Essential Strategies for Optimal Blood Sugar Control and Overall Health
Effective blood sugar management is vital for overall health, preventing complications like kidney disease and heart problems. Regular monitoring using charts and devices helps individuals, especially diabetics, maintain balance. Key strategies include proper diet, exercise, medication, and stress control for optimal glucose levels and well-being.
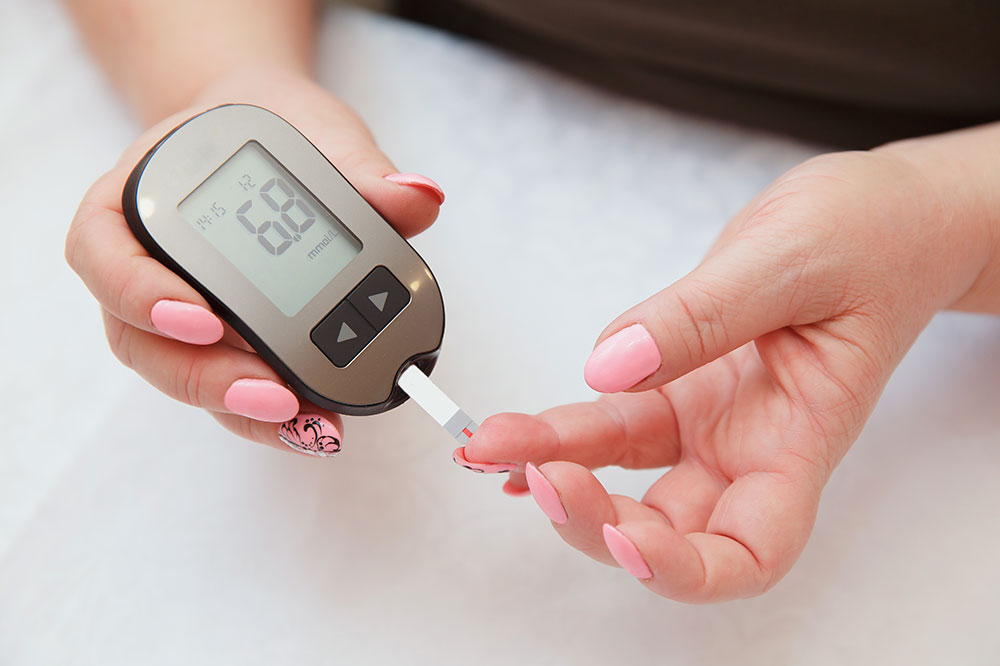

Importance of Maintaining Healthy Blood Glucose Levels
Blood sugar, or glucose, indicates the amount of sugar present in your bloodstream at any given time. This energy source is crucial for fueling body cells and supporting daily activities. Our dietary intake supplies the necessary nutrients to regulate blood glucose, while the body’s internal systems work to keep these levels within safe ranges.
Unlike common table sugar, the primary focus is on glucose in the blood. Fluctuations occur throughout the day based on eating habits and fasting periods.
In healthy individuals, fasting blood glucose usually stays below 99 mg/dl. For those with diabetes, levels may vary more widely. The target is to maintain blood sugar below 130 mg/dl before meals and under 180 mg/dl after eating.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Effectively
Keeping blood glucose levels within safe limits requires a balanced diet, proper medication, and regular physical activity. Blood sugar charts help visualize daily variations, offering valuable insights. Monitoring is essential for managing diabetes by identifying periods of abnormal highs or lows in sugar levels.
The Importance of Regular Blood Sugar Checks
Similar to tracking blood pressure, consistent blood sugar recordings provide a snapshot of overall health. Maintaining accurate records is important for everyone, especially diabetics. Unregulated blood sugar can harm kidneys, eyesight, and heart health. Regular checks allow early detection of issues, reducing the risk of complications.
Tools and Techniques for Tracking Blood Sugar
Various devices are available for monitoring blood sugar, but professional guidance is crucial for correct use. For diabetics, measuring fasting and post-meal glucose levels helps evaluate health status. Abnormal readings suggest the need for adjustments in diet, medication, or lifestyle.
Optimal blood sugar levels are generally below 100 mg/dl fasting and less than 140 mg/dl after meals. Achieving this balance involves a nutritious diet, sufficient sleep, consistent exercise such as walking or jogging, and avoiding alcohol and tobacco. Managing stress plays a vital role in maintaining stable glucose levels.