Comprehensive Guide to Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Strategies
This article provides a detailed overview of gout, including its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies. Learn how genetics, lifestyle, and diet contribute to this painful condition and discover ways to prevent and treat gout through medication and lifestyle changes.

Comprehensive Guide to Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Strategies
Gout is a painful joint condition that affects many individuals, especially men over 40 and postmenopausal women. It typically presents as sudden flare-ups lasting from days to weeks, which may improve naturally or with medication. Persistent pain and swelling should prompt consultation with a healthcare professional for appropriate management.
Causes
The primary cause is genetics; family history can increase risk. Additional factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, excessive alcohol intake, and red meat consumption. Obesity and certain medications may also impair uric acid elimination, triggering attacks.
Signs and Symptoms
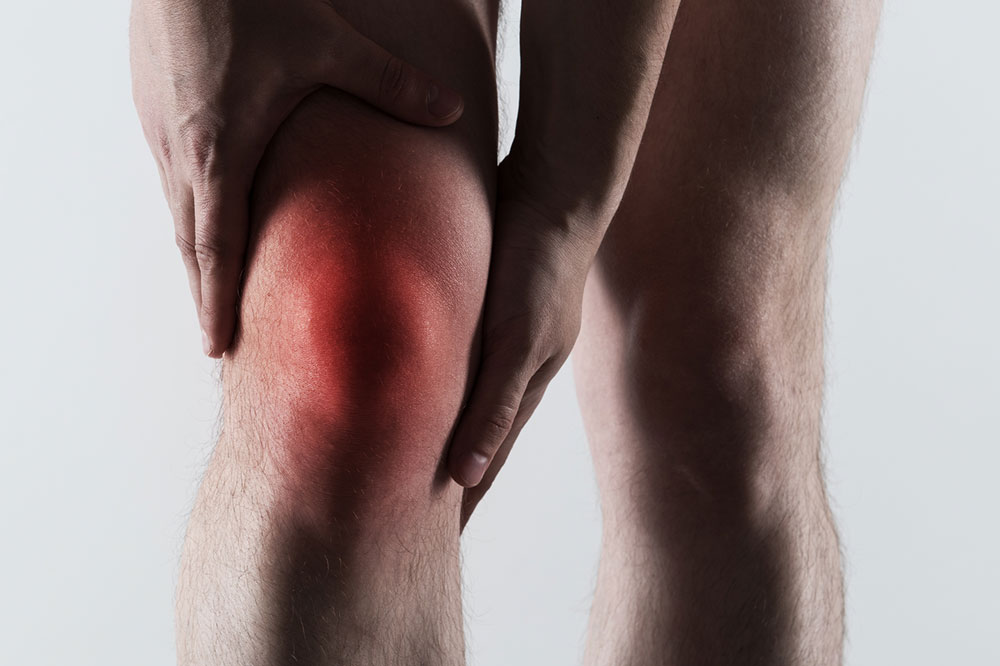
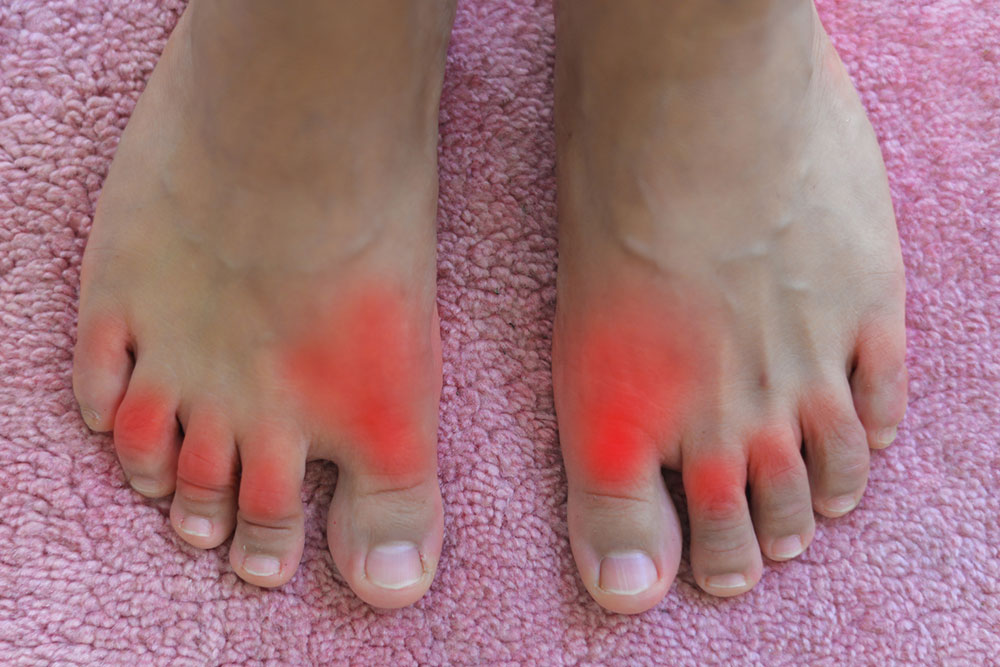
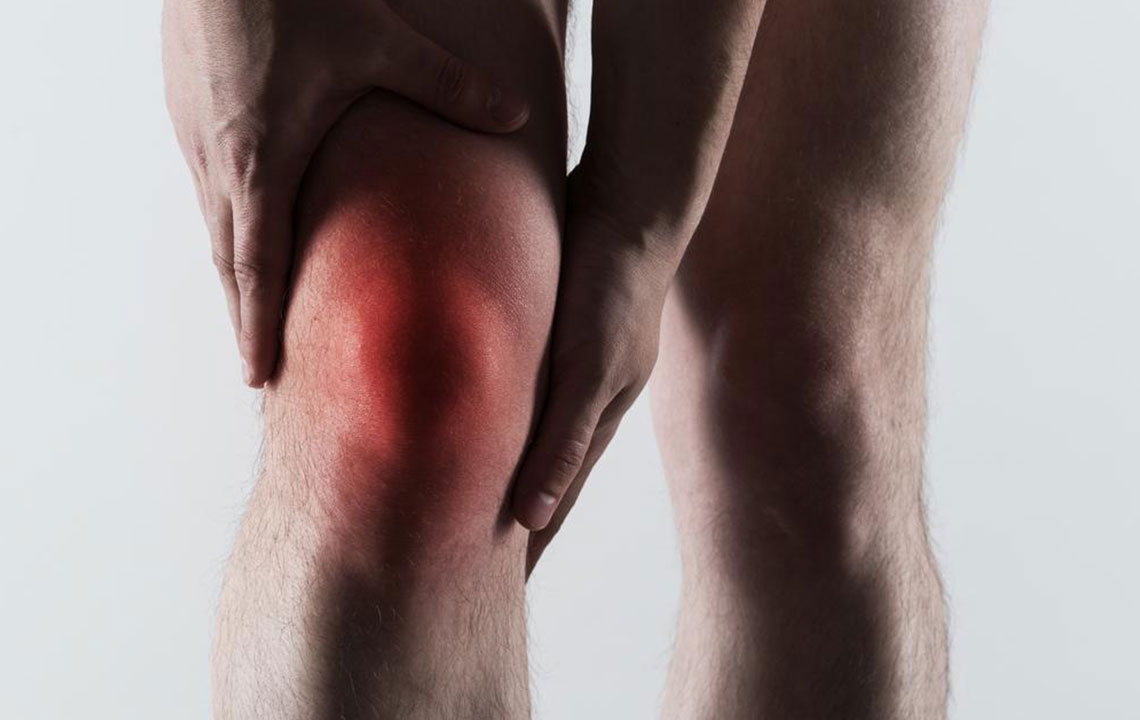
Severe joint pain: Usually occurs in the big toe but can affect ankles, wrists, elbows, or knees, with pain intensifying quickly.
Lingering discomfort: Mild soreness may persist for days or weeks after an attack, with recurrent episodes affecting more joints over time.
Restricted movement: Severe pain hampers joint mobility, making routine actions difficult.
Redness and swelling: Affected areas become tender, warm, swollen, and visibly red.
Tophi formation: If untreated, nodules under the skin may develop, indicating joint damage.
Management and Treatment
Anti-inflammatory drugs: Used during flare-ups; should be taken under medical supervision due to potential side effects like stomach ulcers.
Pain relief medications: These help alleviate discomfort but require proper medical guidance.
Uric acid-lowering medications: Drugs that reduce uric acid levels and improve kidney function to prevent future attacks.
Lifestyle adjustments: Quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, avoiding purine-rich foods such as red meat and seafood, and engaging in regular exercise can decrease attack frequency and enhance overall health.
Natural approaches: Adequate hydration and consumption of vitamin C-rich fruits may assist in lowering uric acid levels.