Recognizing Unseen Symptoms of Hepatitis C: What You Need to Know
Hepatitis C often shows subtle signs that are easy to overlook, such as fatigue, nausea, and skin changes. Recognizing these early symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. This article highlights the key indicators and risks associated with hepatitis C, which remains a significant global health concern. Early detection can prevent progression to severe liver damage, cirrhosis, or cancer. Understanding the symptoms, incubation period, and the importance of medical testing can help protect your health and prevent transmission.

Recognizing Unseen Symptoms of Hepatitis C: What You Need to Know
Could subtle signs like fatigue, nausea, or skin changes actually signal hepatitis C?
Since its identification in 1989, hepatitis C is a contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). It remains a leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide, with increasing cases each year. The World Health Organization estimates that about 150 million people are infected, with roughly 350,000 annual deaths due to liver-related complications. If not treated, it can lead to severe liver damage, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
Hepatitis C manifests mainly in two forms:
Acute (short-term but intense)
Chronic (long-term infection)
Signs of Acute Hepatitis C
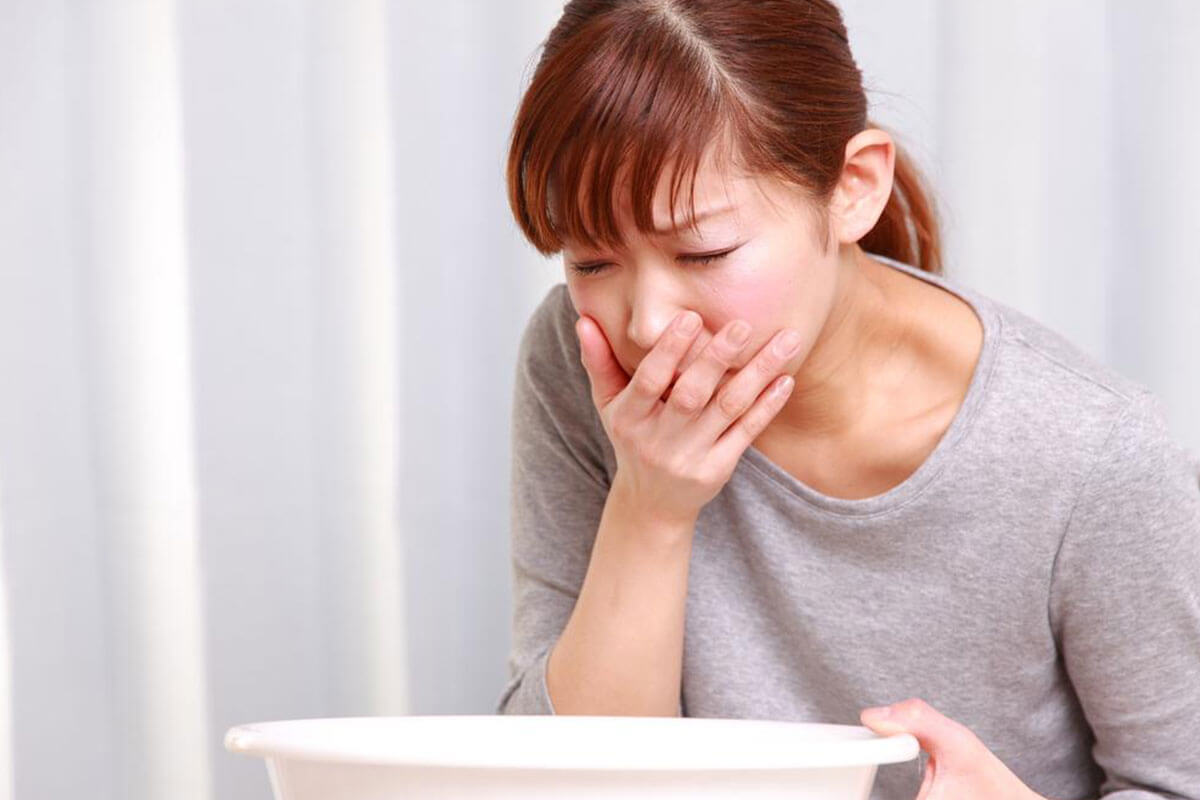
Many individuals with acute hepatitis C remain asymptomatic, though some may experience flu-like symptoms, joint discomfort, or mild skin rashes. Those with existing hepatitis B infections are more at risk of severe symptoms. Common signs include loss of appetite, stomach pain, dark urine, pale stools, jaundice, tiredness, joint ache, itchy skin, and muscle soreness. Without treatment, it can progress to liver cirrhosis.
As cirrhosis develops, symptoms might include:
Red palms due to enlarged blood vessels
Spider veins on chest, shoulders, or face
Swelling in abdomen, legs, and feet
Muscle loss
Bleeding from enlarged veins in the digestive tract (varices)
Confusion, memory issues, and concentration problems (hepatic encephalopathy)
Chronic Hepatitis C Symptoms
Many with chronic hepatitis C stay symptom-free for years, often diagnosed during routine testing or blood donations. When symptoms emerge, common signs include fever, muscle and joint pain, loss of appetite, weight loss, jaundice, fatigue, and liver discomfort. The virus can also affect other organs, leading to kidney issues from cryoglobulinemia, which can cause skin rashes or kidney failure. Additional symptoms encompass anxiety, mood swings, abdominal swelling, vision problems, chills, dark urine, decreased libido, dizziness, swelling, bleeding, gas, persistent headaches, joint inflammation, sleep issues, memory lapses, menstrual irregularities, muscle pain, nausea, skin rashes, water retention, tiredness, weight changes, and flu-like symptoms.
HCV Incubation Period
Symptoms typically appear within 2 weeks to 6 months post-infection, but many people remain asymptomatic initially. This can result in unintentional transmission. Due to non-specific symptoms, early detection can be difficult but is vital. If you suspect exposure, seek medical advice promptly.