Understanding the Main Causes of Neck and Shoulder Discomfort
This article explores the primary causes of neck and shoulder discomfort, highlighting the interconnected nature of these regions. It discusses factors like posture, injuries, and degenerative conditions, emphasizing the importance of proper diagnosis and treatment. Understanding these causes helps in managing symptoms effectively through conservative methods such as physical therapy and medication, with surgery as a last resort for severe cases.

The neck and shoulder areas feature complex anatomy, including bones, muscles, and connective tissues. These regions often suffer from discomfort, stiffness, injuries, and degenerative changes. Such pain can stem from multiple factors, sometimes occurring together. Recognizing common causes of neck and shoulder pain is crucial for effective management.
What triggers neck pain?
Neck muscles are constantly active, even unconsciously, making them susceptible to strains, sprains, or injuries. Overuse, sudden movements, or poor posture often contribute to muscle strain.
Other causes include trauma, degenerative diseases, tumors, and bone deformities affecting the cervical spine.
What are the common causes of shoulder pain?
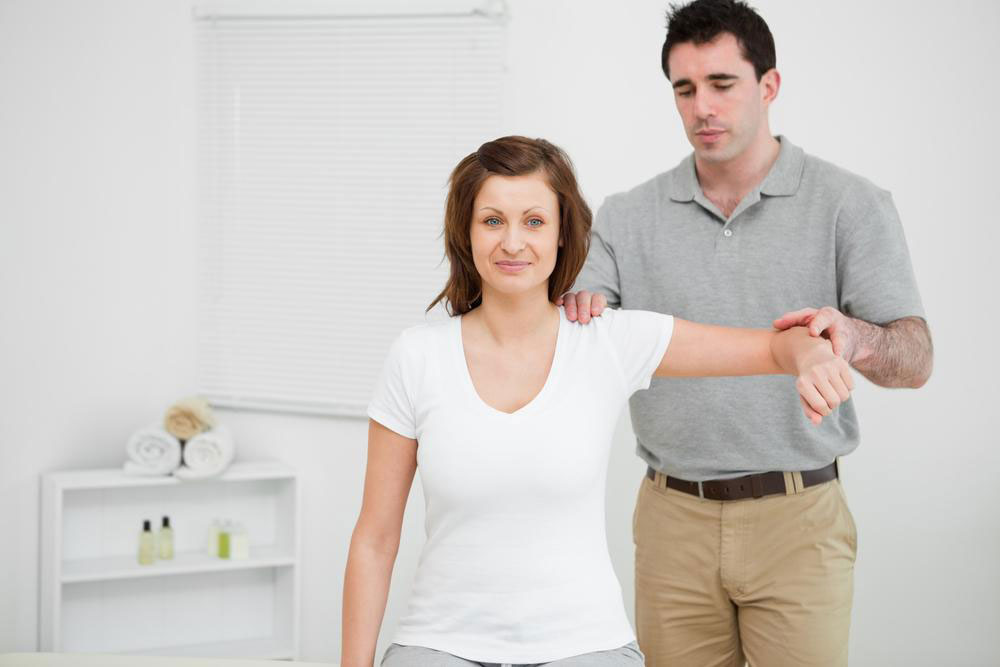
The shoulder joint's broad range of motion exposes it to injuries like tendinitis, dislocations, fractures, frozen shoulder, and instability caused by overexertion or trauma.
Are neck and shoulder issues connected?
Yes, problems in the neck and shoulder frequently overlap. The cervical spine's seven small vertebrae are prone to misalignments, arthritis, and degeneration. Conditions such as cervical radiculopathy, resulting from nerve compression by bone spurs or spinal stenosis, can cause pain radiating into the shoulders. Conversely, shoulder injuries like rotator cuff tears and bursitis can also lead to neck discomfort. Postural issues, including forward head posture and soft tissue injuries, significantly contribute to both regions.
Muscle, tendon, and ligament injuries from incidents like whiplash or sustained poor posture can cause pain in both areas. Cold therapy, medications, and physical therapy are typically effective treatments. Severe cases involving nerve damage might require surgery.
Note: This content is for educational purposes only and not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment options. The website disclaims responsibility for external discrepancies or additional offers.