Key Screening Methods for Diabetes Identification
This article highlights essential diabetes screening tests, including the Random Glucose Test, HbA1c, fasting glucose, and oral glucose tolerance tests. Proper testing is vital for early detection, enabling timely management of diabetes. Consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and treatment plans.
Accurate monitoring of blood sugar is essential for individuals diagnosed with diabetes or those at potential risk. Regular testing enables early detection and prevents serious complications by maintaining optimal glucose levels. Suitable across all age groups, especially for those with a family history of diabetes or cardiovascular issues, various diagnostic tests are available. Below are the main methods used by healthcare professionals to evaluate blood sugar status.
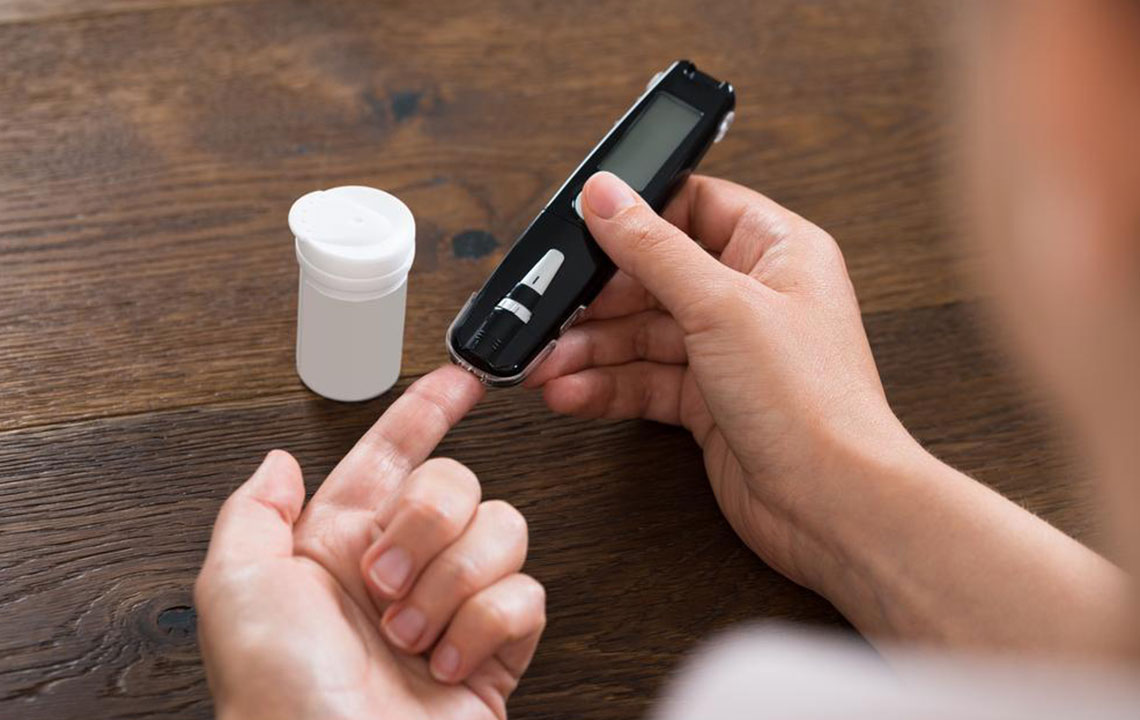
Casual Blood Glucose Test
Also known as the Random Plasma Glucose (RPG) test, this procedure involves taking a blood sample without regard to last meal. It provides a quick snapshot of blood sugar but may be influenced by recent food intake.
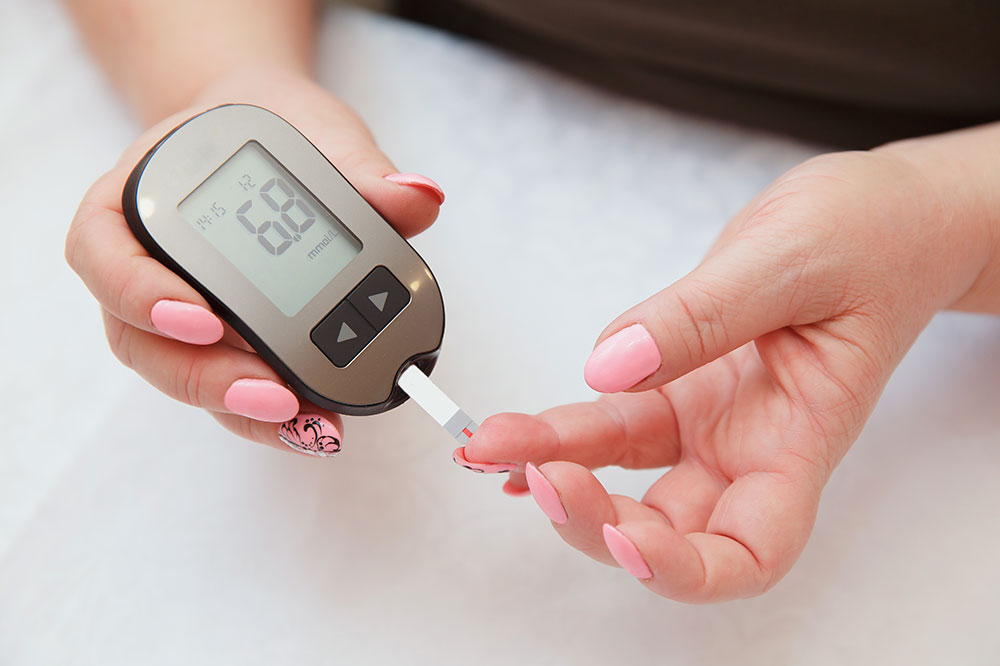
HbA1c Test
This highly recommended test measures the average blood glucose over past months. It doesn't require fasting, though results may be affected by conditions like anemia, as it assesses hemoglobin-bound glucose.
Fasting Blood Sugar Evaluation
This test involves fasting overnight, with blood drawn in the morning after minimal water intake. It offers a precise measurement of baseline blood glucose levels.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
Following an overnight fast, the patient consumes a glucose-rich liquid, with subsequent blood tests at specific intervals. It is especially valuable for diagnosing gestational diabetes.
These diagnostic procedures are crucial tools recommended by healthcare providers for effective blood sugar monitoring. Early diagnosis enhances ability to intervene promptly and manage diabetes effectively.
Note:
The information regarding symptoms, testing, and health conditions is for educational purposes only. It does not replace professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from qualified healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment.