Ultimate Endoscopy Overview: Techniques and Diagnostic Insights
This comprehensive guide explains endoscopy procedures, their diagnostic uses, and preparation tips. It highlights how endoscopy helps identify gastrointestinal issues like bleeding, ulcers, and tumors with clarity. The article emphasizes its importance as a minimally invasive diagnostic tool, offering detailed internal views to aid accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Clear patient instructions and safety precautions are discussed, making this a valuable resource for understanding endoscopy's role in healthcare.
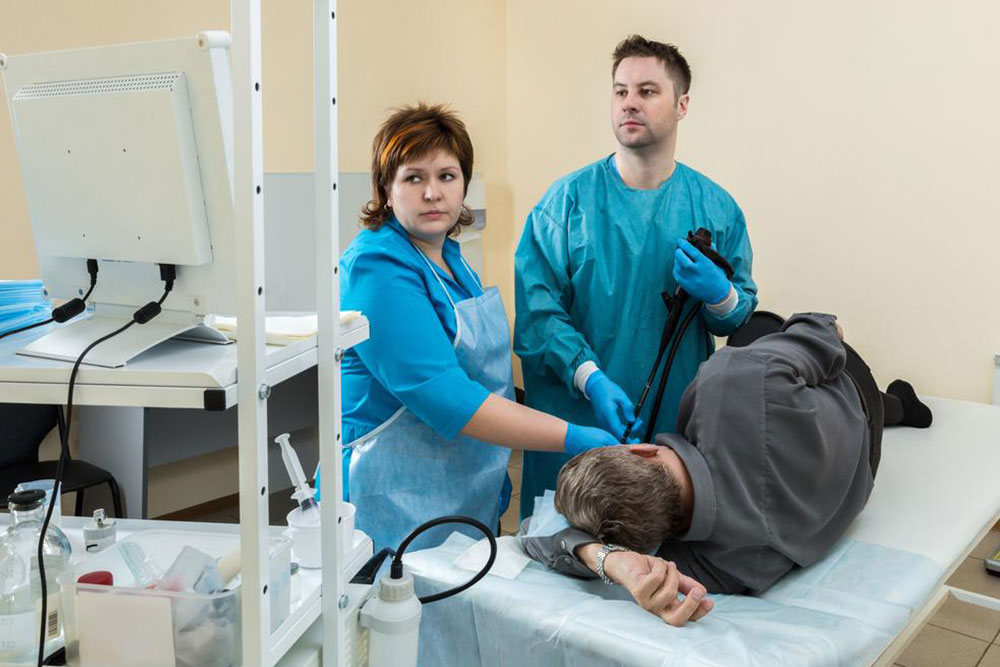
Ultimate Endoscopy Overview: Techniques and Diagnostic Insights
Endoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that uses specialized instruments with a camera and light to visualize internal organs without large cuts. It allows doctors to examine the digestive tract, identify issues like pain, nausea, heartburn, bleeding, or swallowing problems. It also helps detect conditions such as ulcers, inflammation, polyps, and tumors.
Usually performed on an outpatient basis, upper endoscopy is vital for diagnosing gastrointestinal disorders. Compared to imaging like X-rays, endoscopy offers clearer visuals, aiding in accurate detection of benign and malignant growths.
Common issues identified through endoscopy include:
Foreign objects in the esophagus, stomach, or digestive tract
Bleeding sources such as ulcers or tumors
Growths like polyps in the stomach lining
Biopsy collection for further analysis
Reasons for Endoscopy
This procedure provides direct visualization of internal organs to pinpoint problems accurately.
During endoscopy, a camera-equipped scope is inserted via the mouth or minor incision, allowing detailed observation. Tissue samples can be taken if abnormal areas are detected.
Preparation involves fasting for about 12 hours, with possibly laxatives or enemas given beforehand. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about their medical history, medications, and allergies for a smooth procedure.
The camera transmits real-time images to a monitor, assisting diagnosis. Sometimes, biopsies are performed. Blood tests and physical exams help determine treatment options, whether non-invasive or surgical. Following pre-procedure instructions ensures safety and successful outcomes.
Note: This content is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.