Nutritional Strategies for Managing Hypothyroidism Effectively
Discover essential dietary tips and lifestyle strategies to support optimal thyroid function in managing hypothyroidism. Tailored nutrition can alleviate symptoms and improve overall health by balancing hormone levels, reducing inflammation, and enhancing metabolic health. Consulting healthcare professionals is recommended for personalized treatment plans.

Diet Tips for Supporting Thyroid Health in Hypothyroidism
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and overall health, yet many overlook its importance. Misinterpreting thyroid blood tests can lead to confusion, as hypothyroidism occurs when the gland produces too few hormones, slowing bodily functions. Conversely, hyperthyroidism causes excessive hormone production, resulting in symptoms like rapid heartbeat.
Anyone can develop hypothyroidism, though it’s more common in older adults and women. A balanced diet is vital for maintaining healthy thyroid function.
Studies show that around 40% of people worldwide face hypothyroidism at some stage. Risk factors include age, gender, and co-existing conditions like diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis. Early signs involve fatigue, mood changes, sleep issues, hair thinning, weight gain, and digestive discomfort.
Managing hypothyroidism effectively requires medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and targeted dietary changes. Emphasizing foods that support hormone production, reduce inflammation, and supply iodine and selenium can help stabilize thyroid function. Working with a dietitian can help create personalized meal plans focusing on thyroid-supporting foods while limiting triggers.
Include healthy fats like coconut oil to enhance metabolism and reduce inflammation.
Consume omega-3 sources such as salmon and mackerel to benefit neurological health.
Eat probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and fermented vegetables to promote gut health.
Add sprouted seeds like chia and flax for hormone regulation.
Choose high-fiber options like beans, berries, and leafy greens to aid digestion.
Enjoy nutrient-rich bone broth to help combat fatigue.
Maintain hydration by drinking plenty of purified water daily.
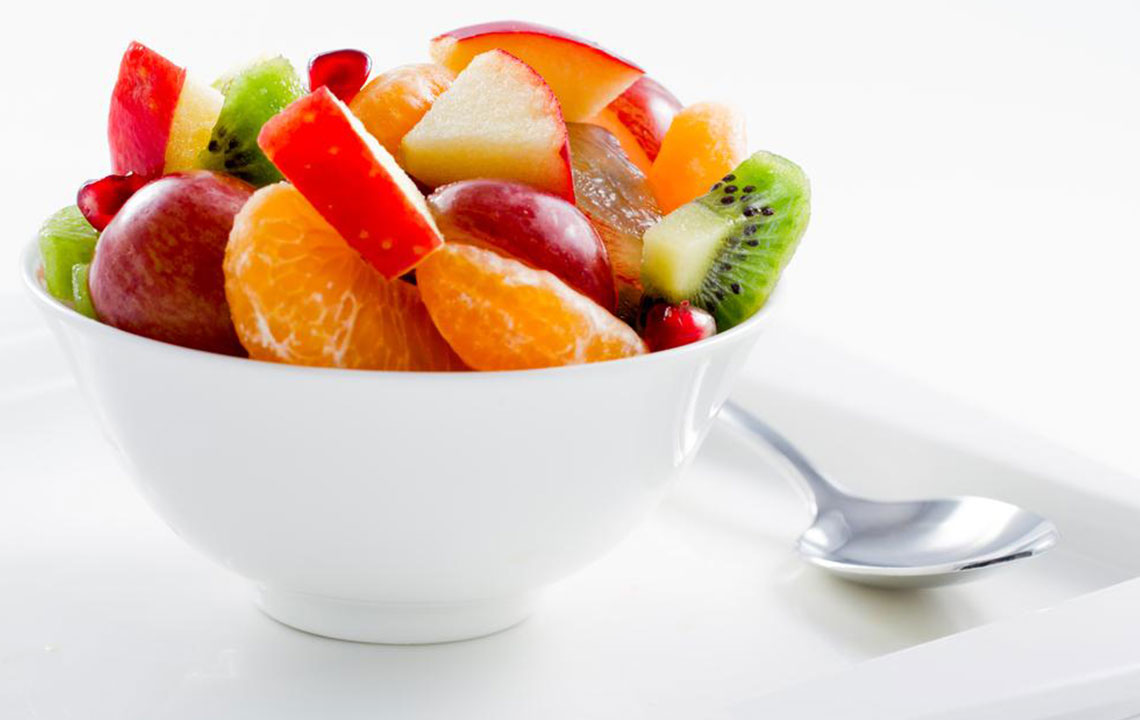
Eat a variety of antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables loaded with essential vitamins.
While medications such as Synthroid are standard, diet and exercise play significant roles in symptom control and quality of life improvement. Avoiding foods that promote inflammation or hinder thyroid health, like gluten, processed foods, refined sugars, and excess goitrogenic vegetables, can enhance management. Proper nutritional choices support overall well-being and disease control.
Note: This article provides educational information and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment tailored to your specific condition.