Home Care Tips for Managing Cellulitis Effectively
Learn effective home management strategies for cellulitis, including symptoms, remedies, and when to seek medical help. Proper care can prevent complications and promote healing.

Home Care Tips for Managing Cellulitis Effectively
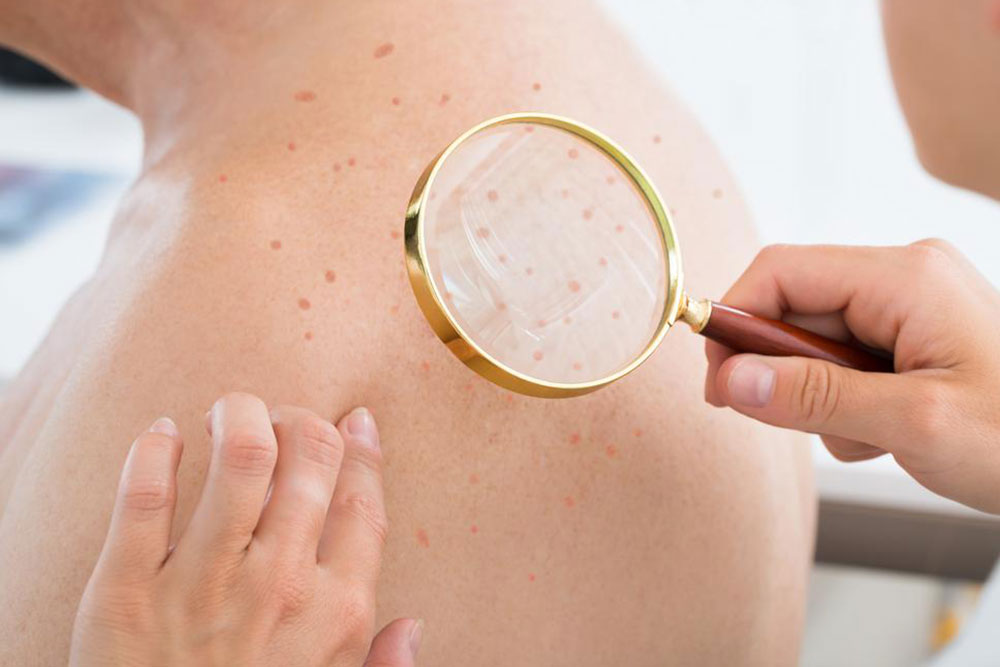
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection mainly caused by Staphylococcus and Streptococcus bacteria. It often starts at cuts, wounds, or skin breaks but can develop on any skin area. Common triggers include bruises, insect bites, or fungal infections like athlete’s foot. It frequently affects the lower legs but can also involve arms or face. Symptoms include redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, and soft tissue changes. Additional signs such as fever, chills, and hardened areas may occur.
For mild cases, simple home remedies can help reduce symptoms:
Using warm compresses with a clean cloth
Soaking the affected skin in lukewarm water
Avoiding harsh chemicals on the skin
Wearing loose, breathable clothing to prevent irritation
Typically, antibiotics are prescribed by healthcare providers for 3 to 10 days, with improvements seen within a few days. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention promptly—hospital treatment and stronger medications might be necessary. Without proper care, cellulitis can spread, causing serious conditions like bloodstream infections or sepsis. Severe cases may require intravenous antibiotics, wound management, and pain control. Duration depends on infection severity and patient health.
Note:
This information aims to educate and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.