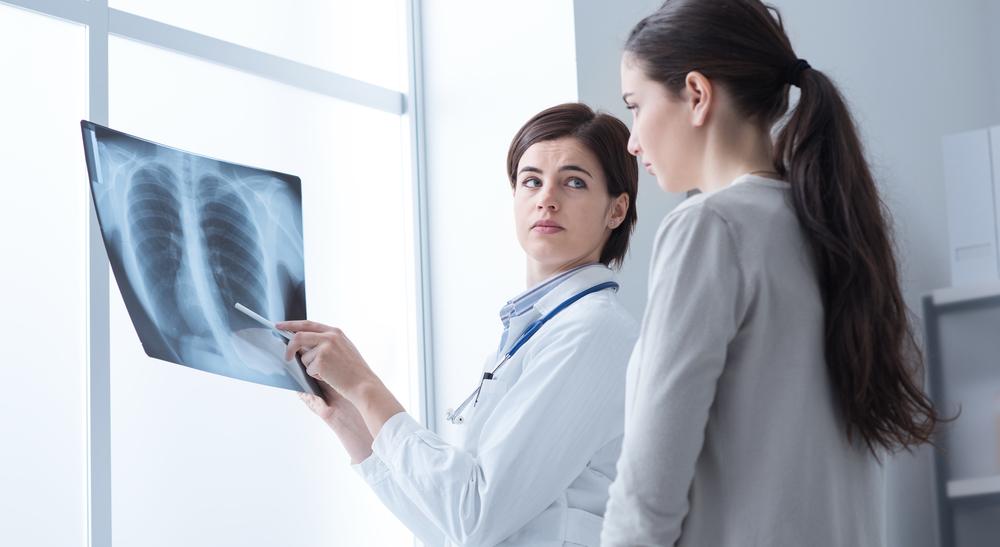
Lung Cancer Insights: Causes, Symptoms, and Therapeutic Options
Lung cancer is among the most deadly cancers, typically caused by smoking and exposure to environmental toxins. Early detection through imaging and biopsies is critical. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and targeted therapies, tailored to cancer type and stage. Awareness of risk factors and symptoms can aid early diagnosis, improving outcomes and quality of life for patients.
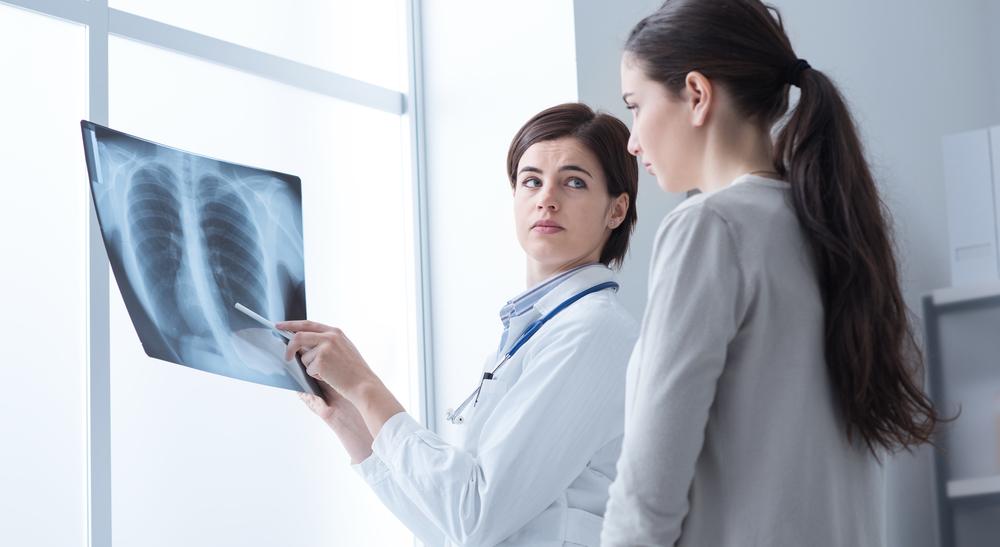

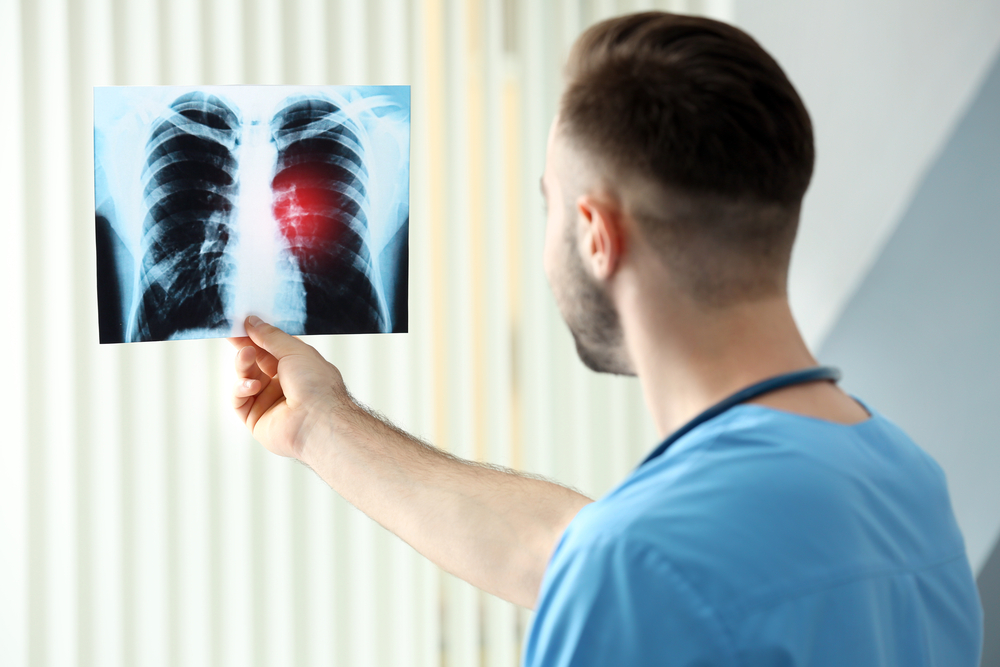
Lung Cancer Insights: Causes, Symptoms, and Therapeutic Options
The human body is made up of countless cells that normally grow, divide, and die in a controlled fashion. When genetic alterations occur, abnormal cell proliferation can happen, leading to tumor development. If these tumors are malignant, they have the potential to invade nearby tissues and spread through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. Benign tumors, however, stay localized. Lung cancer ranks among the deadliest cancers globally, surpassing others like breast cancer since 1987. It originates in lung tissue and may metastasize to lymph nodes or farther organs such as the brain.
The disease is categorized into small cell and non-small cell types, each requiring distinct treatment strategies. Non-small cell carcinoma is more common. Early stages often lack symptoms, but signs like persistent pneumonia, continual fatigue, unexplained weight loss, chronic cough, and breathing issues such as wheezing or shortness of breath can occur.
Key risk factors encompass exposure to carcinogens like asbestos, radon gas, diesel fumes, and silica dust, especially with extended contact. Smoking tobacco is the leading cause, accounting for 80-90% of incidences. Passive inhalation of tobacco smoke also elevates risk, with studies indicating high lung cancer rates among non-smokers exposed to secondhand smoke.
Diagnostic procedures include chest X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and PET imaging to identify anomalies. Confirmatory tests like sputum analysis and tissue biopsies via bronchoscopy are essential. Treatment options vary by cancer type and stage, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and targeted drug therapies. Post-treatment support from healthcare teams and support groups aids patients in recovery and lifestyle adjustment.