Key Factors Contributing to Gout-Related Foot Pain
Gout causes foot pain due to uric acid crystal buildup, with factors like diet, dehydration, alcohol, and stress playing key roles. Managing these triggers alongside medication helps control symptoms and prevent attacks.
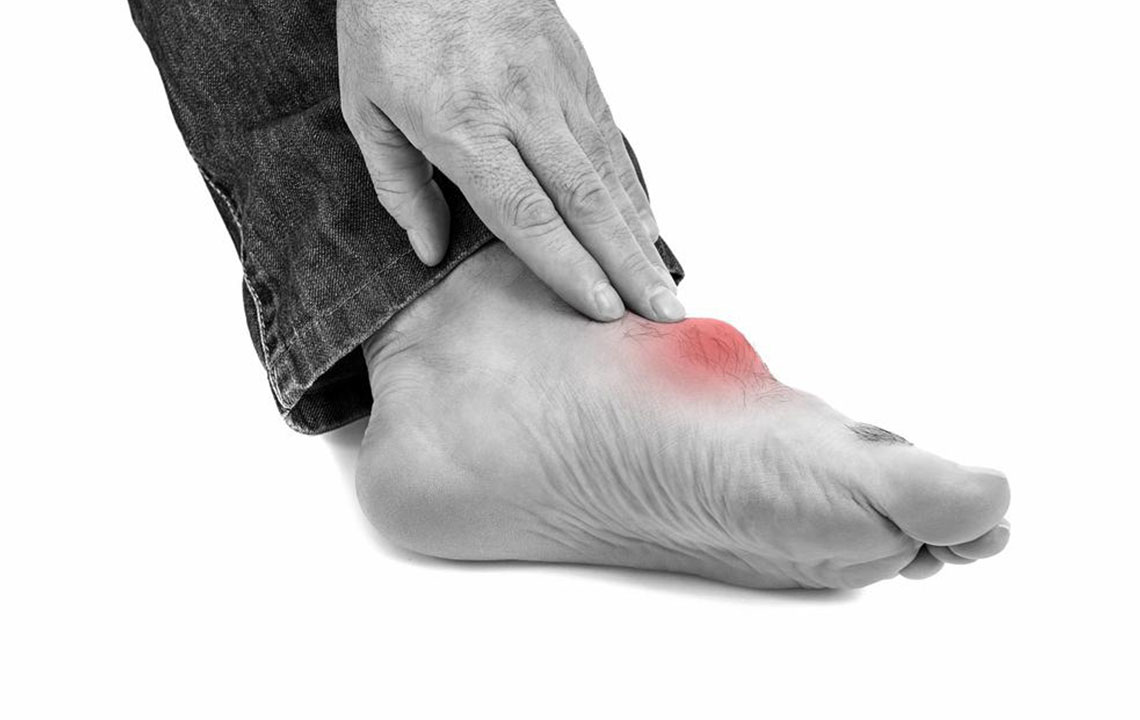
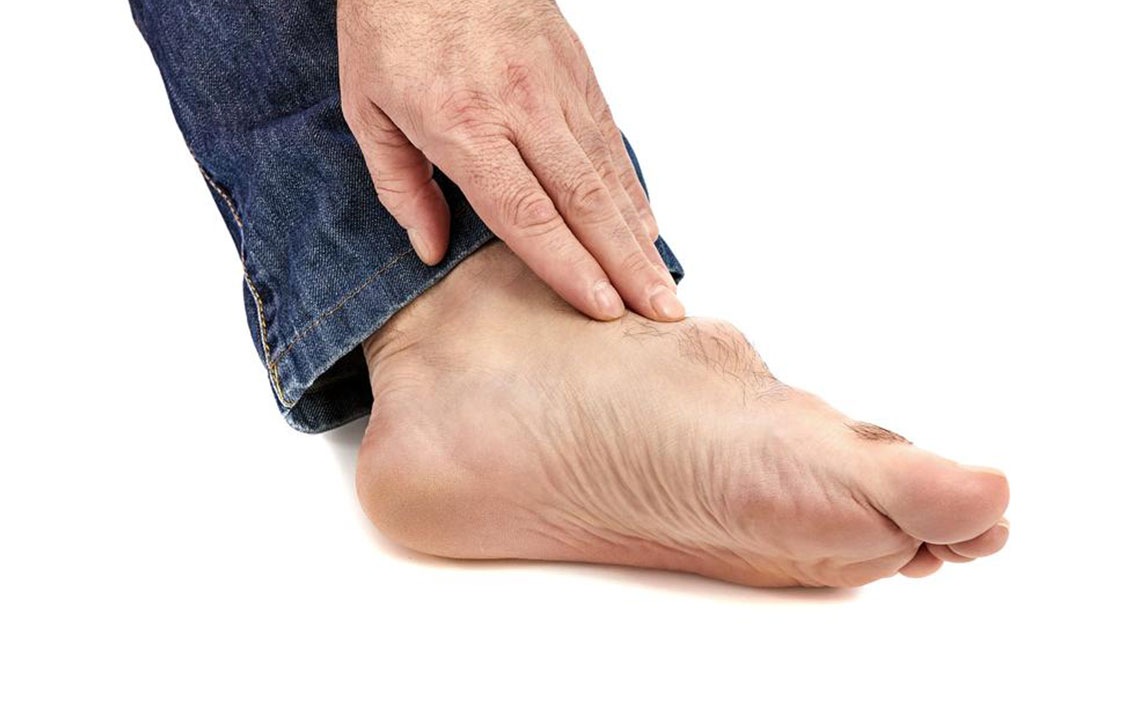
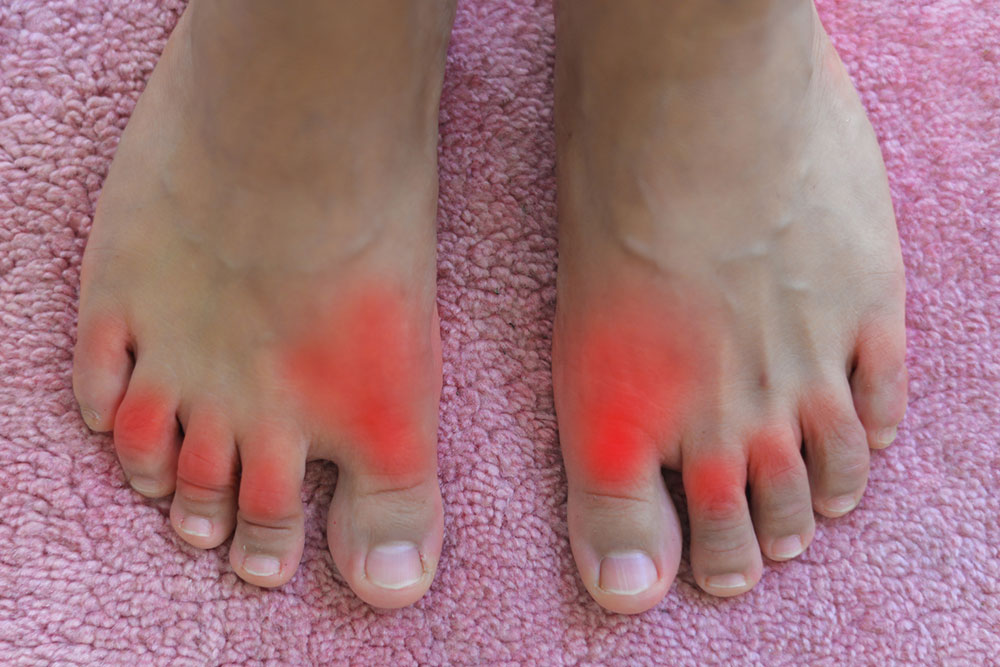
Gout is an inflammatory form of arthritis characterized by severe joint pain, swelling, and redness, predominantly affecting the big toe. It occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate within the joint, resulting from excess uric acid in the blood. Normally, kidneys remove uric acid through urine, but impaired kidney function or increased production can cause hyperuricemia and subsequent crystal formation. Effective management includes medication and lifestyle changes to avoid specific triggers that can exacerbate episodes.
Foods rich in purines like bacon, turkey liver, sardines, shellfish, spinach, mushrooms, and asparagus can trigger flare-ups.
Dehydration hampers kidney function, reducing uric acid clearance and increasing attack risk.
Beverages with high fructose corn syrup, such as sodas and fruit juices, can boost uric acid levels.
Alcohol consumption, particularly beer, interferes with uric acid elimination.
Crash dieting and fasting can lead to increased uric acid due to rapid protein breakdown.
Some blood pressure medications may raise gout risk.
High stress levels are linked to gout attacks, as stress decreases Vitamin B5, essential for uric acid metabolism.
Besides medication, avoiding these triggers is crucial for managing gout foot discomfort effectively.