A Comprehensive Guide to Lung Cancer: Symptoms, Detection, and Causes
This article offers an in-depth overview of lung cancer, covering its symptoms, diagnostic methods, and risk factors. It emphasizes early detection through awareness of warning signs and exposure risks, crucial for successful treatment outcomes.

A Comprehensive Guide to Lung Cancer: Symptoms, Detection, and Causes
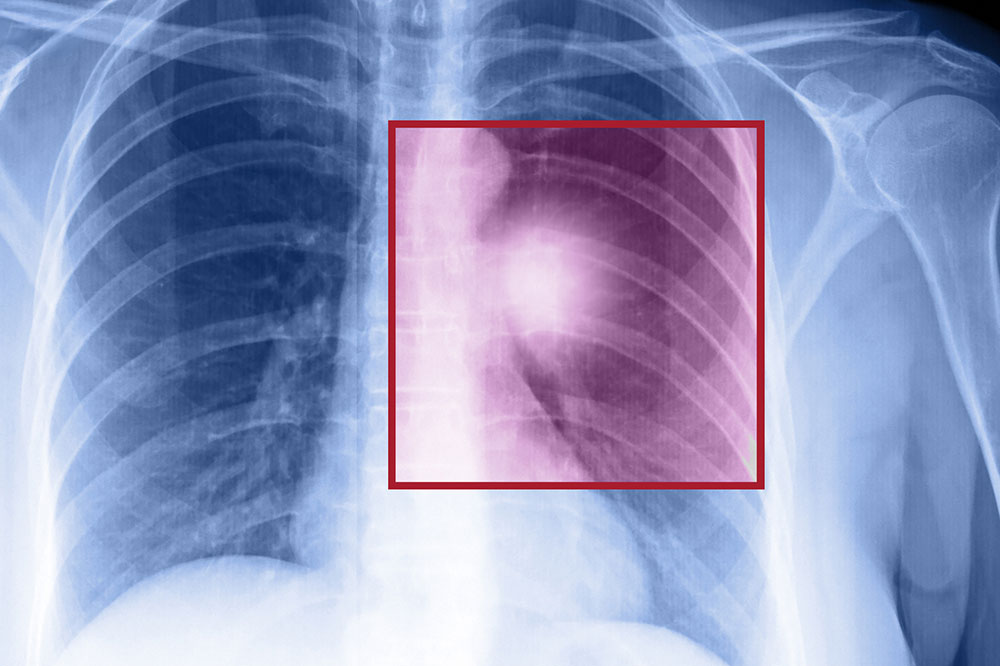
The lungs are essential organs that facilitate oxygen intake and removal of carbon dioxide. They consist of various cell types, mainly epithelial cells, which line the airways and produce mucus for protection. Lung cancer occurs when genetic mutations cause abnormal cell growth, resulting in tumors that may invade surrounding tissues. Diagnosis involves multiple procedures such as biopsies, medical history evaluation, blood tests, sputum analysis, and imaging techniques like X-rays, CT scans, MRI, PET scans, and bone scans. Early symptoms are often subtle, including a persistent cough, blood-stained sputum, chest discomfort, hoarseness, shortness of breath, fatigue, and frequent respiratory infections. Advanced stages may show symptoms like back pain, headaches, dizziness, jaundice, or neurological signs due to metastasis. Risk factors encompass smoking (active or passive), exposure to substances like asbestos or arsenic, air pollution, family history, existing lung conditions, and radiation exposure. Recognizing these indicators and risks enhances early diagnosis and effective treatment planning.