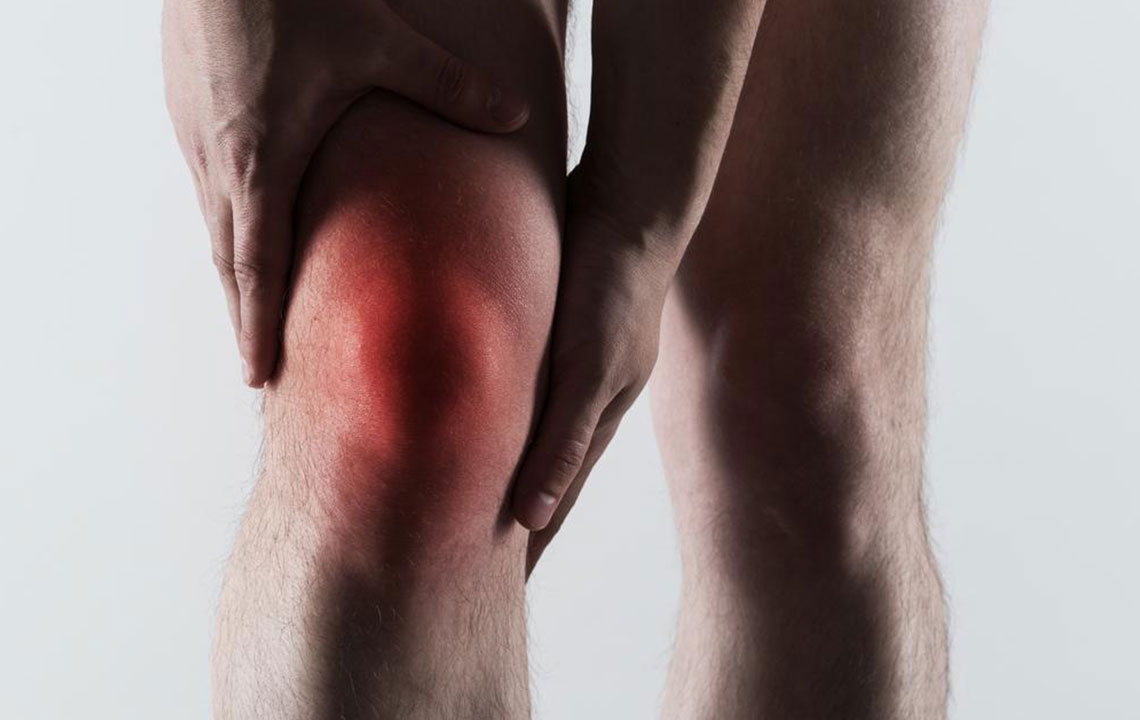
Common Risk Factors and Medical Conditions Contributing to Gout Episodes
Gout is a painful arthritis linked to uric acid buildup, often triggered by genetic, lifestyle, and medical factors. Understanding these risk factors helps in prevention and effective management. Common triggers include joint injuries, medications, and underlying health conditions such as hypertension and diabetes. Awareness and medical advice are essential for those prone to gout attacks.
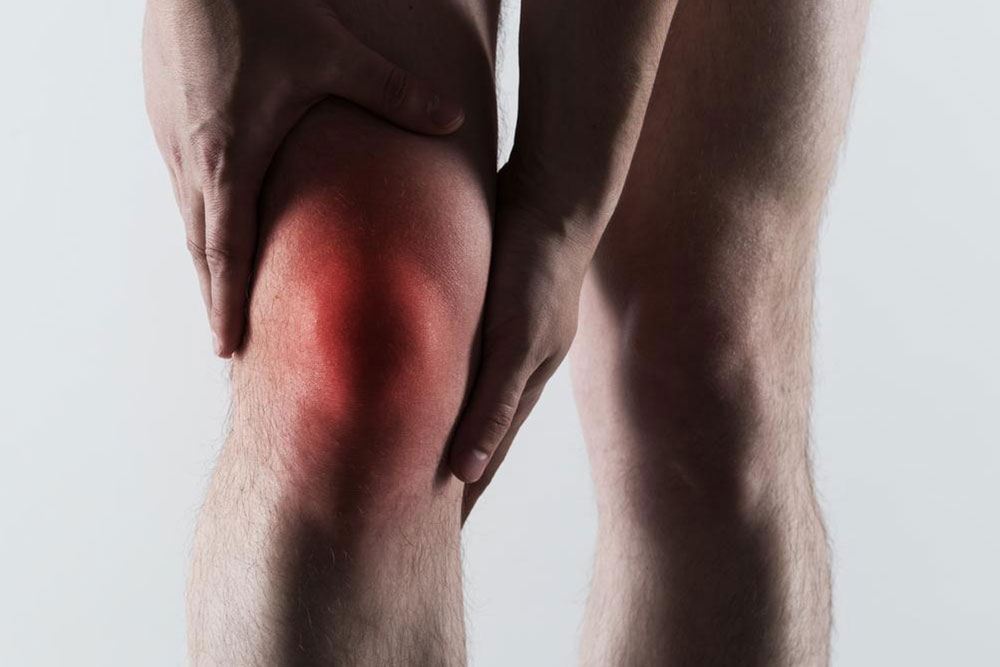
Gout is a distressing form of arthritis characterized by sudden and severe joint pain, swelling, and redness, primarily affecting the big toe. It results from uric acid crystals depositing in the joints. Various health conditions and lifestyle factors can increase the likelihood of gout attacks. Genetics influence susceptibility, with a family history elevating risk. Men are more commonly affected, though women’s risk grows post-menopause. Joint injuries, certain medications like diuretics, and recent surgeries can also trigger flare-ups. Additionally, conditions such as high blood pressure, kidney issues, diabetes, and thyroid problems are linked to higher gout risk. Recognizing these factors is crucial for prevention and management. Consult healthcare professionals for tailored advice and treatment to control gout effectively.