Ultimate Guide to Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
This comprehensive guide on gout covers its causes, symptoms, and treatment strategies. It explains how uric acid crystals form, presents key signs to watch for, and offers effective management tips including lifestyle modifications, medications, and home remedies. Early diagnosis and consistent care are essential for controlling this painful condition and preventing complications, making this article a valuable resource for those seeking to understand and manage gout effectively.
Ultimate Guide to Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in joints. Uric acid originates from certain foods, and when the body cannot eliminate it effectively, crystals develop, leading to pain and swelling. These crystals can also block kidney filters, increasing the risk of kidney stones or failure.
There are two main types of gout:
Primary gout, which appears without an underlying condition.
Secondary gout, associated with other health issues.
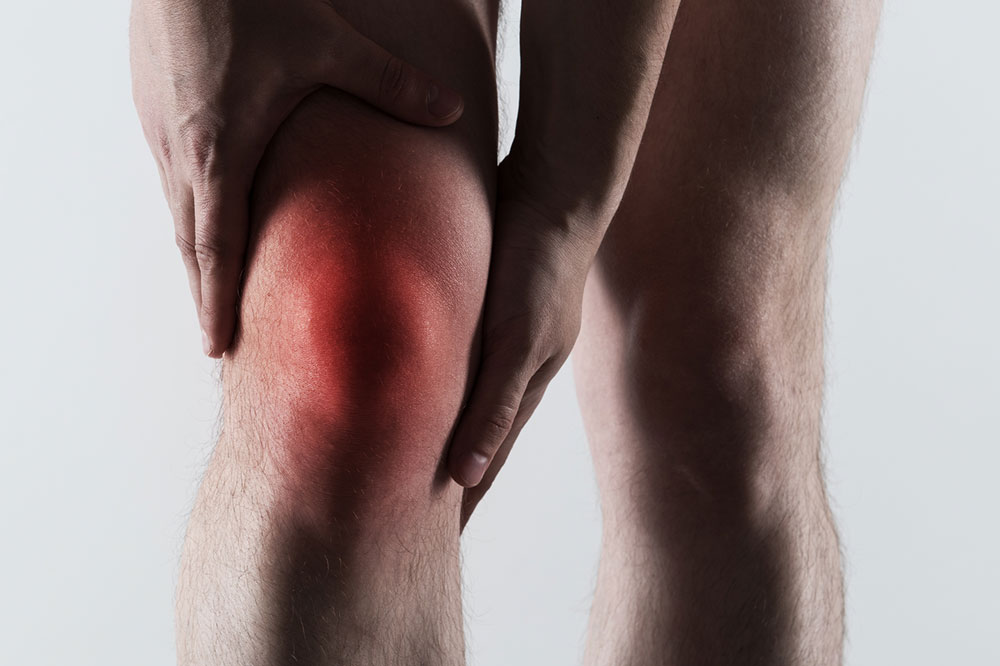
Gout typically causes sudden, severe pain with redness, warmth, swelling, and tenderness, often affecting the big toe. Men over 40 are more vulnerable, but symptoms can also include:
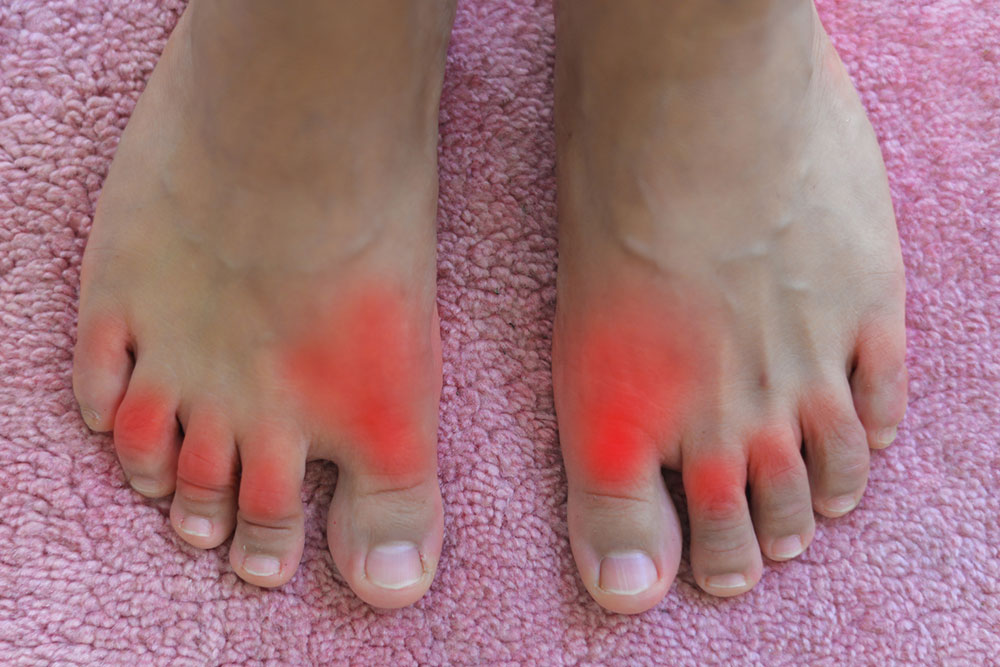
Gout Symptoms
Intense joint pain with redness and swelling.
Usually impacts the big toe, ankles, knees, wrists, or fingers.
Pain intensity varies, can last from hours to days.
During attacks, even minimal contact can cause discomfort. Symptoms might subside within a few days, but recurrent episodes are common.
Diagnosing Gout
Doctors diagnose gout through joint fluid analysis to detect uric acid crystals and blood tests to evaluate uric acid levels. Recurrent joint pain warrants early diagnosis for effective management.
Managing Gout Effectively
Early intervention is essential to relieve pain and prevent damage. Lifestyle and dietary changes may suffice for mild cases, including:
Avoiding high-purine foods like shellfish and organ meats.
Reducing intake of sugary drinks, sodas, honey, and sweets.
Eating more fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and tofu.
Choosing whole grains and low-fat dairy products.
Medication might be required if lifestyle changes alone are insufficient.
Medical Treatment Options
For frequent or severe attacks, doctors may prescribe medications to lower uric acid and alleviate pain, including:
Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs for immediate relief, with potential side effects like stomach discomfort.
NSAIDs for acute symptoms, which may cause dizziness or stomach upset.
Uric acid-lowering medications for long-term control.
Home Care Tips
During flare-ups, rest the affected joint, apply ice packs, and stay hydrated to help eliminate uric acid. Patience and consistent treatment can effectively manage symptoms. Always consult healthcare professionals before making medication adjustments for personalized care. Combining proper medication with lifestyle changes offers the best results.