Proven Methods to Alleviate Gout Discomforts
Learn effective strategies for managing gout symptoms through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes. Early recognition and proper treatment can reduce pain, prevent future attacks, and improve quality of life. This comprehensive guide covers the stages of gout, causes, symptoms, and proven management tips to help those affected take control of their condition.
Proven Methods to Alleviate Gout Discomforts
Recognizing the early signs of a gout attack enables quick intervention. Gout episodes often strike suddenly, leaving limited prevention options once triggered. Although a complete cure remains elusive, a range of medications and natural remedies can help manage symptoms. Known as gouty arthritis, this condition has been documented since ancient times and earned the nickname "the king's disease," due to its association with rich foods and alcohol consumption.
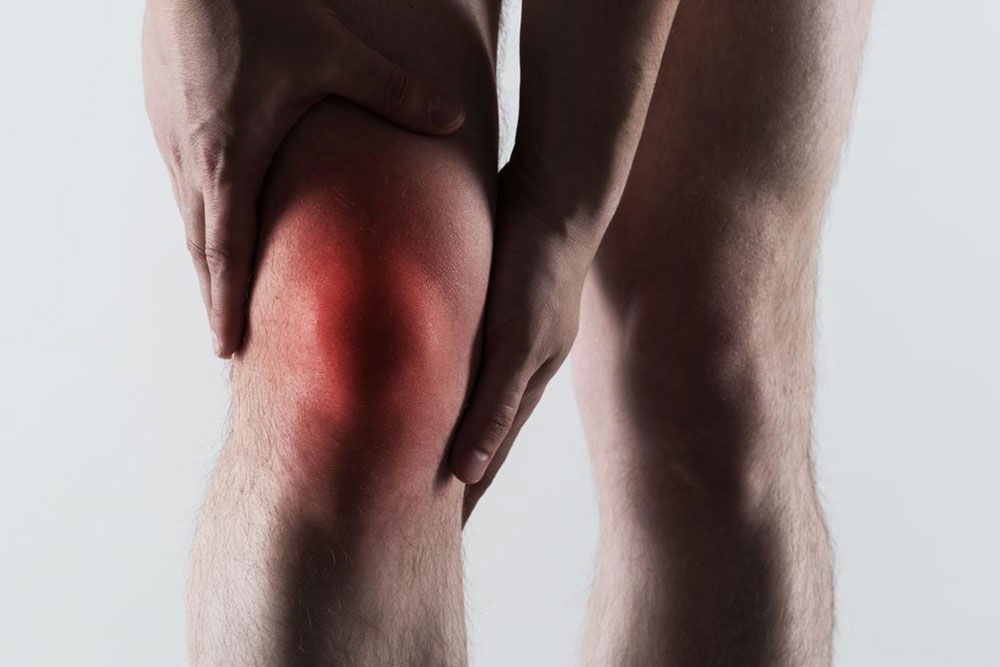
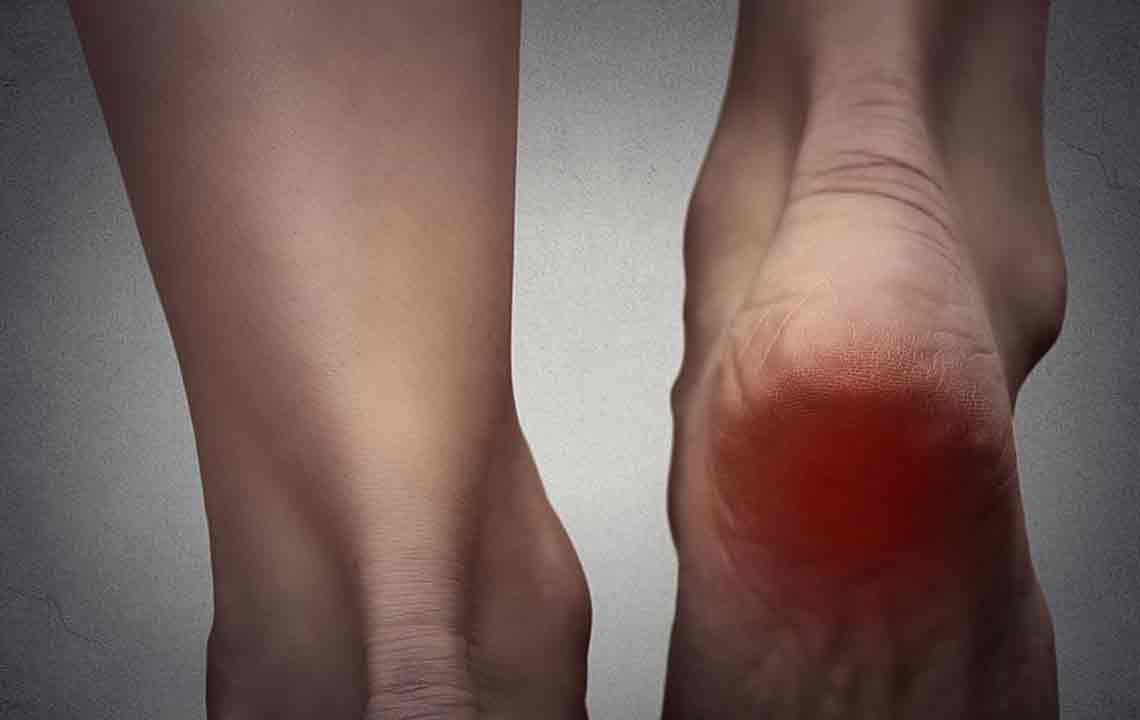
An attack may have precursors or occur unexpectedly. Gout progresses through four stages: asymptomatic hyperuricemia, acute flare, intercritical period, and chronic tophaceous gout, each with unique signs and treatments. The big toe is the most common target, with other joints like knees and ankles also affected. Combining medication and home remedies effectively alleviates pain and swelling.
Gout pain results from uric acid crystal deposits in joints, causing inflammation. Elevated uric acid levels can be due to dietary choices, alcohol intake, kidney or thyroid issues, and genetics. Consuming foods like shellfish, red meats, organ meats, sugary drinks, and salty foods raises uric acid. Kidney problems may also contribute. People with a family history or high alcohol consumption are at increased risk. While the big toe is primarily affected, other joints may also experience pain, peaking within 12-24 hours and lasting up to two weeks.
Effective gout management combines various treatments:
Pain Relief Medications: NSAIDs like ibuprofen, naproxen, colchicine, and corticosteroids help control pain and swelling during attacks.
Uric Acid Reduction: Medications such as allopurinol and probenecid lower uric acid levels to prevent future episodes. Use under medical supervision.
Dietary Changes: Avoiding high-purine foods, reducing alcohol, and increasing hydration can decrease attack frequency and severity.
Home Care: Cold compresses soothe inflamed joints. Rest and elevation promote recovery.
Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol intake contribute to fewer attacks.
Prevention plays a crucial role. Healthy habits like limiting purine-rich foods, staying hydrated, managing weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding alcohol and tobacco can lower the risk of flare-ups. With early intervention and proper lifestyle adjustments, gout can be managed effectively, enhancing overall well-being.
Note:
This article offers health insights based on research and expert advice. However, it should not replace professional medical consultation. Always seek advice from a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. Verify information from trusted sources before making health decisions.