Lupus Uncovered: Symptoms, Risks, and Management Tips
This comprehensive guide explores lupus, highlighting its symptoms, risk factors, and management methods. It emphasizes the importance of early detection, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle adjustments to improve quality of life for those affected. While no cure exists, understanding the disease and adhering to medical advice can greatly enhance daily well-being.
Lupus, or Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects multiple organs within the body. It develops when the immune system mistakenly targets healthy tissues, with causes linked to genetics and lifestyle factors, though it isn’t always hereditary. The Lupus Foundation of America estimates around 1.6 million people in the U.S. live with lupus. While anyone can develop the disease, women between 14 and 45 are most frequently diagnosed.
Typical symptoms include:
Persistent fatigue that intensifies over time
Low-grade fevers (99°F–101°F), indicating possible inflammation
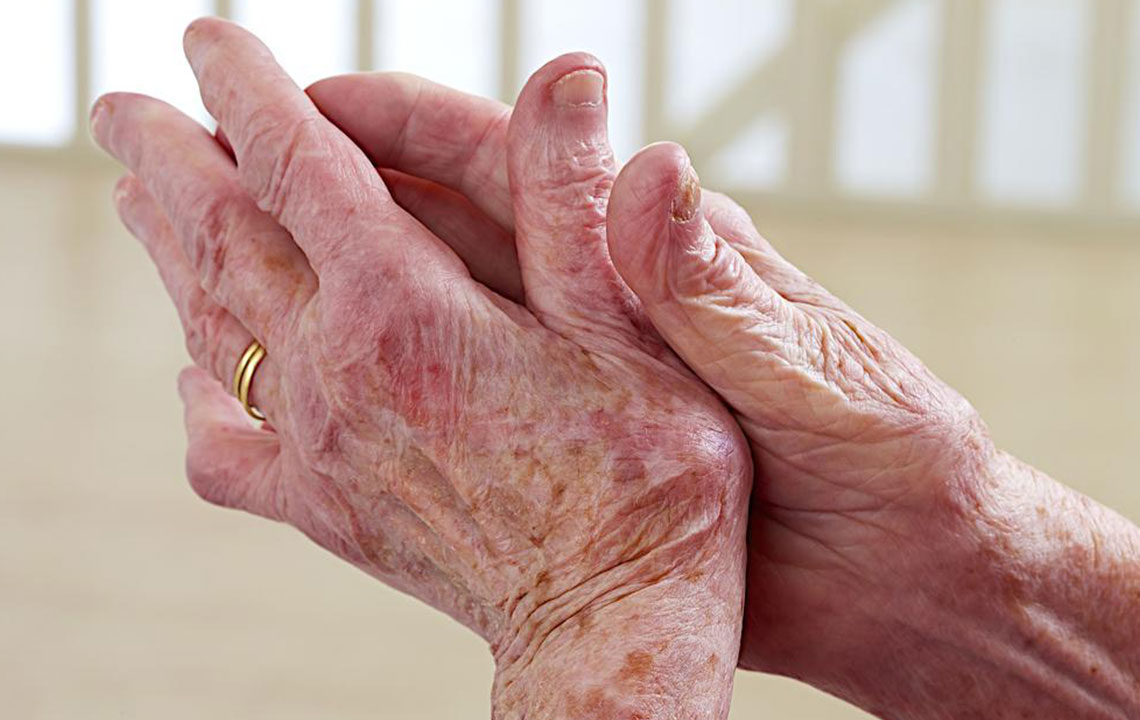
Joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, especially in the mornings
A butterfly-shaped rash on cheeks and nose, often worsened by sunlight
Chest pain related to lung inflammation
Dry eyes and mouth, potentially due to blood vessel damage
Digestive discomfort like acid reflux and unexplained weight loss
Hair loss and brittle hair, including thinning eyebrows and eyelashes
Hormonal fluctuations causing vaginal dryness and irregular periods in females
Managing and Treating Lupus:
Effective lupus management involves continuous care tailored to individual needs and health status. Mild cases may need minimal intervention, while severe cases often require long-term medication, such as:
Topical and systemic steroids to reduce inflammation
Plaquenil for joint and muscle discomfort
Cytoxan for kidney or neurological complications
Imuran to control severe symptoms and prevent organ damage
Rheumatrex for skin and arthritis symptoms
CellCept to suppress immune response and organ rejection
Rituxan for resistant cases involving lymphoma or joint issues
Improving Life with Lupus:
Engage in regular physical activity such as walking or swimming to increase energy and strengthen bones
Follow a nutritious diet and ensure ample rest
Avoid alcohol and smoking, as they can impair medication effectiveness and overall health
Protect skin from sunlight by applying sunscreen and wearing protective gear during peak hours
Monitor and report low-grade fevers promptly, as they may signal infections
Stay in close contact with healthcare providers and strictly follow treatment plans
Educate yourself about lupus symptoms for early detection and intervention
While a cure remains elusive, these strategies can boost daily well-being
Note: The information provided here aims to offer helpful insights. However, it does not replace professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from healthcare professionals for diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. The website assumes no responsibility for data accuracy or discrepancies.