Comprehensive Guide to Lung Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Learn about lung cancer's causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment strategies. This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into risk factors such as smoking and radon, early detection methods, symptom recognition, and available therapies including surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted treatments. Understanding these aspects is crucial for prevention and effective management of lung cancer, a leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally.
Comprehensive Guide to Lung Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Lung Cancer: Key Information on Causes, Detection, Symptoms, and Management
Lung cancer is one of the top causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide, accounting for roughly 27% of all cancer fatalities. Public awareness campaigns have promoted quitting smoking, which plays a major role in preventing the disease.
It is characterized by abnormal growth of cells in one or both lungs, often affecting airway linings. Tumors may be benign or malignant; malignant ones can spread beyond the lungs, affecting other organs and systems.
Primary lung cancer originates within the lung tissue itself, while secondary lung cancer results from metastasis. Here are crucial details about risk factors, detection methods, symptoms, and treatment options for lung cancer.
Major Risk Factors for Lung Cancer
Smoking, including cigars and pipes, remains the leading cause of lung cancer. Tobacco smoke damages lung cells with carcinogens and also poses risks to passive smokers. Smoking links to other cancers such as throat, voice box, esophagus, stomach, colon, liver, and more.
Radon, a naturally occurring invisible gas found in soil and rocks, can accumulate indoors, raising lung cancer risk. About 200,000 cases each year are linked to radon exposure, emphasizing the importance of home testing.
Lung cancer survivors, especially those who continue smoking, face higher recurrence risks. A family history also increases vulnerability to developing the disease.
Diagnostic Methods for Lung Cancer
The disease often remains unnoticed until advanced stages, making early testing vital for at-risk populations.
Symptoms such as a persistent cough with blood in sputum require diagnostic tests like sputum cytology.
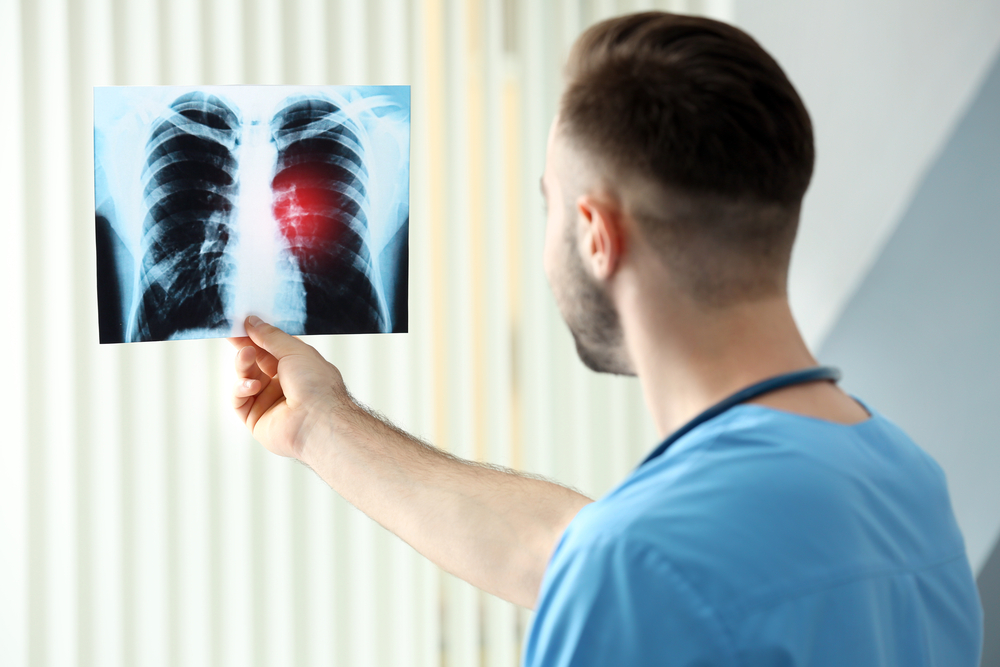
Imaging tests, including X-rays, CT scans, PET scans, MRIs, and bone scans, help detect abnormalities and stage the disease more precisely.
Symptoms to Watch For
Common signs include a persistent cough, hemoptysis, chest pain, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss.
Recurrent pneumonia or swelling of lymph nodes causing chest discomfort may also be indicators.
Therapeutic Approaches for Lung Cancer
Treatment options vary based on the stage and patient's overall health and include:
Surgical Intervention – Removal of localized tumors along with nearby tissue.
Radiation Therapy – Uses high-energy rays, often combined with chemotherapy, to destroy cancer cells, administered before or after surgery.
Chemotherapy – Post-surgical treatment to eliminate residual cancer cells, delivered orally or via IV.
Additional Therapies – Immunotherapy, targeted treatments, radiosurgery, and clinical trials offer further options for certain patients.
Important Reminder: The information provided is for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized diagnosis and treatment planning. This content may not encompass all available treatment options or programs.