Recognizing the Symptoms and Early Warning Signs of Hepatitis C
This article explains the key symptoms and early signs of Hepatitis C, highlighting the importance of early detection. It covers both acute and chronic stages, the subtle nature of symptoms, and long-term complications like cirrhosis and liver cancer. Recognizing early warning signs enables timely diagnosis and treatment, preventing severe liver damage. Regular testing and medical consultation are vital for those at risk. Stay informed about Hepatitis C to protect your health and seek prompt medical care if necessary.
What Is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is a viral infection targeting the liver, caused by the Hepatitis C virus. It can develop quickly or over many years, leading to various health issues. Symptoms are often subtle or absent, making early detection challenging. The virus causes liver inflammation and is considered the most severe among hepatitis types. Without early diagnosis, it can progress silently to serious liver damage, cirrhosis, or cancer. Awareness of key signs is vital for timely intervention and treatment.
Important Facts About Hepatitis C Symptoms
The symptoms may appear and fade, which can complicate diagnosis. The virus affects both the liver and immune system, leading to recurring issues such as fatigue and abdominal discomfort. Because these signs resemble flu or jaundice, both patients and healthcare providers may overlook them. Recognizing early indicators is essential to avoid severe liver damage. Detecting the virus early enables effective treatment and better health outcomes.
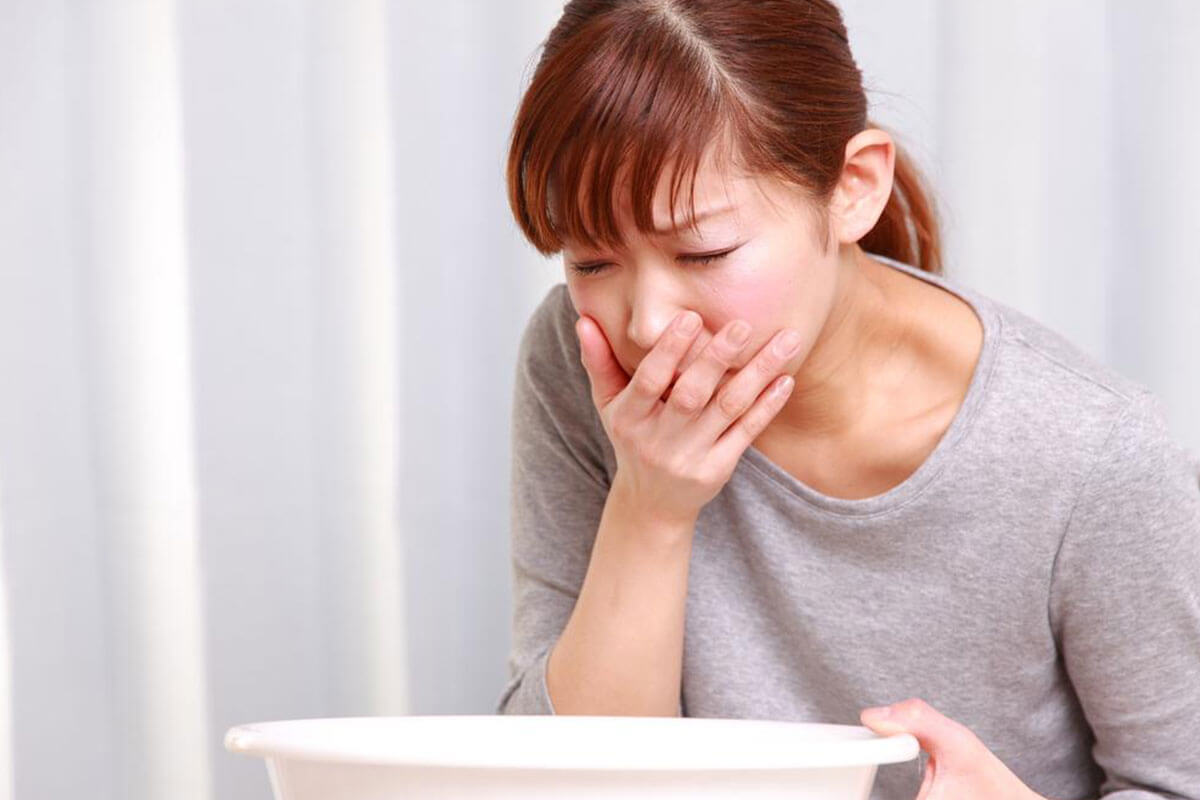
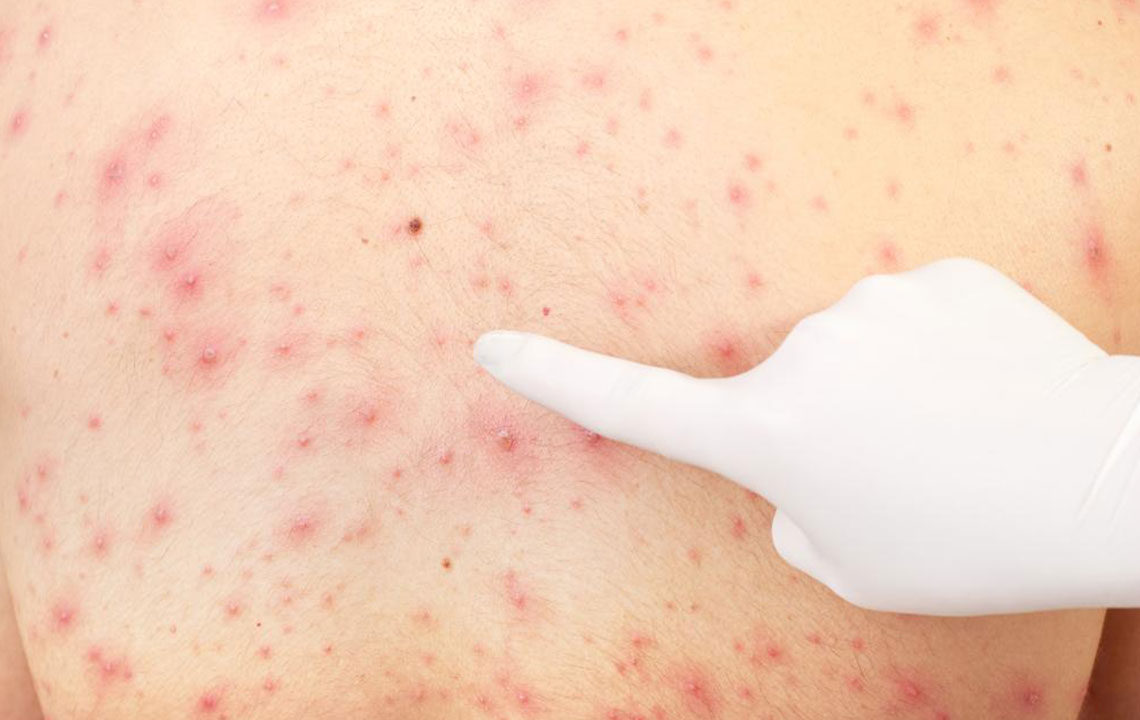
In the first few months—referred to as acute hepatitis C—common symptoms include fatigue, upper stomach pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Mild fever and dark urine may also occur. These symptoms usually last several weeks but can extend up to three months. If left untreated, they can worsen into jaundice, pale stools, and more severe liver issues. Persistent infection can become chronic, gradually damaging the liver and potentially resulting in cirrhosis. Signs of chronic hepatitis include easy bruising, skin itching, swelling, and weight loss. Blood tests are often required for diagnosis, particularly with ongoing symptoms.
Long-term effects include liver scarring—cirrhosis—that can take decades to develop, impairing liver function. Advanced cirrhosis may lead to liver failure or cancer. Regular check-ups and testing are crucial for anyone at risk. Early detection can prevent serious complications and improve treatment success.
Note: Our blog offers detailed health information based on current research. However, it should not replace professional medical advice. For accurate diagnosis and treatment, always consult a healthcare provider. We are not responsible for potential inaccuracies or differing medical opinions. Stay informed and seek medical guidance for any health concerns.