How Hepatitis C Affects Liver Health and Function
Hepatitis C is a viral infection impacting the liver, with potential progression to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Early detection and medical guidance are essential for managing the disease effectively.
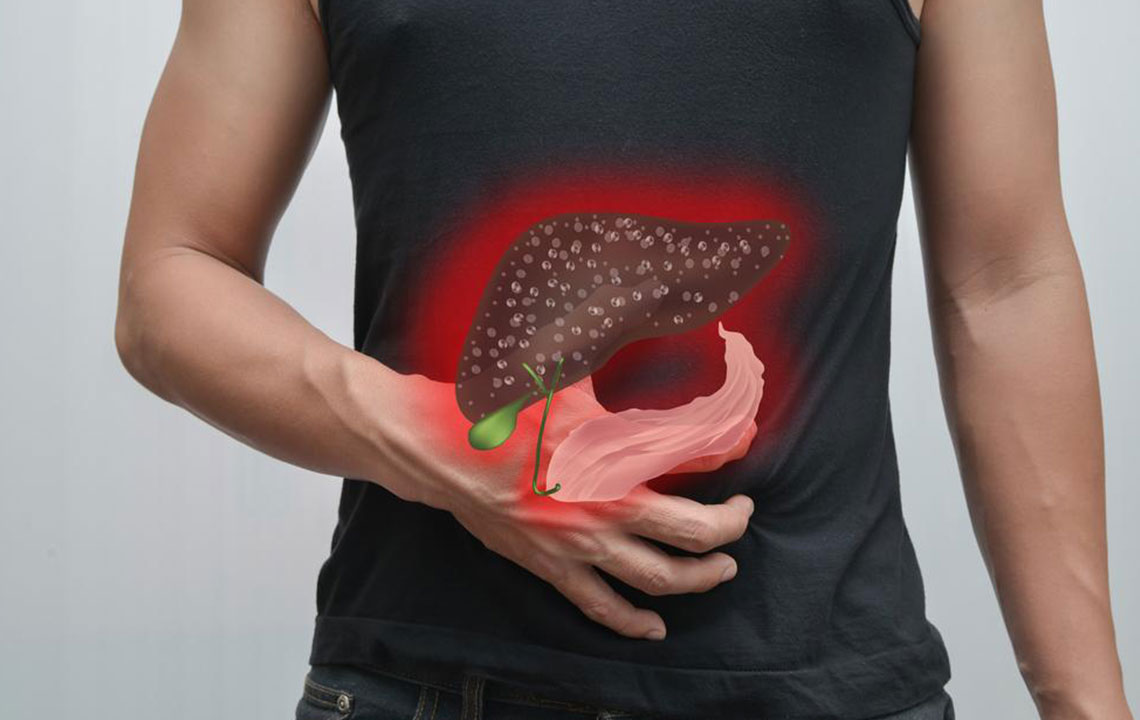
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver. It occurs in two phases: the initial acute stage and a prolonged chronic phase lasting more than six months. While some individuals clear the virus early, approximately 85% develop long-term hepatitis C. This ongoing infection can lead to liver fibrosis, a scarring process that often progresses silently. Persistent scarring may compromise liver performance and elevate the risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Factors such as alcohol consumption and age at infection influence the severity of liver damage. In severe cases, liver failure may occur, necessitating transplantation. Regular medical consultation is crucial throughout the disease course.
Note: The information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Consult healthcare providers for proper diagnosis and treatment.