Comprehensive Guide to HIV: Symptoms, Stages, and Treatment Options
This article provides a detailed overview of HIV, including symptoms across different stages, the importance of early diagnosis, and effective management strategies through antiretroviral therapy. Understanding these elements is vital for early intervention and maintaining health.
Comprehensive Guide to HIV: Symptoms, Stages, and Treatment Options
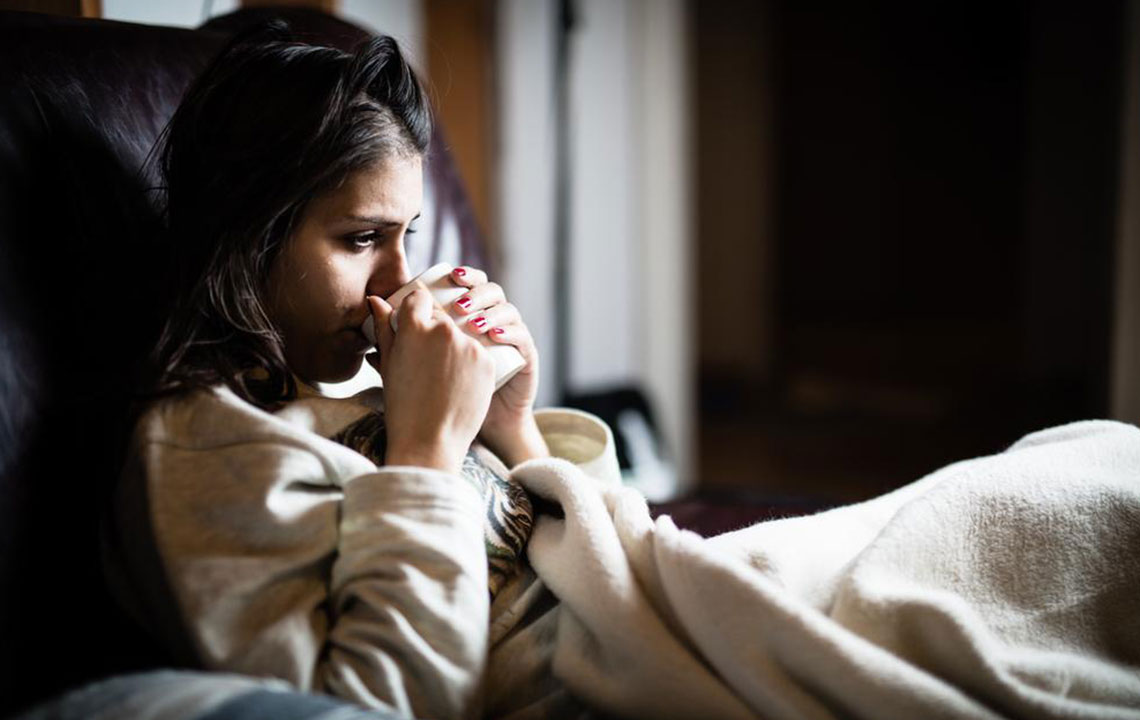
HIV, the virus behind AIDS, attacks the immune system by infecting CD4 cells vital for infection defense. Symptoms can emerge within weeks of infection and differ across phases. Initial signs include fever, skin rashes, muscle pain, swollen lymph nodes, and sore throat. In the asymptomatic stage, symptoms often are minimal or absent, lasting for years. If untreated, HIV progresses to AIDS, with symptoms like prolonged fever, night sweats, weight loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph glands, pneumonia, and neurological issues. Early antiretroviral treatment is critical to control the virus and enhance health. Treatment regimens involve personalized medication plans aimed at viral suppression and resistance prevention. Regular medical visits are key to successful management.