Effective Strategies for Managing Type 2 Diabetes
This article offers practical guidance for managing type 2 diabetes through lifestyle modifications, diet, and exercise. It highlights key symptoms, the importance of blood sugar monitoring, and current treatment options, empowering individuals to take control of their health. Always seek medical advice for personalized care and treatment strategies.

Effective Strategies for Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Newly diagnosed with diabetes or caring for someone with the condition? Understanding how to manage it is essential. While healthcare professionals offer personalized guidance, this article provides a detailed overview of diabetes, its effects on the body, and current treatment options. We explore what diabetes is, how it influences bodily functions, and recent advances in managing this chronic disease.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus includes various disorders that disrupt how your body handles sugar.
Many newly diagnosed individuals worry that consuming sugar is off-limits. However, sugar itself isn't harmful—it's vital for energy in muscles, tissues, and the brain. Choosing natural sources like fruits supports health, while excessive processed sugars can be harmful.
Glucose energy fuels every cell in the body, supporting overall health and brain function. Effective management involves maintaining this balance thoughtfully.
Recognizing Diabetes Symptoms
Recent diagnoses can be overwhelming, but millions in the U.S. live with diabetes. Data from 2014 shows around 29.1 million Americans (9.3%) are affected.
The way your body processes sugar depends on insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood glucose. Proper insulin function keeps sugar levels stable. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
Persistent thirst
Frequent urination
Intense hunger
Fatigue
Irritability
Blurred vision
Slow-healing cuts
Recurrent infections
Consult a healthcare provider for blood tests to confirm diagnosis and develop a treatment plan.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Lifestyle changes, especially dietary adjustments and exercise, are key. Managing carbohydrate intake from fruits, grains, and vegetables helps keep blood sugars in check. A registered dietitian can craft a tailored nutrition plan.
Eat mostly whole, unprocessed foods like fresh produce, beans, and lean proteins. Hydration with water is important, as dehydration can impair circulation and add stress to the heart, complicating management efforts.
Physical Activity's Role
Regular exercise such as a 30-minute walk daily can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by around 30%. Exercise supports weight management, lowers blood pressure, boosts mood, increases energy, improves sleep, and strengthens social interactions. Since obesity is closely linked to diabetes, staying active is crucial.
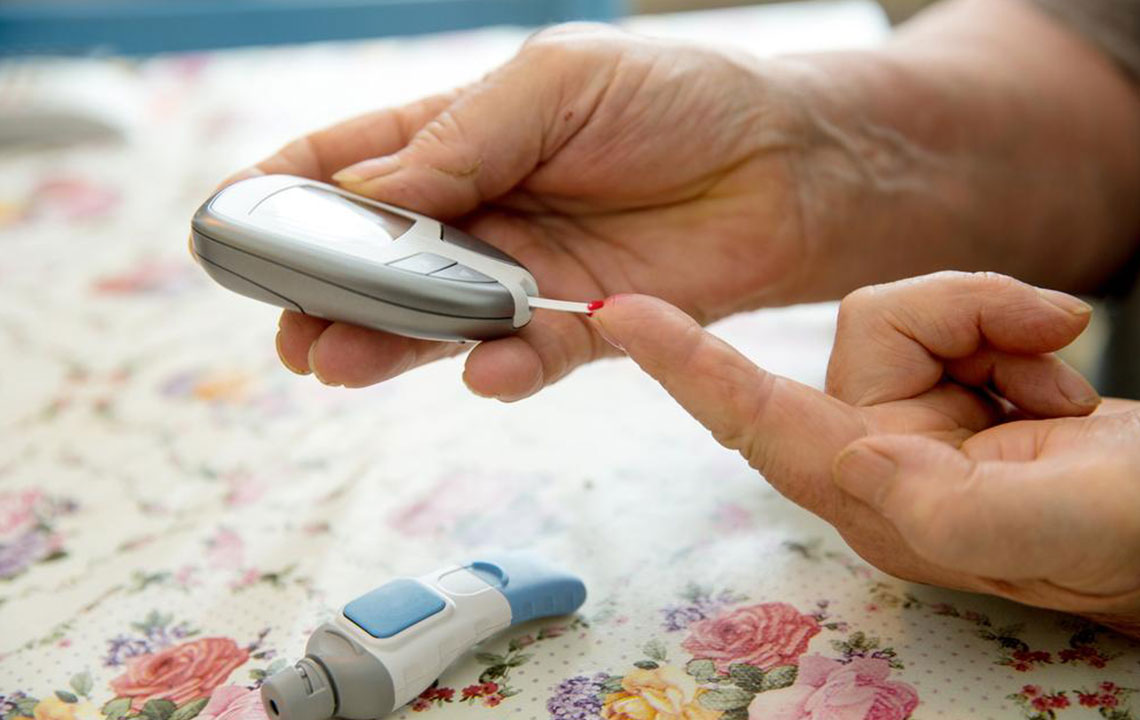
Blood sugar monitoring is essential. Home testing under medical guidance can help assess progress. When necessary, medications can be prescribed to keep blood glucose levels within target ranges.
Important Note:
This information is meant for educational use only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult qualified healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment decisions. Exercise caution when using online health information.