups, soaking affected areas for about 10 minutes twice weekly.
Since the exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, it's important to seek medical advice for personalized treatment plans. Following professional guidance can lead to better symptom management.
Note:
This article offers an overview of eczema, including causes, symptoms, and effective management tips. It aims to educate readers but should not replace professional medical consultation. Always seek advice from a healthcare provider for diagnosis and personalized treatment.