Recognizing and Addressing Advanced Melanoma Early
This article highlights the importance of early detection and treatment of advanced melanoma. It explains how melanoma spreads, common risk factors, symptoms to watch for, and the significance of timely medical intervention. Recognizing early signs can help improve prognosis and prevent further metastasis.

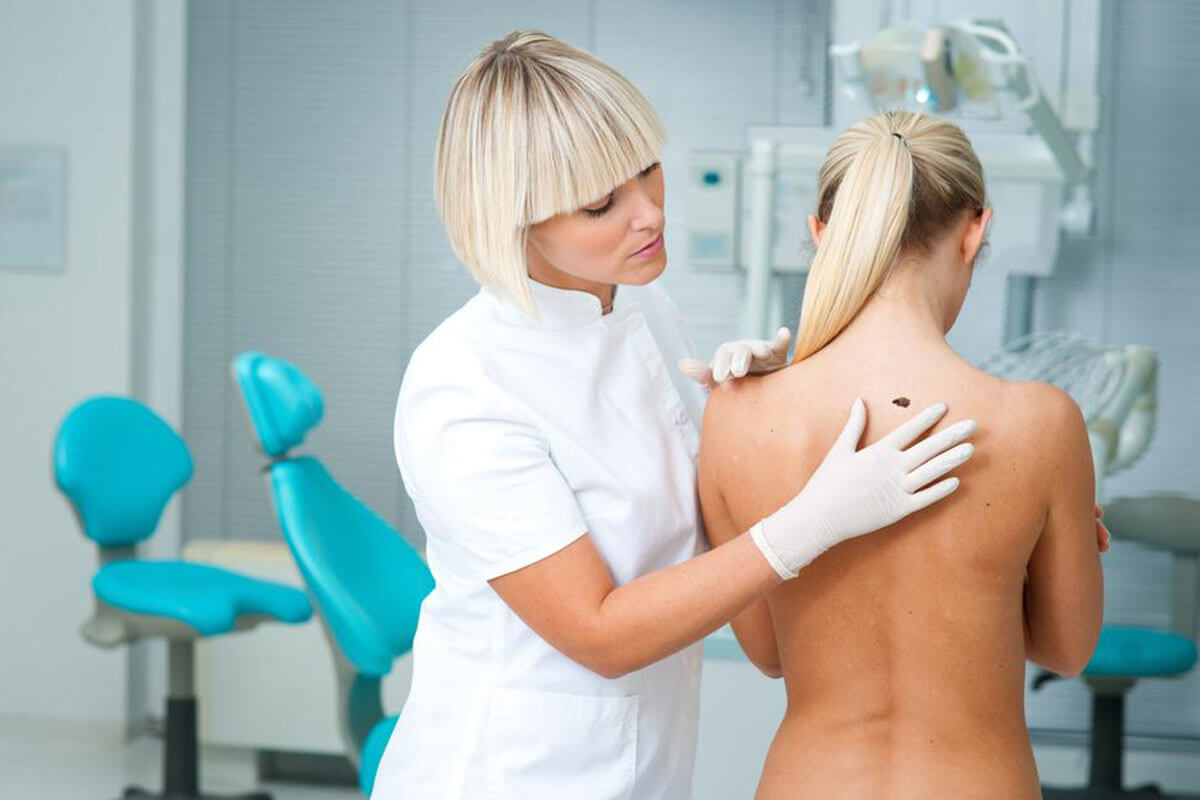
Metastatic melanoma describes the aggressive spread of skin cancer from the original site to other parts of the body. When melanoma reaches this advanced stage—Stage IV—it progresses through lymphatic pathways to vital organs like the brain, lungs, liver, or bones. Detecting early indicators such as unusual skin color changes or new moles is essential, as early-stage melanoma can resemble benign skin alterations. Ultraviolet exposure from sunlight or tanning devices is a leading cause, but melanoma can also develop independently of UV rays, commonly appearing on the palms, thighs, or groin. Symptoms like firm lumps, irregular bleeding, or neurological symptoms should be examined promptly. Early intervention is crucial to prevent further spread and improve outcomes.
Note: This article aims to educate about melanoma but is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment options. Raising awareness of early signs and risk factors is vital in managing this serious condition.