Eczema Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Approaches
This comprehensive guide explains eczema's causes, symptoms, and management techniques. It covers factors influencing the condition, detection methods, and practical tips for prevention and treatment. Suitable for all ages, it emphasizes personalized skincare routines and lifestyle adjustments to alleviate discomfort and reduce flare-ups, helping individuals maintain healthy skin and improve their quality of life.

Understanding Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
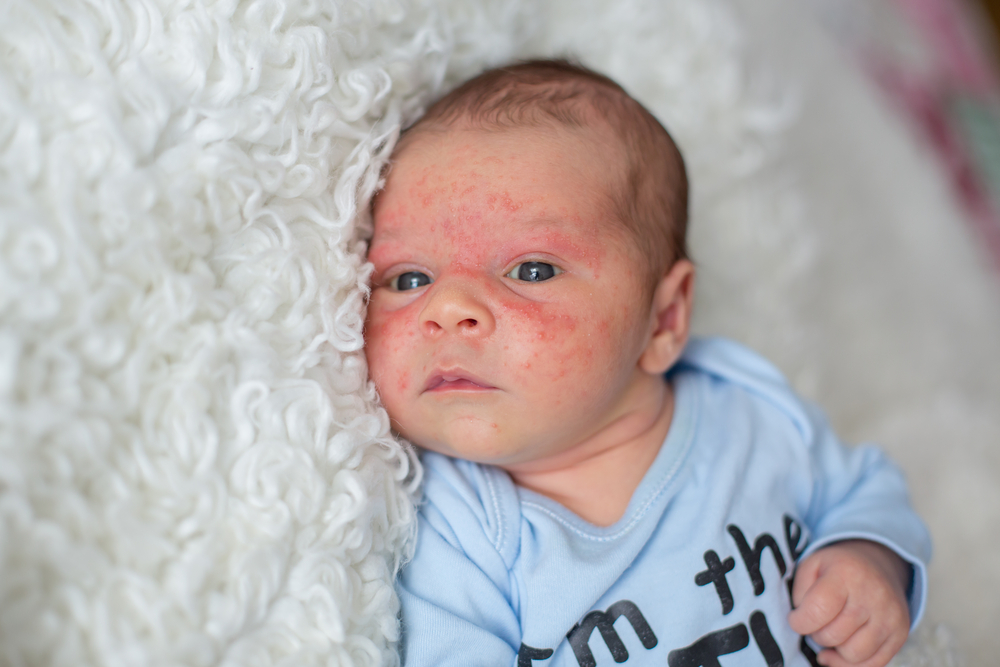
Eczema refers to a group of skin disorders characterized by inflammation, dryness, and irritation. It disrupts the skin’s protective barrier, making it more prone to moisture loss, sensitivity, and infections. Common signs include flaky patches, redness, sores, and intense itching. Although it can impact people of all ages, its severity varies. Proper skin care routines, avoiding irritants, and identifying triggers are crucial steps in controlling eczema symptoms.
Factors Influencing Eczema Development
While the exact cause of eczema is unclear, multiple factors play a role. Genetic factors, immune system irregularities, environmental pollutants, and compromised skin barriers that allow microbes and moisture to escape contribute to its onset. Exposure to harsh chemicals, weather extremes, and allergens also increases risk. Individuals with allergies, asthma, or hay fever are particularly vulnerable.
Environmental factors such as air pollution, strong soaps, and harsh skincare products can dry out the skin, causing itching and irritation. Hot and humid weather can induce sweating, worsening symptoms. An overactive immune response also contributes. People with allergic conditions are at higher risk. Although eczema often improves over time, some individuals experience persistent episodes requiring ongoing attention and management.
Signs and Diagnosis of Eczema
Symptoms depend on age but generally involve dry, flaky patches, redness, and itching in areas like elbows, knees, neck, and face. Adults might notice scaly, irritated skin with persistent dryness. Rubbing and scratching can lead to infections or worsen inflammation. Diagnosis is based on physical exam, symptom assessment, and may include allergy testing, blood analysis, or skin biopsy to exclude other conditions.
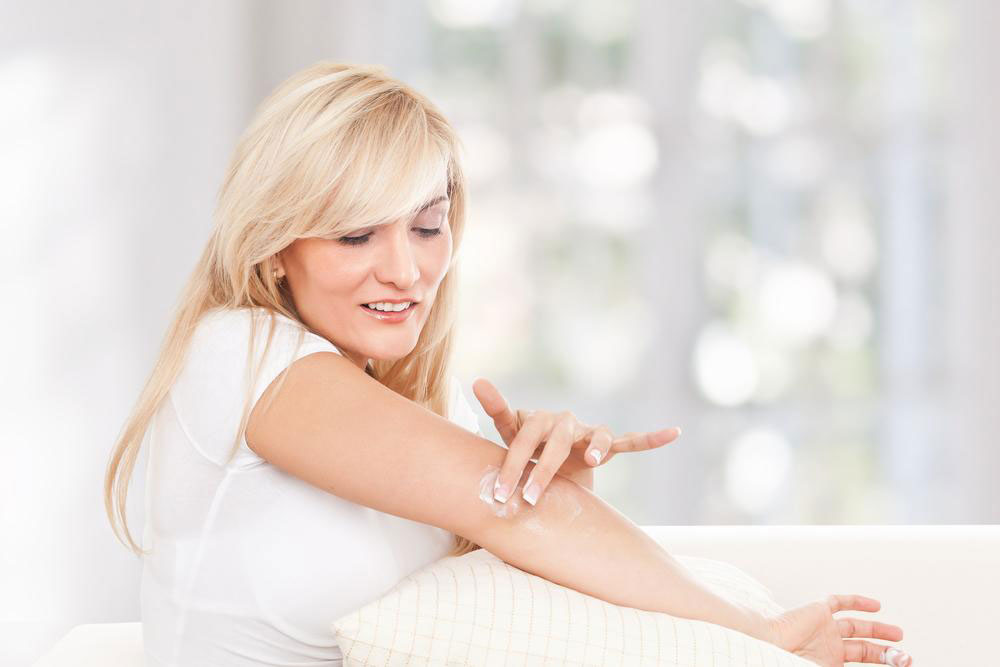
Proper management involves recognizing triggers and following a personalized skincare routine to reduce inflammation and keep skin hydrated.
Types of Eczema and Treatment Strategies
The most common form is atopic dermatitis, prevalent among children but also affecting adults. Many children outgrow it, though some experience long-term symptoms. Effective treatment includes skincare, environmental adjustments, and medical interventions when necessary. Managing stress, avoiding irritants, and using prescribed moisturizers can enhance quality of life.
Prevent flare-ups by establishing a consistent skincare routine, wearing breathable fabrics like cotton or silk, and avoiding harsh cleansers. Lukewarm baths, regular moisturizing, and protecting skin from environmental triggers are essential. Using gloves during work or winter can prevent damage. Staying hydrated and reducing stress are also key to managing eczema effectively.