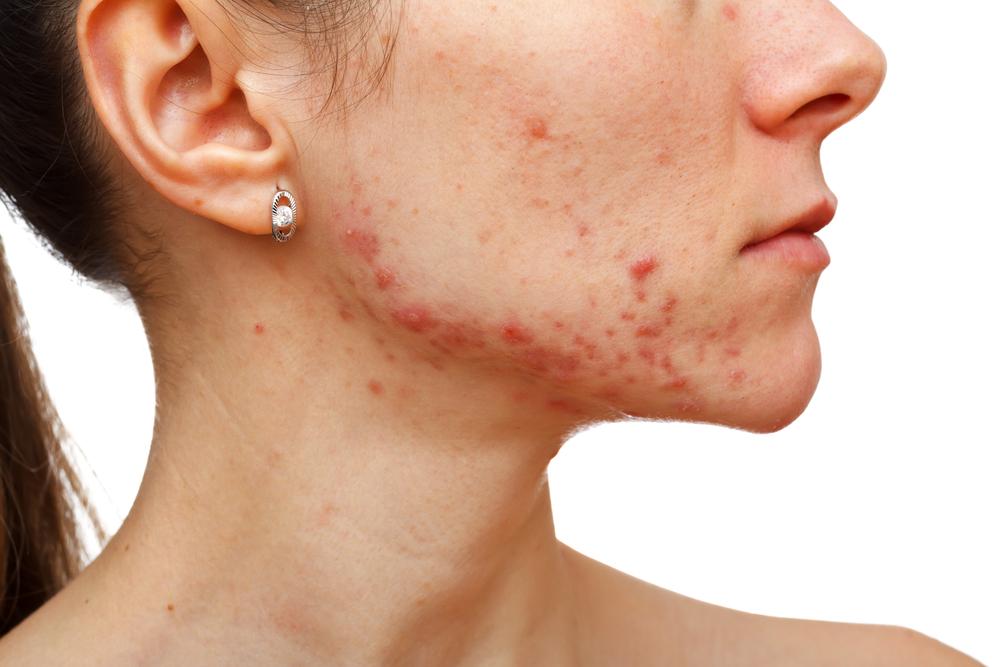
Eczema Uncovered: Symptoms, Causes, Varieties, and Care Strategies
Eczema is a common skin condition causing red, itchy, and flaky patches. Recognizing its symptoms, understanding various types, and managing triggers can significantly improve quality of life. Effective treatments include moisturization, avoiding irritants, and medical therapies. Proper care helps individuals live comfortably despite eczema challenges.
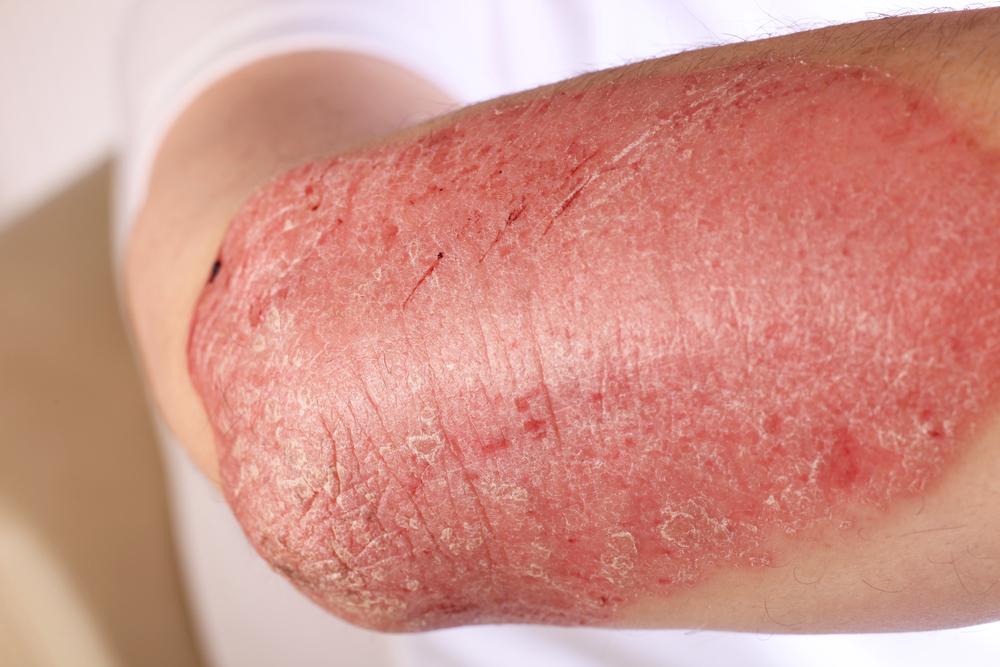
Exploring Eczema: Signs, Origins, Types, and Management
Eczema encompasses a range of skin conditions marked by inflamed, itchy, and often flaky patches. Identifying key symptoms is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment. Different eczema types affect various skin regions, each needing specific care methods.
This widespread skin issue can be well-managed by recognizing triggers and avoiding irritants. Proper skin care enables those with eczema to live comfortably despite their condition.
Symptoms of Eczema
Early signs include red, swollen areas that may itch intensely. Other symptoms include dryness, flaking, thickened skin, blisters that may ooze, and color changes in skin tone. Scratching can worsen the condition and lead to infections.
Common indicators include:
Red, inflamed skin
Persistent itching
Dry, peeling patches
Thickened, leathery areas
Blisters that crust over
Frequent scratching sensations
What Causes Eczema?
While infections like fungi or mites can play a role, most cases are due to an immune system overreaction to triggers. Typical factors include rough fabrics, weather extremes, allergens like pet dander, harsh soaps, and detergents. Stress, cold temperatures, and respiratory conditions such as asthma may worsen symptoms. Eczema is not contagious.
Types of Eczema
Atopic dermatitis: The most common type, often alongside allergies like asthma, affecting the face, neck, elbows, and knees, primarily in children.
Stasis dermatitis: Common in those with circulation issues, mainly on lower legs.
Scabies: Mite infestation that mimics eczema symptoms.
Fungal dermatitis: Fungal rashes diagnosed by skin tests.
Pompholyx: Vesicular eruptions on palms, soles, fingers, and toes.
Nummular eczema: Coin-shaped patches, often on lower limbs.
Lichen simplex chronicus: Thickened patches on neck and shins.
Seborrheic dermatitis: Affects face, scalp, ears, and chest; in infants, it may cause widespread oozing blisters.
Xerotic eczema: Very dry, cracked skin prone to oozing.
Allergic contact dermatitis: Reaction to repeated allergen exposure causing localized eczema.
Managing Eczema Symptoms
Keeping skin moist is crucial to prevent dryness and itching. Gentle cleansing and regular moisturizing significantly reduce flare-ups. Over-the-counter corticosteroids help reduce inflammation. Infections may require antibiotics. For oozing blisters, gentle cleaning and air-drying accelerate healing. Severe cases might need antihistamines, light therapy, tar-based treatments, or immunosuppressants like cyclosporine.
Living with Eczema
Awareness of personal triggers such as irritant fabrics, soaps, certain foods, and temperature swings is essential. Consistent skin hydration and following medical guidance can lessen flare-ups. Collaborating with healthcare professionals ensures optimal management, allowing eczema sufferers to maintain a comfortable lifestyle.