Essential Nutrients and Foods for Supporting Thyroid Function and the Role of Iodine
This article explores essential nutrients and foods that promote thyroid health, emphasizing the importance of iodine. It provides practical dietary tips and highlights key nutrients like selenium, magnesium, and probiotics to support thyroid function. Proper nutrition, balanced intake of iodine, and lifestyle measures are crucial for maintaining optimal thyroid health and preventing disorders.

The thyroid gland plays a vital role in controlling metabolism, temperature regulation, and energy levels by producing essential hormones. Ensuring its proper function is key to overall health. Eating a nutrient-rich diet can promote thyroid wellness, with certain foods naturally boosting its activity while others may hinder it. This article discusses the essential nutrients for thyroid health, highlights iodine's importance, and shares practical dietary tips for maintaining a healthy thyroid.
Foods Supporting Thyroid Health
Incorporating specific foods can help prevent issues like hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. These readily available, versatile options include:
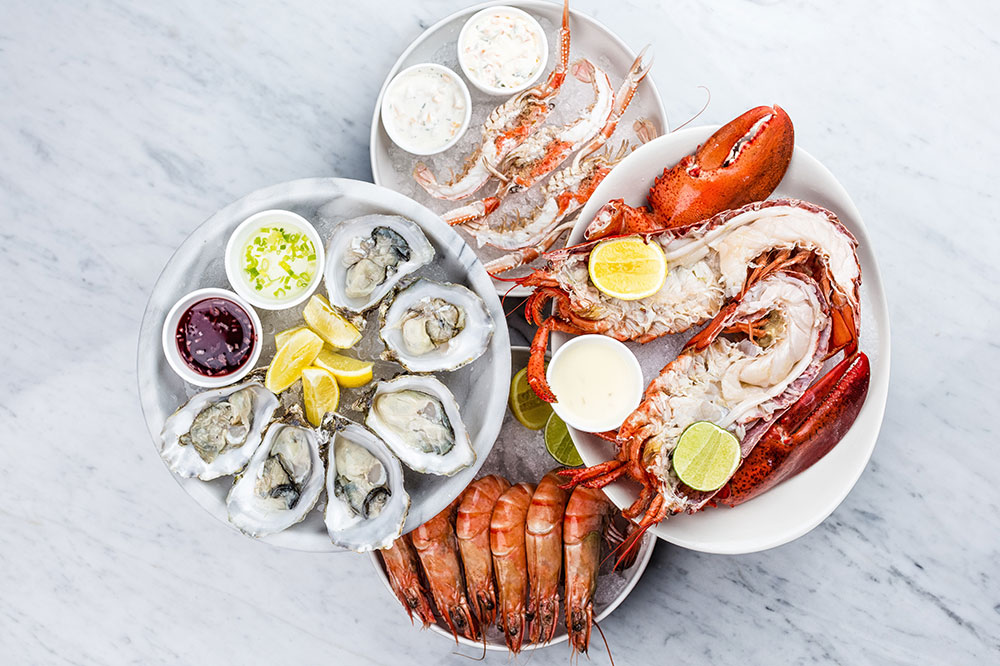
Seafood
Fish such as salmon, sardines, and shrimp are excellent iodine sources, essential for hormone production. They also contain omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce thyroid-related inflammation.
Brazil Nuts
Rich in selenium, these nuts support conversion of thyroid hormones and promote metabolic health. Eggs, dairy, and organ meats also supply selenium.
Dark Leafy Greens
Spinach, kale, and collard greens are high in magnesium, aiding in the conversion of T4 to T3 and supporting thyroid activity.
Yogurt
Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and kefir enhance gut health, which is vital for hormone production and conversion.
Eggs
Providing high-quality protein and vitamin D, eggs help sustain thyroid function.
Berries
Berries such as blueberries and raspberries are packed with antioxidants that protect the thyroid from free radical damage.
Whole Grains
Brown rice, oats, and quinoa provide fiber that supports blood sugar regulation, essential for thyroid health.
Including these nutrients—iodine, selenium, magnesium, probiotics, antioxidants, protein, and fiber—in your diet can promote thyroid health. Always consult a healthcare provider before making dietary adjustments.
Role of Iodine in Thyroid Health
Iodine is a crucial mineral needed for producing thyroid hormones that influence growth and metabolism. Deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism. Good sources include seafood, seaweed, iodized salt, and dairy. Excessive iodine intake, however, can be harmful. Use iodized salt in moderation, avoid unnecessary supplements, and seek medical advice—especially for pregnant women or those with existing thyroid issues.
Dietary Strategies for Thyroid Wellness
Nutritional strategies should be tailored to individual needs. Recommendations include maintaining a balanced diet, supplementing iodine if deficient, limiting goitrogenic foods like broccoli and cabbage in excess, and ensuring adequate selenium intake. Managing stress and regular health check-ups further support thyroid health.