Understanding the Main Causes of Eczema and How to Manage Them
This article explores the primary causes of eczema, including skin dryness, genetics, and allergies. It offers insights into managing symptoms effectively through proper skincare and medical advice, emphasizing the importance of early detection and professional consultation for better outcomes.

Understanding the Main Causes of Eczema and How to Manage Them
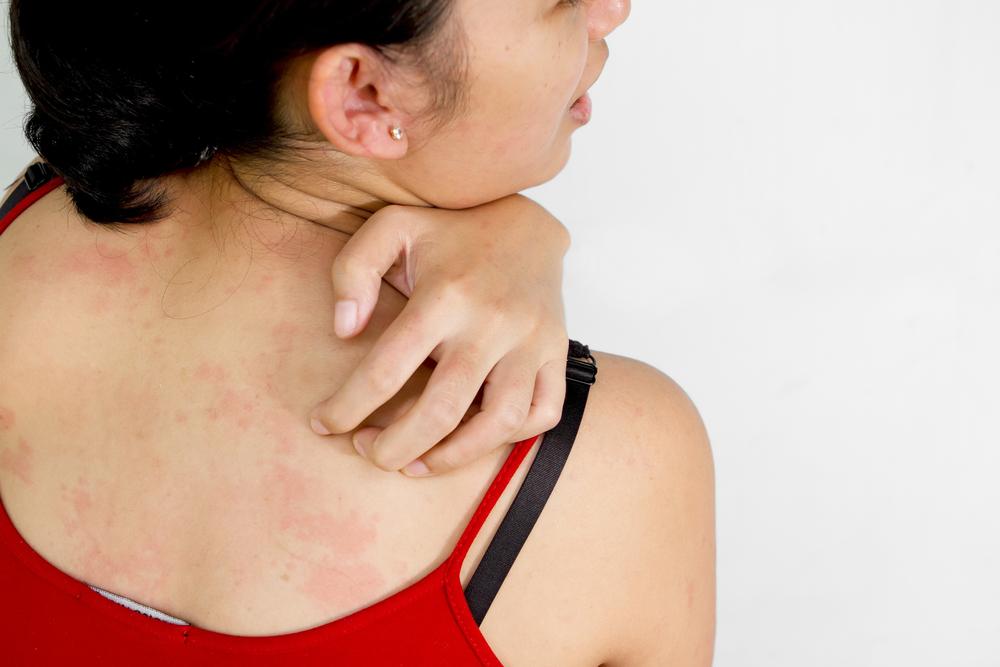
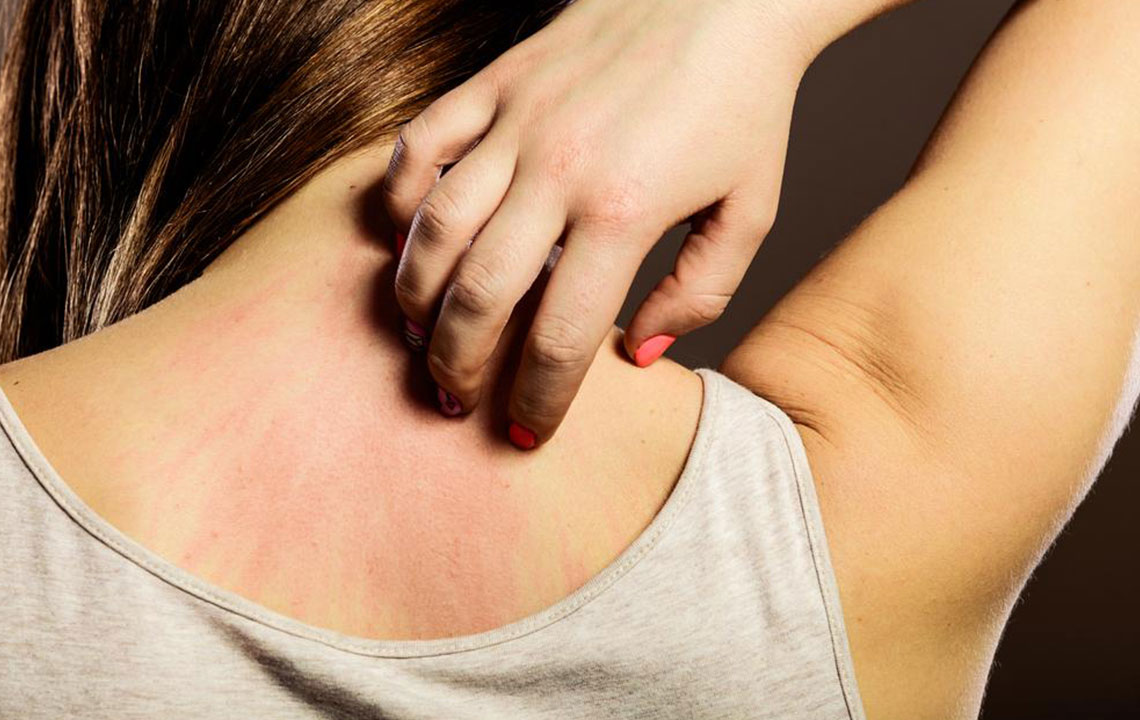
Eczema is a widespread skin disorder affecting individuals of all ages under various weather conditions. It is most common among children, characterized by red, itchy patches on the skin.
What is Eczema? Atopic dermatitis is a prominent form of eczema. Managing it involves consistent moisturizing and avoiding harsh soaps. Medical treatments can reduce redness and discomfort, but a complete cure remains unavailable despite ongoing research.
Current Remedies for Eczema While medications help control symptoms, they don't offer a permanent solution. Proper management can provide significant symptom relief, even though the condition itself cannot be entirely eradicated.
Factors Contributing to Eczema The precise cause of eczema is still unknown, but several elements are thought to contribute:
Damaged skin barrier function in eczema-prone skin leads to dryness and increased sensitivity to triggers.
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with children inheriting tendencies from parents with atopic dermatitis.
Close exposure to individuals with eczema or similar skin issues may raise risk, though genetics are more influential.
Additionally, children with food allergies are more prone to eczema flare-ups. Early detection and prompt medical consultation are vital to prevent worsening symptoms, such as excessive scratching and skin peeling.
Important Reminder:
Information about symptoms, treatments, and conditions is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.