Understanding Blood Pressure Levels and Their Importance
Learn how to interpret blood pressure readings accurately with our comprehensive guide. Understand the different categories, what your numbers mean, and steps to maintain healthy levels. Regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments are essential for preventing hypertension and related health problems. This article offers practical tips for using blood pressure charts effectively, ensuring better heart health and overall well-being.
Understanding Blood Pressure Levels and Their Importance
Maintaining healthy blood pressure is key to overall well-being. Abnormal readings can increase the risk of heart disease or organ damage by impairing blood and oxygen flow. Knowing what counts as a healthy level helps in managing your health effectively. By learning about blood pressure categories and correctly interpreting your measurements, you can make informed decisions to stay healthy. Continue reading to understand blood pressure classifications and how to accurately read your blood pressure results.
Blood pressure is divided into five main categories, ranging from low (hypotension) to severe hypertension (Stage 2).
For reliable readings, avoid relying on a single measurement; instead, take multiple readings over different days and calculate the average.
A systolic pressure of 90 mm Hg or less along with a diastolic of 60 mm Hg or lower suggests hypotension, which can result from dehydration or low blood sugar.
Normal blood pressure generally features a systolic below 120 mm Hg and a diastolic under 80 mm Hg.
If systolic values fall between 120-129 mm Hg with diastolic below 80 mm Hg, it indicates elevated blood pressure. Lifestyle changes are recommended to prevent progressing to hypertension.
Stage 1 hypertension is characterized by systolic readings from 130-139 mm Hg and diastolic between 80-89 mm Hg. Medical advice and possible treatment are advised.
Readings of 140 mm Hg systolic or higher, or 90 mm Hg diastolic or more, indicate Stage 2 hypertension requiring immediate medical attention.
Key tips before using a blood pressure chart
The chart offers general ranges and should serve as a guide rather than a definitive diagnosis.
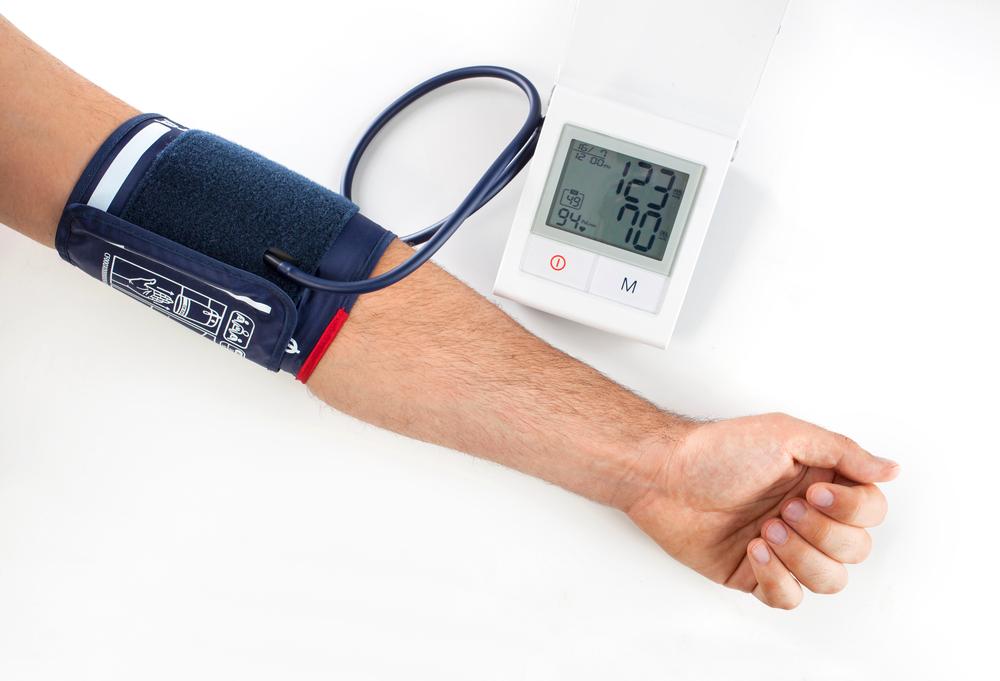
Accurate monitoring involves checking both systolic (upper number) and diastolic (lower number) values.
Systolic pressure reflects arterial pressure during heartbeats, whereas diastolic indicates pressure when the heart rests between beats.
Abnormal readings, whether high or low, should prompt medical evaluation to prevent health complications.
Consistent blood pressure checking is critical. Maintaining levels within a healthy range through lifestyle, diet, and medication can help avoid serious health issues.