Essential Insights into Cellulitis: Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
This article provides a comprehensive overview of cellulitis, emphasizing early symptoms, risk factors, and effective treatments. It highlights important prevention strategies and when to seek medical attention. Understanding these key points can help manage the infection effectively and avoid serious complications.

Essential Insights into Cellulitis: Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
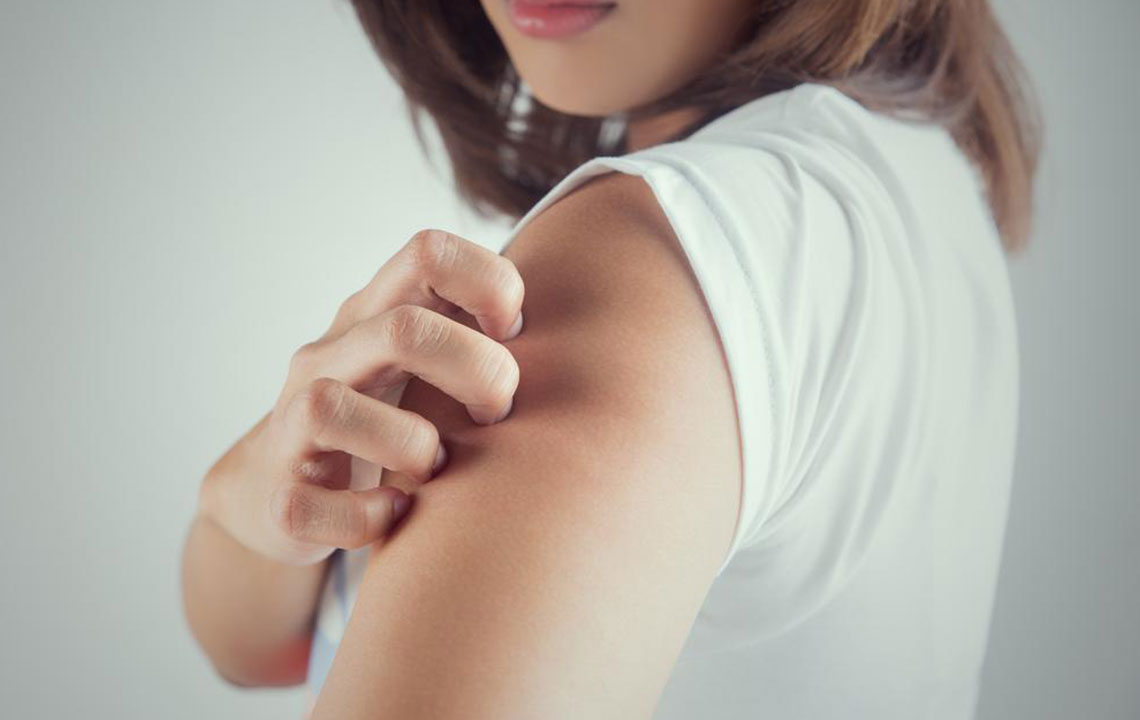
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that affects deeper layers of the skin and underlying tissues. Those who are overweight, suffer from athlete's foot, or have psoriasis are more susceptible. Early intervention is critical to prevent severe complications. Small wounds, if left untreated, can allow bacteria to enter. Protecting skin integrity and avoiding injuries help lower infection risk. High-risk groups include individuals with poor blood flow, weakened immune systems, diabetics, and those undergoing chemotherapy. Initial signs include redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, and pain.
People with limited mobility due to aging, disability, or obesity.
Individuals with compromised immune defenses from illness.
People with long-term diabetes are more vulnerable to infections like cellulitis.
Patients recovering from chemotherapy may also face increased risk.
Early cellulitis is often manageable with 3 to 10 days of oral antibiotics. Noticeable improvements usually occur within 24-48 hours. Completing the full course helps prevent recurrence. Warm compresses can soothe discomfort and reduce swelling. If symptoms persist or worsen, medical interventions like IV antibiotics or surgical drainage may be needed. Proper wound care, skin hydration, and injury prevention are essential. Penicillin is commonly prescribed, but alternate antibiotics may be used based on individual health conditions. Ignoring cellulitis can lead to serious issues, including bloodstream infections or limb loss.
Important Notice:
This article offers general information on cellulitis symptoms, prevention, and management. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult qualified healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment options. Relying solely on online guidance is not recommended.