Comprehensive Approach to Gout Management and Relief
This guide offers essential insights into gout, covering causes, symptoms, medications, dietary tips, and lifestyle changes. Effective management strategies help prevent attacks and improve quality of life, emphasizing the importance of medical advice and proper treatment planning.
Comprehensive Approach to Gout Management and Relief
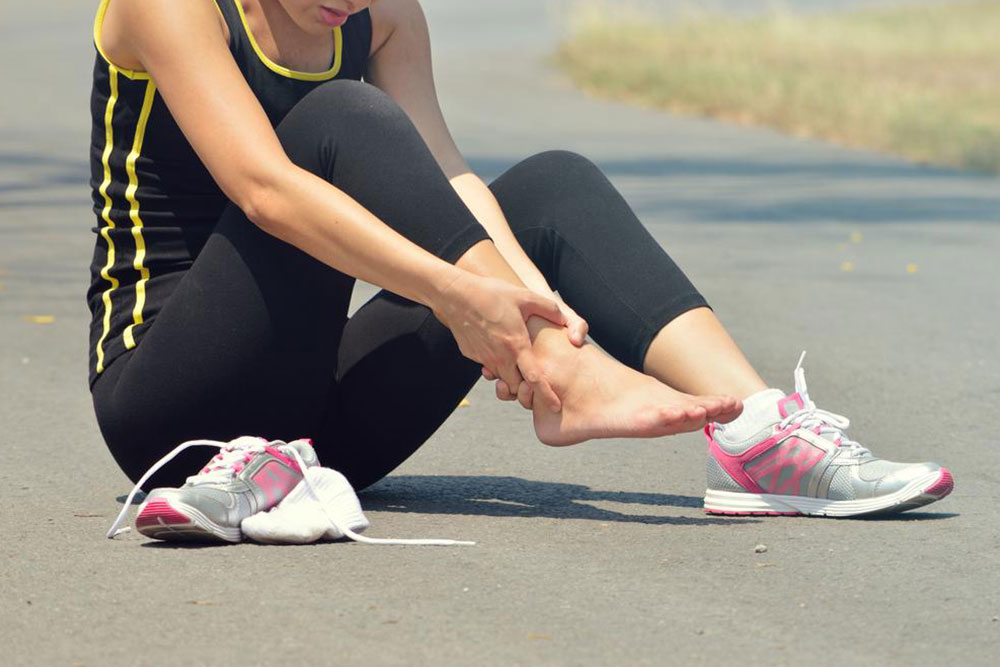
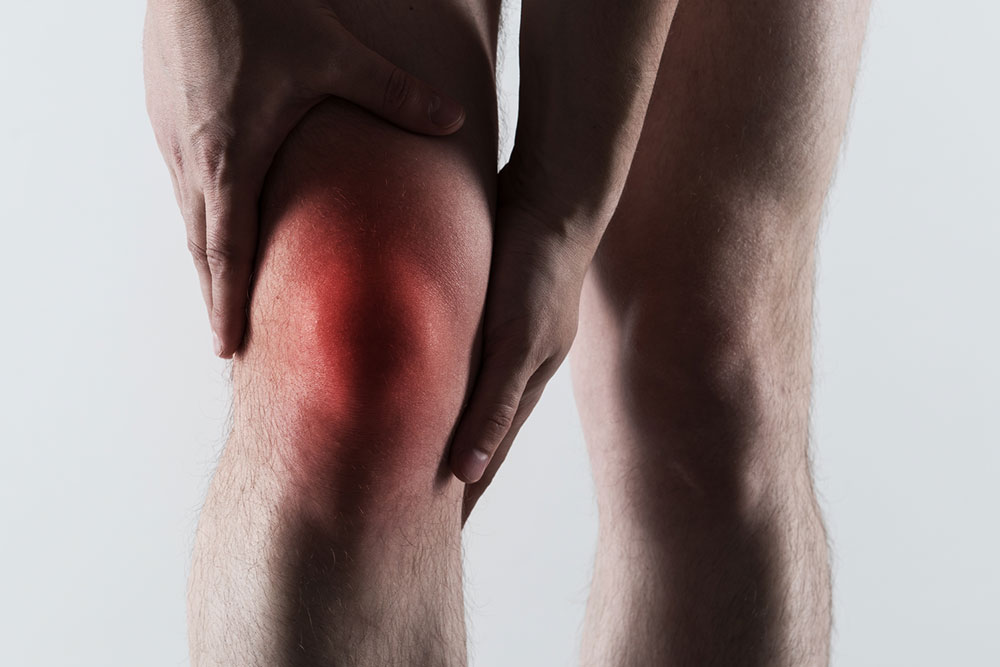
Gout is a painful joint condition caused by sudden inflammation and swelling. Proper understanding and treatment are essential for relief.
Symptoms include intense joint pain, redness, swelling, and tenderness. Attacks occur unexpectedly, often accompanied by a burning sensation in affected joints.
What Causes Gout?
Elevated uric acid levels lead to urate crystal deposits in joints. Factors such as obesity, alcohol use, and diet contribute to increased uric acid. Foods high in purines, like red meats, processed foods, and refined grains, can trigger gout episodes.
Managing gout involves medications such as NSAIDs—like ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin, or celecoxib—that help reduce inflammation and pain. Colchicine provides rapid relief by decreasing swelling and uric acid crystal formation. Corticosteroids are another option to control inflammation. Adhering to treatment and making dietary choices—like limiting purine-rich foods and reducing alcohol—are vital for prevention.
Managing Gout Complications
Lowering uric acid levels with medications such as febuxostat or probenecid is key. Lifestyle modifications like reducing alcohol, maintaining a healthy weight, and eating vitamin C-rich foods like oranges and broccoli support management. Although coffee isn't a cure, it may help lessen symptoms. Always seek advice from healthcare professionals before making changes to treatment or diet.