Gout Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
This article explores gout, a painful joint condition caused by uric acid crystals. It covers causes, common symptoms, and effective treatment options, emphasizing lifestyle and dietary changes as key to management. Understanding the triggers and treatments helps those affected prevent future episodes and improve quality of life.
Gout Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
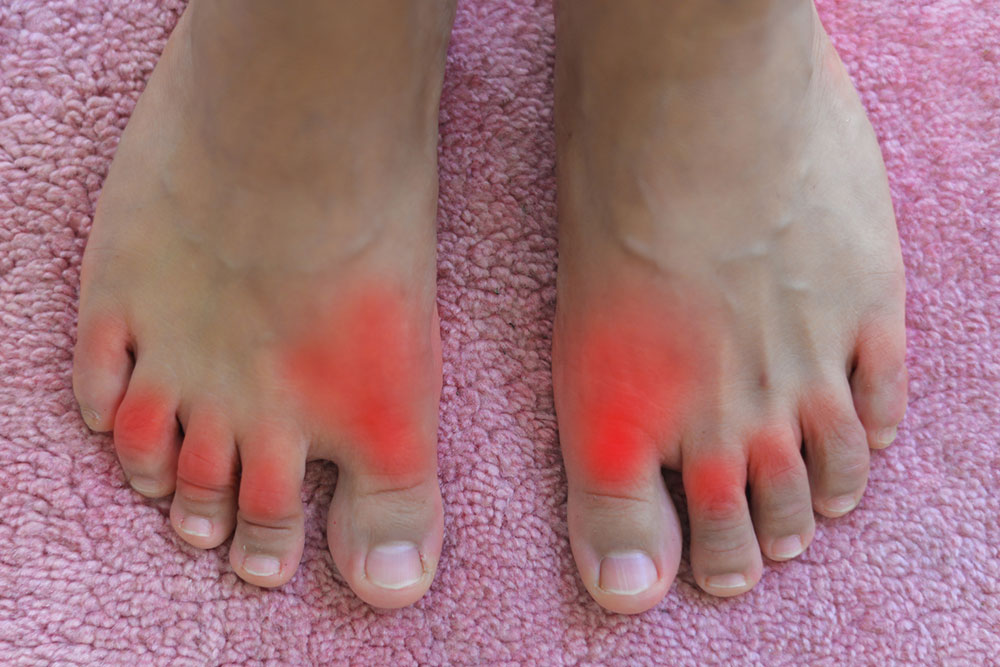
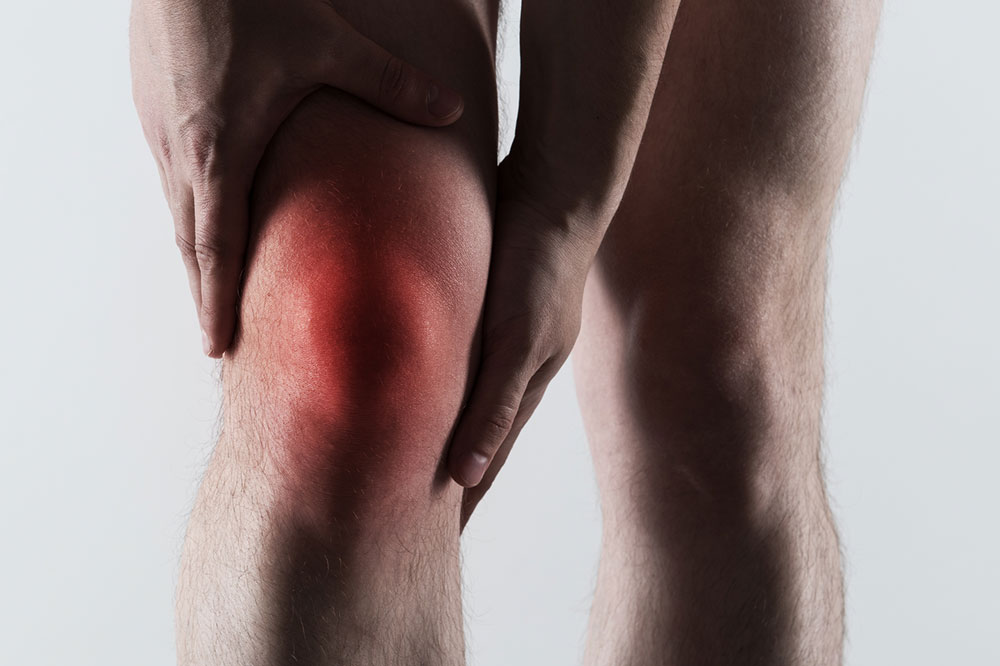
Gout is a joint disorder caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals, leading to intense pain and swelling. As a common form of arthritis, it typically impacts the toes but can involve other joints. Understanding its causes and management strategies is key to effective relief.
What triggers gout?
Elevated uric acid levels in the bloodstream lead to crystal formation in joints, resulting in inflammation. Uric acid is generated when the body breaks down purines found in certain foods. Normally, it's expelled via the kidneys, but factors like genetics, obesity, kidney problems, or high purine intake can cause buildup.
Symptoms include sudden, severe joint pain, redness, swelling, and warmth, often starting in the big toe. Over time, persistent attacks may lead to uric acid deposits called tophi. Limiting certain foods and making lifestyle changes can help manage the condition.
Managing gout effectively
Approaches vary based on attack frequency. Mild cases may improve with diet and lifestyle tweaks, but frequent or severe episodes require medication. Uric acid-lowering drugs such as allopurinol, probenecid, or pegloticase reduce crystal formation. Anti-inflammatory medications like NSAIDs and febuxostat help control pain during flare-ups. Dietary changes, including reducing alcohol and purine-rich foods like red meats and organ meats, are crucial for prevention.
Note:
This information is for educational purposes only and shouldn't replace professional medical advice. Always seek consultation from healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment.