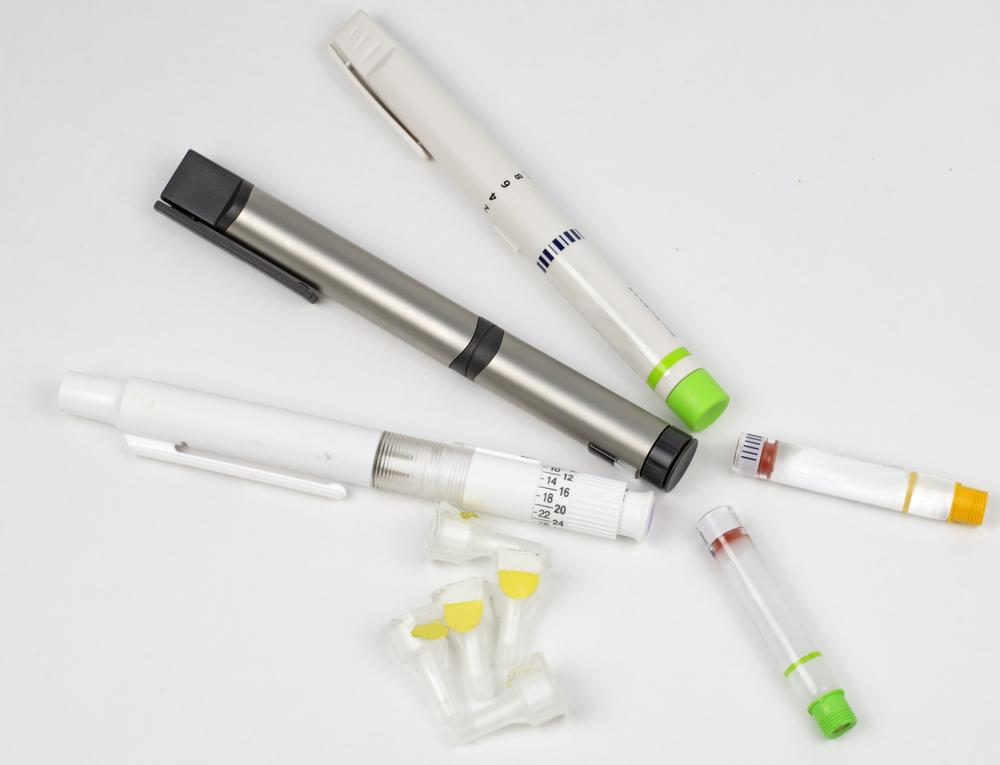
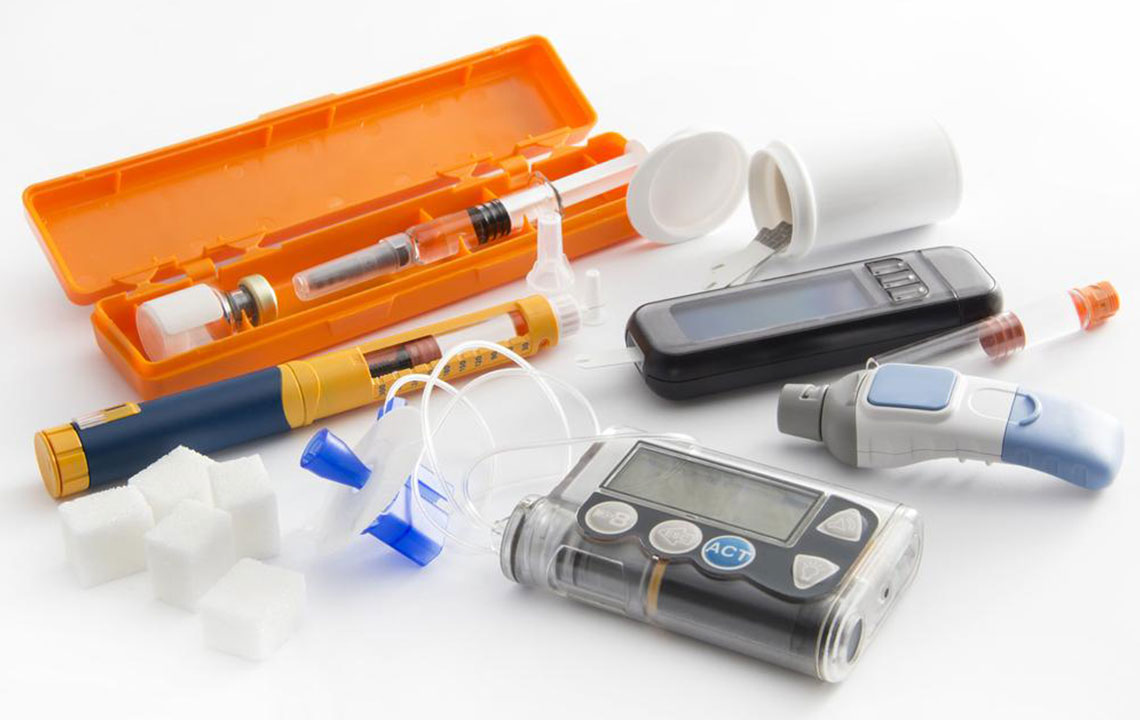
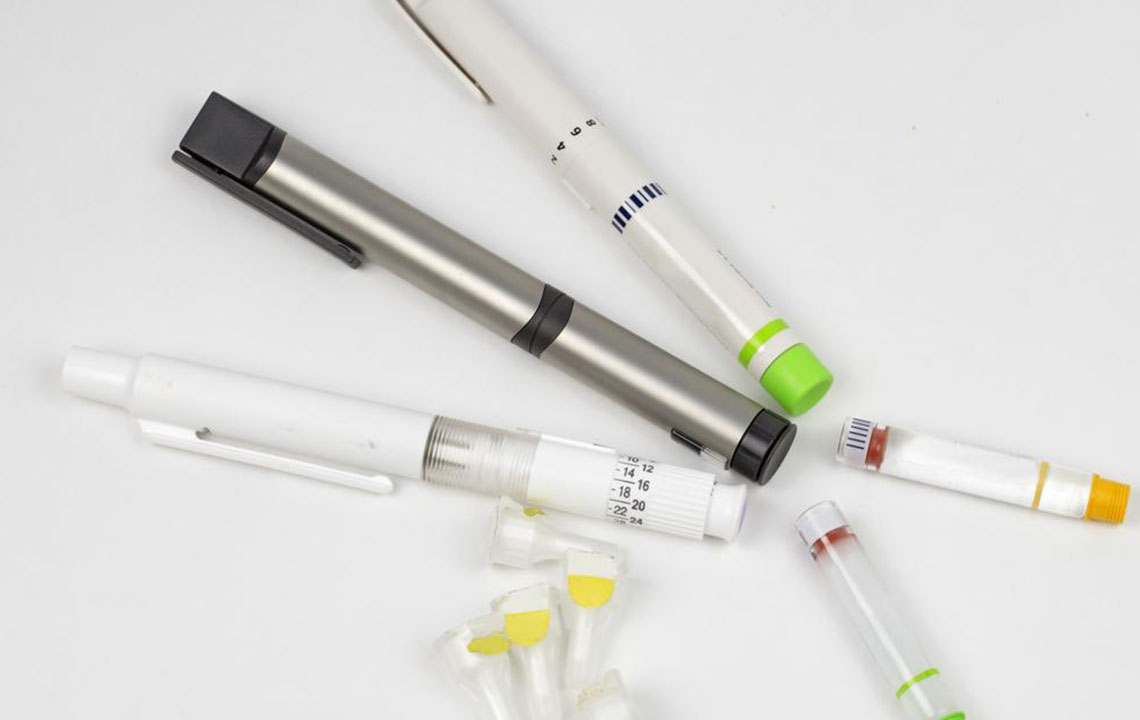
Comprehensive Overview of Insulin Types and Their Role in Managing Diabetes
This comprehensive guide explains the various types of insulin used in diabetes treatment, including their functions and administration timing. It emphasizes personalized healthcare and the importance of consulting medical professionals for effective management.
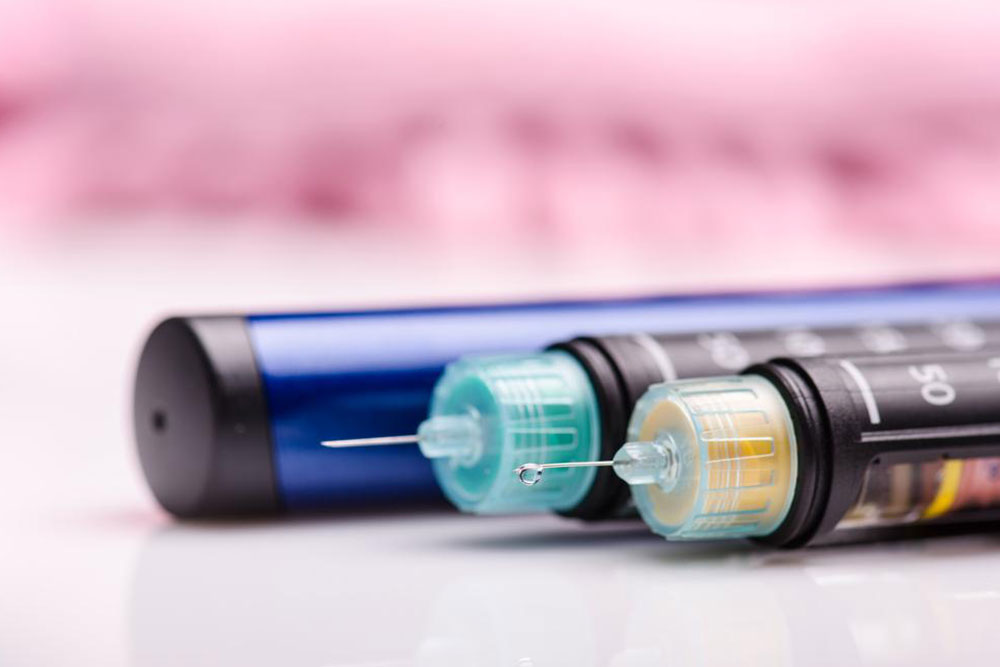
An In-Depth Look at Insulin Varieties and Their Functions in Diabetes Care
Insulin is an essential hormone produced naturally by the pancreas in healthy individuals. It helps the body utilize glucose from dietary carbohydrates, supplying energy for daily activities.
Maintaining proper cellular function relies on stable blood sugar levels, but glucose can’t enter cells without help. Insulin acts as the key that unlocks cells for glucose entry. After eating, blood sugar levels rise, triggering insulin release to clear excess glucose and keep blood sugar balanced.
Beyond blood sugar regulation, insulin directs surplus glucose to the liver for storage and releases it when needed, ensuring consistent blood sugar levels. A lack of insulin production can lead to hyperglycemia and increase diabetes risk.
Diabetes is primarily classified into Type 1, characterized by an inability of the pancreas to produce insulin, and Type 2, marked by insulin resistance. Managing diabetes often involves synthetic insulin, especially for Type 1, requiring regular doses to prevent complications.
Various insulin types are utilized in treatment:
Fast-acting insulin – Administered at mealtimes to control rapid blood sugar surges; begins working within 15 minutes and is often used with long-acting insulin.
Basal insulin – Maintains consistent insulin levels over 24 hours, typically administered once daily.
Mealtime insulin – Used after meals, effective for 3-6 hours, usually combined with basal insulin.
Intermediate-acting insulin – Given at night, lasts up to 12 hours, often in combination with other types.
Your healthcare provider will design the most suitable insulin plan based on your individual needs.
Note:
The content provided here is intended for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized diabetes management strategies. The website might not include all available insulin products or treatment options, so seek detailed guidance from your doctor.