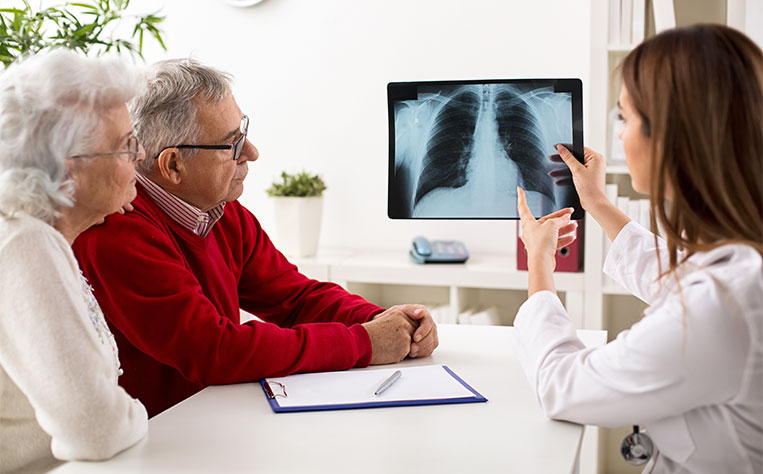
Essential Insights into Lung Cancer Screening and Diagnostic Methods
This comprehensive guide covers key lung cancer screening and diagnostic methods, emphasizing early detection through imaging and invasive procedures. Understanding these techniques is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
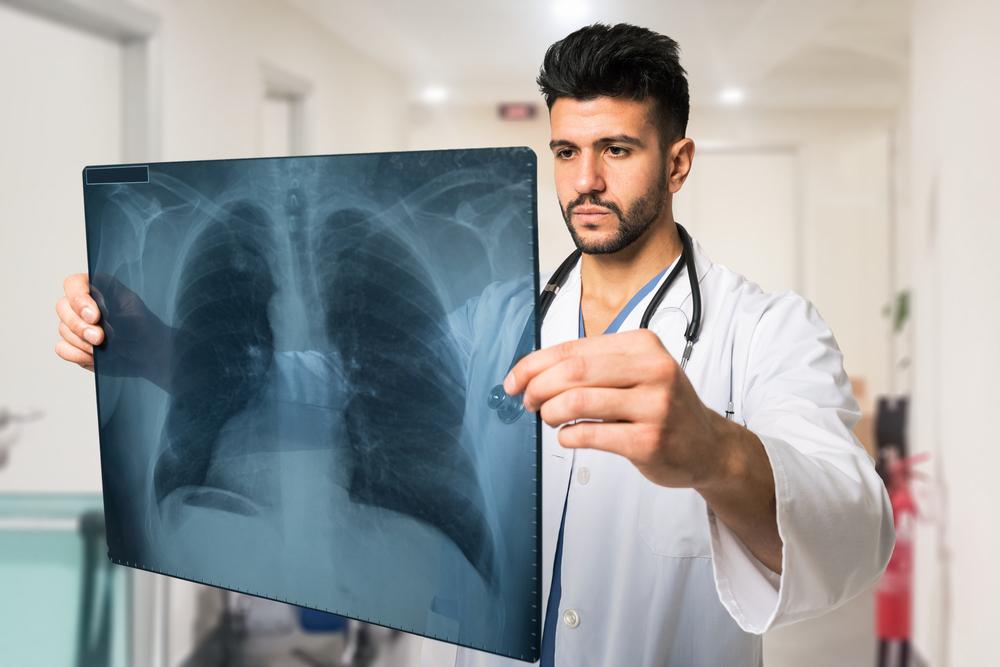
Overview of Lung Cancer Detection and Diagnostic Strategies
Identifying lung cancer requires a combination of diagnostic techniques starting with imaging scans to locate suspicious growths, followed by invasive procedures for confirmation. Initial assessments typically involve non-invasive imaging such as X-rays and CT scans to detect abnormalities. To confirm cancer, tissue sampling through biopsies, sputum analysis, or bronchoscopy may be performed. Additional tests like ultrasound, mediastinoscopy, and thoracoscopy help determine whether the disease has spread. Early detection enhances treatment effectiveness and patient prognosis.
Imaging Techniques: X-ray, CT scan, MRI, PET, Bone scan
Diagnostic Confirmations: Sputum analysis, Biopsy, Bronchoscopy
Assessing Spread: Ultrasound, Mediastinoscopy, Thoracoscopy
Recognizing these diagnostic approaches is vital for timely lung cancer detection, leading to improved treatment strategies and outcomes.